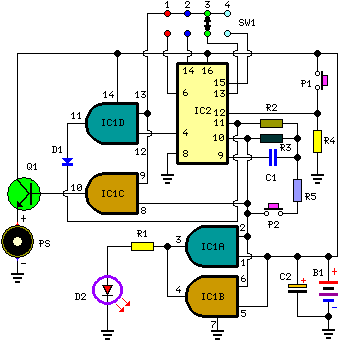
OP amplifier using FET input type long analog timing circuit
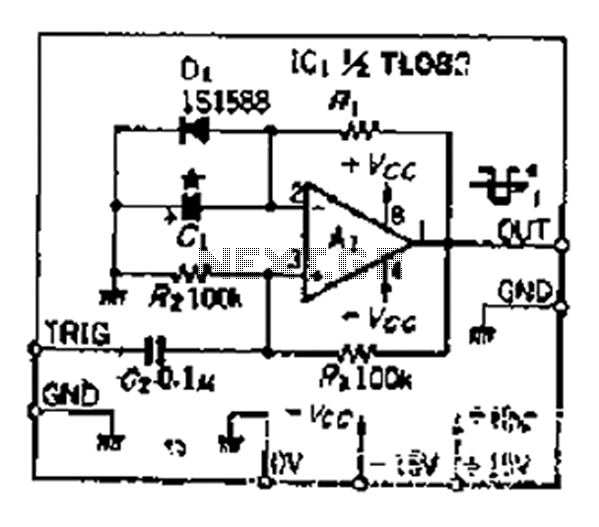
Although people believe that using a timer with an operational amplifier (op-amp) does not yield significant results, it can still be advantageous in certain scenarios. In environments with high noise levels, the application retains its benefits. When the phase voltage input reaches approximately half of the saturation voltage (around 12 V), the voltage applied to the two transistors turns on, fixing the inverting input at about 0.6 V. When the input exceeds -6 V, the op-amp's negative output terminal becomes saturated. Consequently, the inverting input voltage approaches -6 V, causing capacitor C1, through resistor R1, to charge until the voltage surpasses -6 V, resulting in the positive output reaching saturation and completing the cycle.
In this circuit, the operational amplifier serves as a comparator, monitoring the phase voltage input against a reference level. The saturation voltage of the op-amp is critical, as it defines the operational limits of the circuit. The described setup utilizes a feedback mechanism where the charging of capacitor C1 through resistor R1 influences the inverting input voltage. The use of two transistors allows for the control of the input voltage to the op-amp, ensuring that it operates within the desired range.
The circuit can be designed with additional components to enhance its functionality. For instance, incorporating a Schmitt trigger can provide hysteresis, which improves noise immunity and stability in the output signal. Additionally, the values of the resistors and capacitors can be selected based on the desired timing characteristics and response speed of the circuit.
The output of the op-amp can be connected to various loads, depending on the application requirements. For example, it could drive a relay, LED, or another stage of amplification. Proper power supply decoupling should also be considered to minimize the impact of noise on the op-amp performance.
In summary, this circuit demonstrates the utility of an operational amplifier in a timer configuration, particularly in noisy environments, highlighting the importance of component selection and circuit design in achieving reliable operation.Although people think that now use the timer make sense amplifier OP is not large, but after the power is turned Ai as often positive output saturation such a high noise enviro nment, the application still has its advantages. With phase voltage input is saturation voltage (about 12 V) 1/2, since two cast pipe D, the voltage is turned on, the inverting input is fixed to about 0.6V 6 as input - 6V above the trigger, OP amplifier a negative output terminal MG fJ saturated and, at the same Yat-inverting input voltage is about - 6V, capacitor cl by anti-Ri to the charge voltage exceeds - 6V, : positive output reaches saturation, a fixed end of the cycle.
In this circuit, the operational amplifier serves as a comparator, monitoring the phase voltage input against a reference level. The saturation voltage of the op-amp is critical, as it defines the operational limits of the circuit. The described setup utilizes a feedback mechanism where the charging of capacitor C1 through resistor R1 influences the inverting input voltage. The use of two transistors allows for the control of the input voltage to the op-amp, ensuring that it operates within the desired range.
The circuit can be designed with additional components to enhance its functionality. For instance, incorporating a Schmitt trigger can provide hysteresis, which improves noise immunity and stability in the output signal. Additionally, the values of the resistors and capacitors can be selected based on the desired timing characteristics and response speed of the circuit.
The output of the op-amp can be connected to various loads, depending on the application requirements. For example, it could drive a relay, LED, or another stage of amplification. Proper power supply decoupling should also be considered to minimize the impact of noise on the op-amp performance.
In summary, this circuit demonstrates the utility of an operational amplifier in a timer configuration, particularly in noisy environments, highlighting the importance of component selection and circuit design in achieving reliable operation.Although people think that now use the timer make sense amplifier OP is not large, but after the power is turned Ai as often positive output saturation such a high noise enviro nment, the application still has its advantages. With phase voltage input is saturation voltage (about 12 V) 1/2, since two cast pipe D, the voltage is turned on, the inverting input is fixed to about 0.6V 6 as input - 6V above the trigger, OP amplifier a negative output terminal MG fJ saturated and, at the same Yat-inverting input voltage is about - 6V, capacitor cl by anti-Ri to the charge voltage exceeds - 6V, : positive output reaches saturation, a fixed end of the cycle.