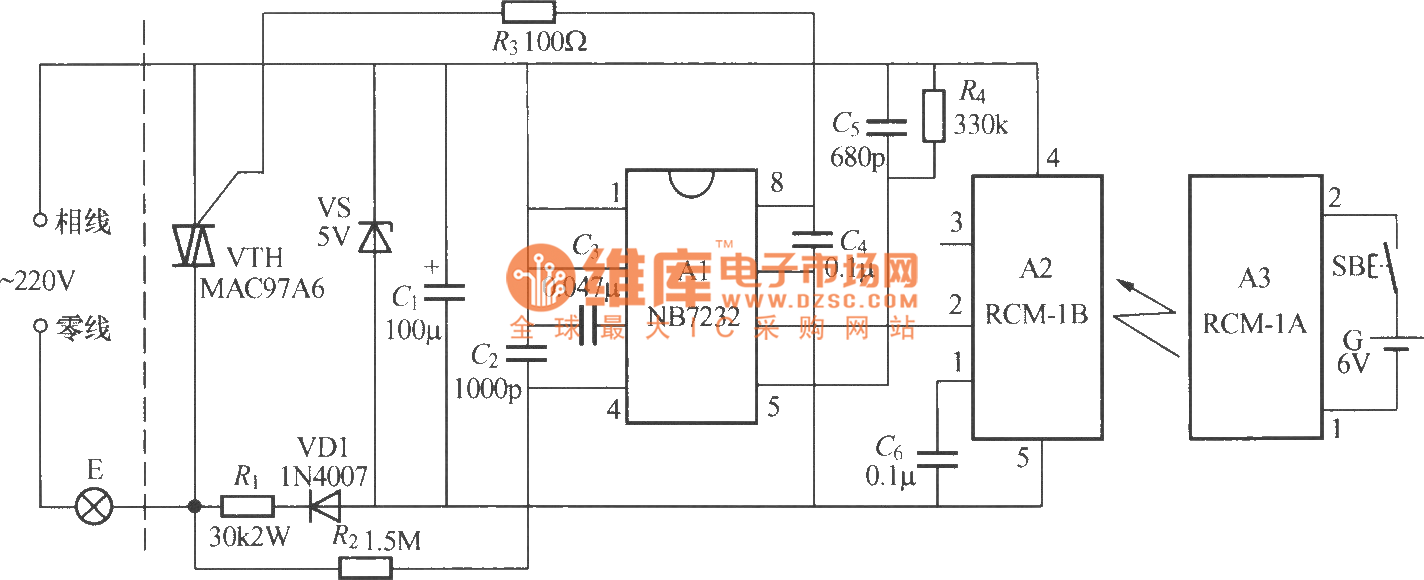
One battery fast charge circuit
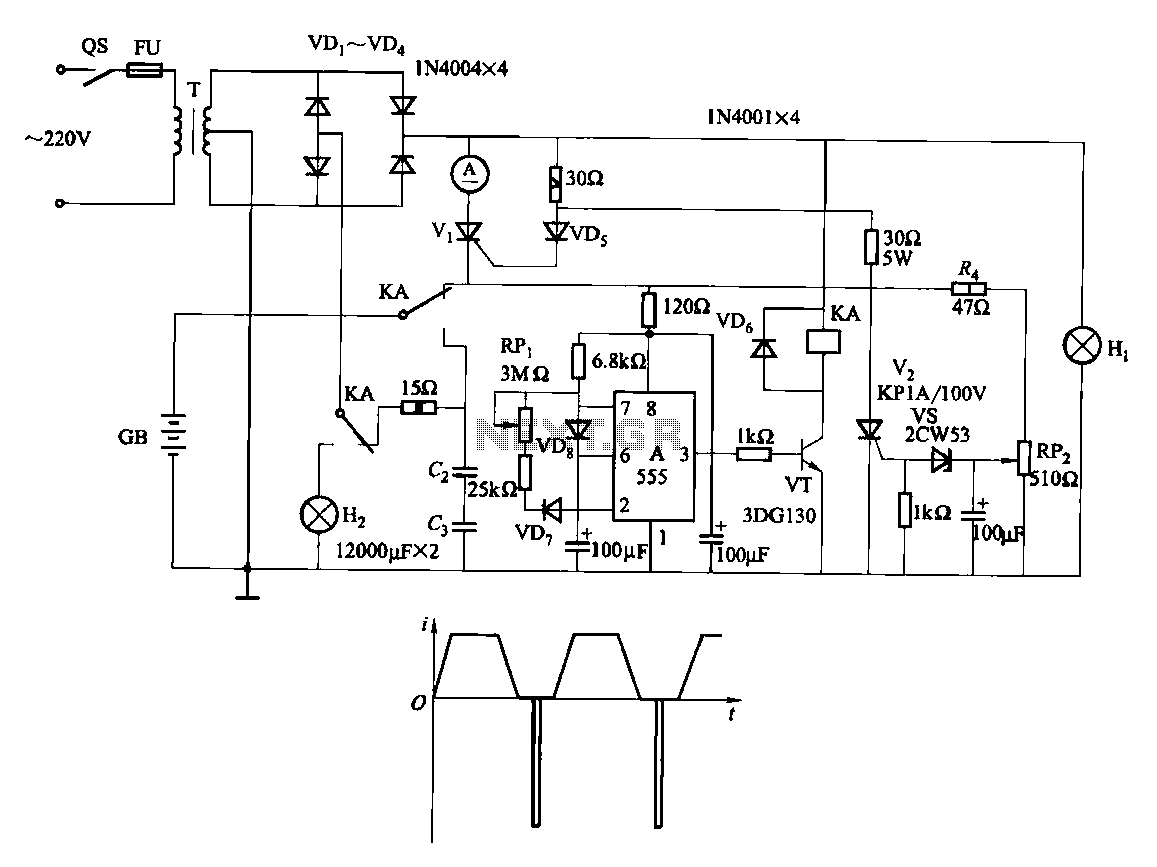
Fast and efficient charging is significantly higher than conventional charging, achieving a current charge that is ten to several times greater. When the battery voltage reaches a predetermined level (known as the polarization point), polarization within the cell becomes more pronounced, necessitating a halt in charging. Following this, the battery undergoes a rapid large current discharge, resulting in a swift drop in battery voltage, which quickly alleviates polarization. This allows for continued charging with a large current, thus preventing complex circulation. This charging method maintains a low temperature, with charging speeds and efficiencies reaching up to 90%, thereby enhancing the storage life of the battery. Fast charging can reduce the original charging time from approximately 20 hours to just 1-2 hours, while also saving energy by 20% to 25%. The circuit can be applied to a 12V car battery. An adjustment potentiometer (RPi) is utilized to modify the discharge time interval. It is crucial to pay attention to the charging and discharging time intervals to match the electrochemical reaction rate of the battery. When the battery voltage is low, the electrochemical reaction occurs rapidly, necessitating shorter time intervals; conversely, when the battery is nearly full, longer intervals should be implemented.
