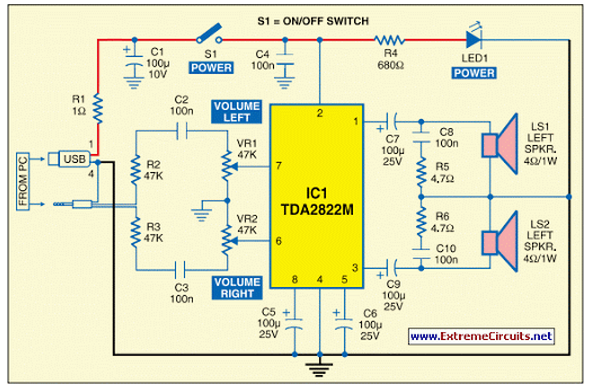
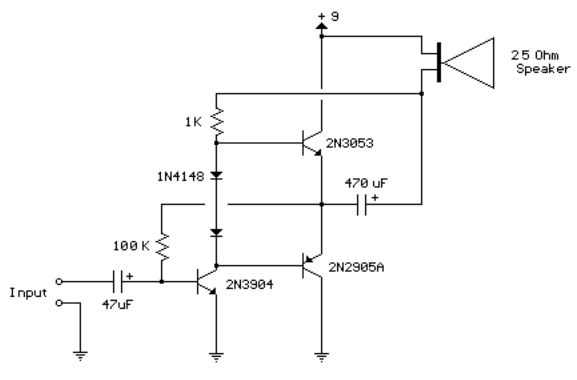
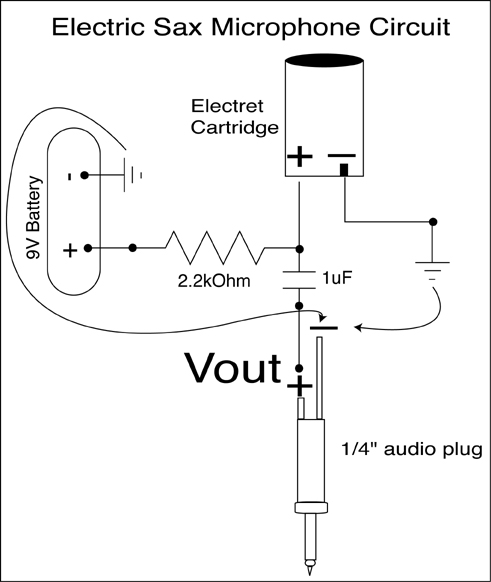
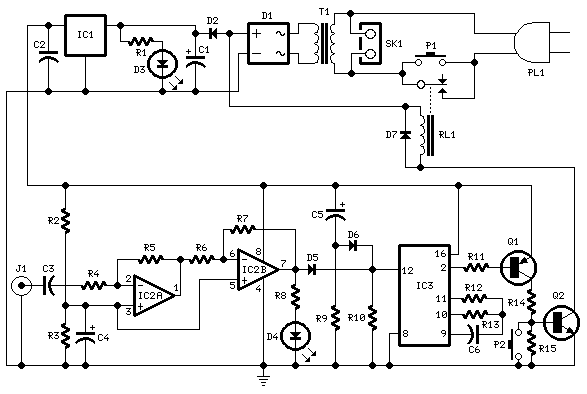
op amp lm741 pre amp mic schematic
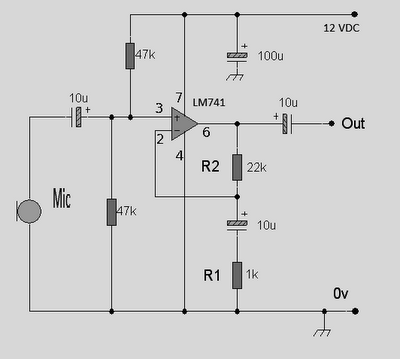
This circuit is an Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier that operates using a single power supply. It is suitable for both dynamic and electret microphones. The schematic illustrates the configuration with a dynamic microphone; however, for electret microphones, a pair of appropriate biasing resistors is necessary to provide power. The design follows a standard non-inverting configuration, where the input is connected to the non-inverting input of the op-amp, typically pin 3. The input impedance is 23.5 kΩ, and the overall voltage gain is determined by resistors R2 and R1, according to the specified formula.
The Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier circuit is designed to amplify low-level audio signals from microphones, making it suitable for various audio applications, including recording and live sound reinforcement. The circuit employs a single power supply, simplifying the design and making it more versatile for portable applications.
In the non-inverting configuration, the op-amp amplifies the input signal without inverting its phase. The input signal from the microphone is fed into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp, allowing for high input impedance, which is crucial for interfacing with microphones that typically have high output impedance. The input impedance of 23.5 kΩ ensures minimal loading on the microphone, preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
For dynamic microphones, the schematic directly connects the microphone output to the non-inverting input of the op-amp. In contrast, electret microphones require additional biasing to operate correctly. This is achieved by connecting a pair of resistors to the power supply, which provides the necessary voltage for the electret microphone while also allowing the audio signal to pass through to the op-amp.
The gain of the amplifier is set by the feedback network formed by resistors R1 and R2. The voltage gain (Av) can be calculated using the formula:
Av = 1 + (R2 / R1)
This formula indicates that the gain is determined by the ratio of the resistors, allowing for easy adjustment according to the desired amplification level. Selecting appropriate values for R1 and R2 is critical for optimizing the performance of the preamplifier and ensuring that the output signal is strong enough for further processing or amplification stages.
Overall, this Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier circuit is an effective solution for amplifying audio signals with flexibility for different microphone types, making it a valuable component in audio signal processing systems.This is the circuit of Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier using a single power supply, this circuit suitable for dynamic or electret microphones. Nothing too special here. The Schematic is shown using a dynamic microphone, for use with an electret a pair of suitable biasing resistor is required to power the electret microphone.
The design is a standar d non-inverting design, the input is applied to the non-inverting input of the op-amp, which is pin 3 in most cases. The input impedance is 23. 5k, the overall voltage gain is determined by R2 and R1according to the following formula: 🔗 External reference
The Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier circuit is designed to amplify low-level audio signals from microphones, making it suitable for various audio applications, including recording and live sound reinforcement. The circuit employs a single power supply, simplifying the design and making it more versatile for portable applications.
In the non-inverting configuration, the op-amp amplifies the input signal without inverting its phase. The input signal from the microphone is fed into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp, allowing for high input impedance, which is crucial for interfacing with microphones that typically have high output impedance. The input impedance of 23.5 kΩ ensures minimal loading on the microphone, preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
For dynamic microphones, the schematic directly connects the microphone output to the non-inverting input of the op-amp. In contrast, electret microphones require additional biasing to operate correctly. This is achieved by connecting a pair of resistors to the power supply, which provides the necessary voltage for the electret microphone while also allowing the audio signal to pass through to the op-amp.
The gain of the amplifier is set by the feedback network formed by resistors R1 and R2. The voltage gain (Av) can be calculated using the formula:
Av = 1 + (R2 / R1)
This formula indicates that the gain is determined by the ratio of the resistors, allowing for easy adjustment according to the desired amplification level. Selecting appropriate values for R1 and R2 is critical for optimizing the performance of the preamplifier and ensuring that the output signal is strong enough for further processing or amplification stages.
Overall, this Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier circuit is an effective solution for amplifying audio signals with flexibility for different microphone types, making it a valuable component in audio signal processing systems.This is the circuit of Op-Amp Microphone Preamplifier using a single power supply, this circuit suitable for dynamic or electret microphones. Nothing too special here. The Schematic is shown using a dynamic microphone, for use with an electret a pair of suitable biasing resistor is required to power the electret microphone.
The design is a standar d non-inverting design, the input is applied to the non-inverting input of the op-amp, which is pin 3 in most cases. The input impedance is 23. 5k, the overall voltage gain is determined by R2 and R1according to the following formula: 🔗 External reference