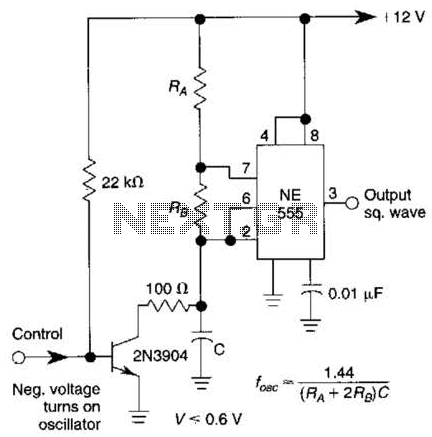
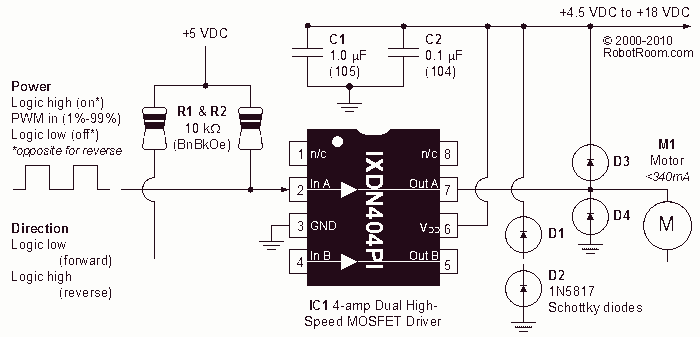
Op-Amp-Based Wien Bridge Oscillator
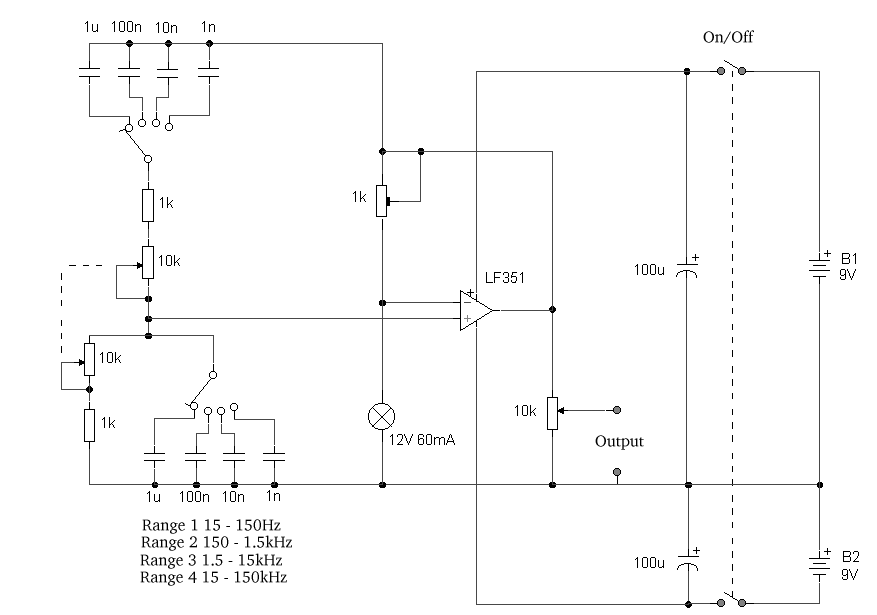
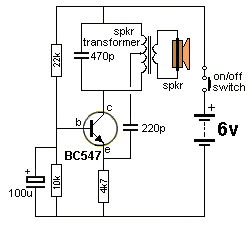
The circuit was designed based on the functionality of an operational amplifier to create a Wien bridge oscillator that generates sine waves in the frequency range of 15 Hz.
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that produces sine waves. It utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) in conjunction with a bridge circuit to achieve oscillation. The circuit typically consists of resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration that allows for frequency stability and low distortion in the output signal.
In this design, the op-amp serves as the active component that amplifies the signal generated by the bridge network. The Wien bridge itself consists of two resistors and two capacitors, which determine the frequency of oscillation. The frequency of the output sine wave can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance and \( C \) is the capacitance in the bridge circuit. For a target frequency of 15 Hz, appropriate values for \( R \) and \( C \) must be selected to satisfy this equation.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate a light bulb or thermistor as a variable resistor to provide automatic gain control. This component helps to stabilize the amplitude of the oscillation, ensuring that the output remains consistent over time. As the amplitude increases, the resistance of the light bulb or thermistor changes, thereby adjusting the gain of the op-amp and maintaining a steady output level.
The output of the Wien bridge oscillator can be taken directly from the op-amp's output pin, providing a clean sine wave signal suitable for various applications, including signal processing, waveform generation, and testing of audio equipment. Proper power supply decoupling and layout considerations are essential to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the oscillator circuit.The circuit was designed based on the functionality of an op-amp to create a Wien bridge oscillator to generate sine waves in the frequency range of 15 Hz.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that produces sine waves. It utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) in conjunction with a bridge circuit to achieve oscillation. The circuit typically consists of resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration that allows for frequency stability and low distortion in the output signal.
In this design, the op-amp serves as the active component that amplifies the signal generated by the bridge network. The Wien bridge itself consists of two resistors and two capacitors, which determine the frequency of oscillation. The frequency of the output sine wave can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance and \( C \) is the capacitance in the bridge circuit. For a target frequency of 15 Hz, appropriate values for \( R \) and \( C \) must be selected to satisfy this equation.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate a light bulb or thermistor as a variable resistor to provide automatic gain control. This component helps to stabilize the amplitude of the oscillation, ensuring that the output remains consistent over time. As the amplitude increases, the resistance of the light bulb or thermistor changes, thereby adjusting the gain of the op-amp and maintaining a steady output level.
The output of the Wien bridge oscillator can be taken directly from the op-amp's output pin, providing a clean sine wave signal suitable for various applications, including signal processing, waveform generation, and testing of audio equipment. Proper power supply decoupling and layout considerations are essential to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the oscillator circuit.The circuit was designed based on the functionality of an op-amp to create a Wien bridge oscillator to generate sine waves in the frequency range of 15 Hz.. 🔗 External reference