The described charging circuit employs a sophisticated method to optimize battery performance by utilizing a rapid charge and discharge cycle. The system is designed to monitor the battery voltage continuously and respond accordingly to prevent excessive polarization, which can lead to reduced battery lifespan and efficiency. The integration of a potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the discharge time interval, adapting the charging process to the specific state of the battery.
In practical terms, this circuit can be implemented using a microcontroller or a dedicated battery management IC that can handle the necessary voltage and current levels. The circuit would typically include components such as a voltage sensor to detect the battery voltage, a current sensor to monitor the charging and discharging currents, and a relay or MOSFET to control the charging path.
The charging algorithm can be programmed to initiate charging at a high current until the voltage reaches the polarization point, at which point the system would switch to a discharge mode to reduce voltage and alleviate polarization. Following this, the system would resume charging at a high current, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently without overheating.
Thermal management is also an essential aspect of this design, as rapid charging can generate heat. Adequate heat sinking or cooling mechanisms should be incorporated to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Overall, this advanced charging circuit not only improves charging efficiency and speed but also extends the life of the battery, making it suitable for applications such as electric vehicles and high-capacity battery systems.Fast and efficient charging is higher than conventional charging ten times to several times the current charge. When the battery voltage rises to a predetermined value when (va porization point), polarization within the cell is more serious, it should stop charging. And then let the battery instantaneous large current discharge, the battery voltage drops rapidly, quickly disappeared polarization, and then use a large current continues to charge, so the anti- complex circulation. When such a charging method, temperature is not high, charging speed, efficiency up to 90%, can improve the storage life of the pool.
Fast-charge, original charging time can be shortened to about 20h 1-2h, and can save energy by 20% - 25%. Circuit is shown. It can be used as 12V car battery. Adjustment potentiometer RPi, change the discharge time interval. Pay special attention to the charging and discharging time interval to be transferred to the battery in the electrochemical reaction rate to adapt.
When the battery voltage is low, the electrochemical reaction quickly, so a shorter time interval some; while the battery close enough, the interval should be longer.
The described charging circuit employs a sophisticated method to optimize battery performance by utilizing a rapid charge and discharge cycle. The system is designed to monitor the battery voltage continuously and respond accordingly to prevent excessive polarization, which can lead to reduced battery lifespan and efficiency. The integration of a potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the discharge time interval, adapting the charging process to the specific state of the battery.
In practical terms, this circuit can be implemented using a microcontroller or a dedicated battery management IC that can handle the necessary voltage and current levels. The circuit would typically include components such as a voltage sensor to detect the battery voltage, a current sensor to monitor the charging and discharging currents, and a relay or MOSFET to control the charging path.
The charging algorithm can be programmed to initiate charging at a high current until the voltage reaches the polarization point, at which point the system would switch to a discharge mode to reduce voltage and alleviate polarization. Following this, the system would resume charging at a high current, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently without overheating.
Thermal management is also an essential aspect of this design, as rapid charging can generate heat. Adequate heat sinking or cooling mechanisms should be incorporated to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Overall, this advanced charging circuit not only improves charging efficiency and speed but also extends the life of the battery, making it suitable for applications such as electric vehicles and high-capacity battery systems.Fast and efficient charging is higher than conventional charging ten times to several times the current charge. When the battery voltage rises to a predetermined value when (va porization point), polarization within the cell is more serious, it should stop charging. And then let the battery instantaneous large current discharge, the battery voltage drops rapidly, quickly disappeared polarization, and then use a large current continues to charge, so the anti- complex circulation. When such a charging method, temperature is not high, charging speed, efficiency up to 90%, can improve the storage life of the pool.
Fast-charge, original charging time can be shortened to about 20h 1-2h, and can save energy by 20% - 25%. Circuit is shown. It can be used as 12V car battery. Adjustment potentiometer RPi, change the discharge time interval. Pay special attention to the charging and discharging time interval to be transferred to the battery in the electrochemical reaction rate to adapt.
When the battery voltage is low, the electrochemical reaction quickly, so a shorter time interval some; while the battery close enough, the interval should be longer.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713