One transistor audio mixer
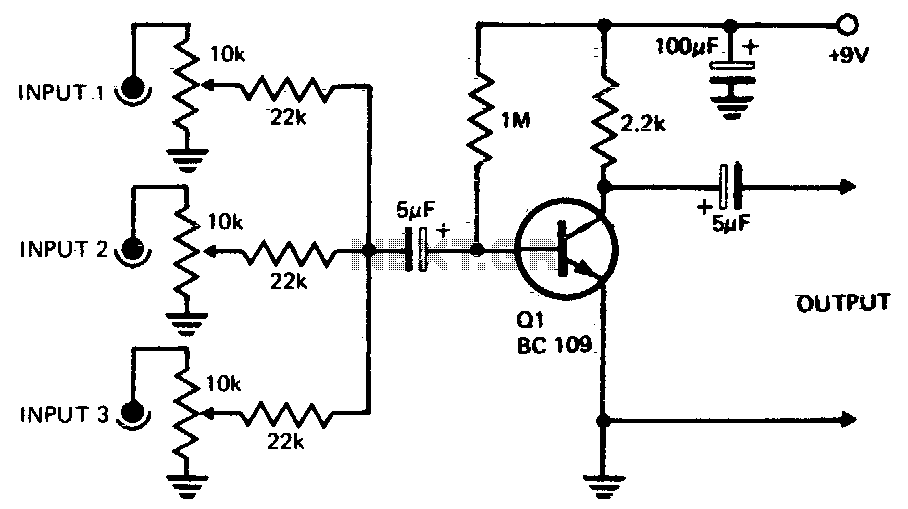
Three or more inputs with individual level controls feed into the base of Q1, which provides a voltage gain of 20.
The circuit design involves a transistor amplifier configuration where three or more input signals are managed through individual level control mechanisms before being directed to the base of the transistor Q1. This arrangement allows for the adjustment of the signal levels to optimize the overall performance of the amplifier. The transistor Q1 functions as a voltage amplifier, providing a significant voltage gain of 20, which indicates that the output voltage will be 20 times greater than the input voltage, assuming ideal conditions.
In this configuration, the individual level controls can be implemented using potentiometers or variable resistors, allowing the user to fine-tune each input signal's amplitude before amplification. The base of Q1 is connected to a resistor network that helps set the biasing conditions of the transistor, ensuring it operates in the active region for linear amplification.
Additionally, proper coupling capacitors may be employed at the input stage to block any DC offset from the input signals while allowing the AC components to pass through. This will help maintain the integrity of the input signals during amplification. The collector of Q1 will be connected to a load resistor, which, in conjunction with the transistor’s characteristics, determines the output voltage swing.
The output can be further processed or sent to subsequent stages of amplification or signal processing, depending on the application requirements. Careful consideration must be given to the power supply voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation of Q1 and to prevent distortion or clipping of the amplified signal.Three or more inputs with individual level controls feed into the base of Q1 that provides a voltage gain of 20. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design involves a transistor amplifier configuration where three or more input signals are managed through individual level control mechanisms before being directed to the base of the transistor Q1. This arrangement allows for the adjustment of the signal levels to optimize the overall performance of the amplifier. The transistor Q1 functions as a voltage amplifier, providing a significant voltage gain of 20, which indicates that the output voltage will be 20 times greater than the input voltage, assuming ideal conditions.
In this configuration, the individual level controls can be implemented using potentiometers or variable resistors, allowing the user to fine-tune each input signal's amplitude before amplification. The base of Q1 is connected to a resistor network that helps set the biasing conditions of the transistor, ensuring it operates in the active region for linear amplification.
Additionally, proper coupling capacitors may be employed at the input stage to block any DC offset from the input signals while allowing the AC components to pass through. This will help maintain the integrity of the input signals during amplification. The collector of Q1 will be connected to a load resistor, which, in conjunction with the transistor’s characteristics, determines the output voltage swing.
The output can be further processed or sent to subsequent stages of amplification or signal processing, depending on the application requirements. Careful consideration must be given to the power supply voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation of Q1 and to prevent distortion or clipping of the amplified signal.Three or more inputs with individual level controls feed into the base of Q1 that provides a voltage gain of 20. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713