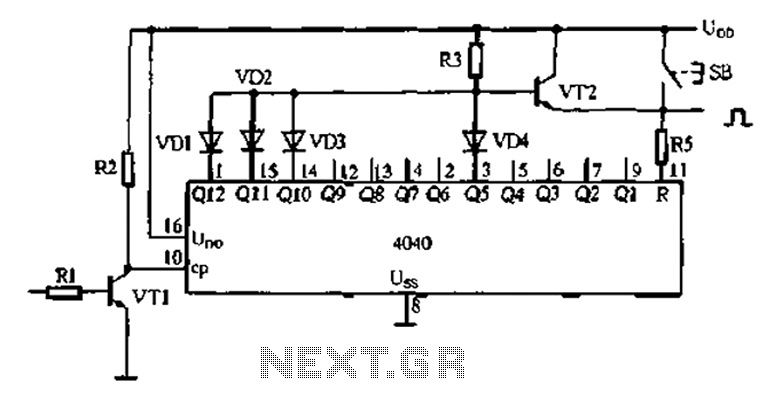
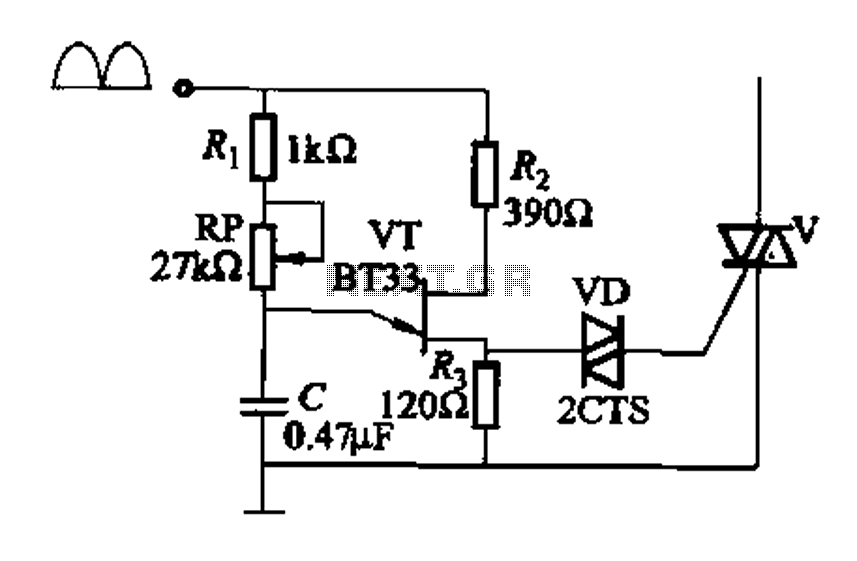
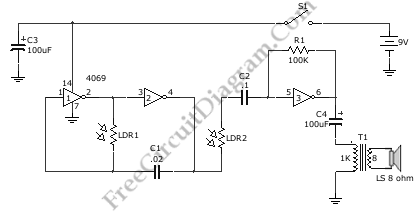
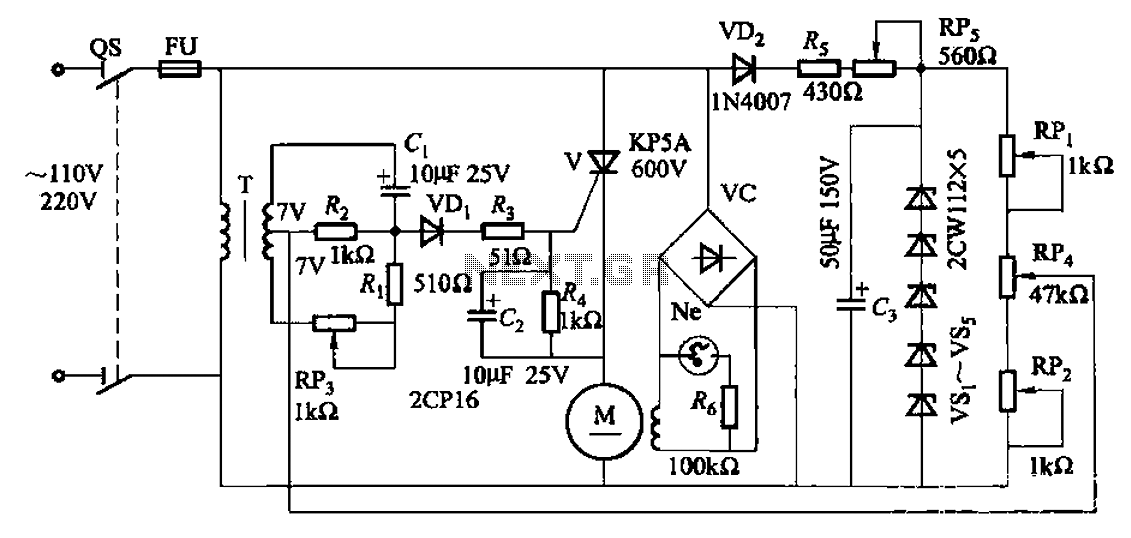
Optical schmitt trigger
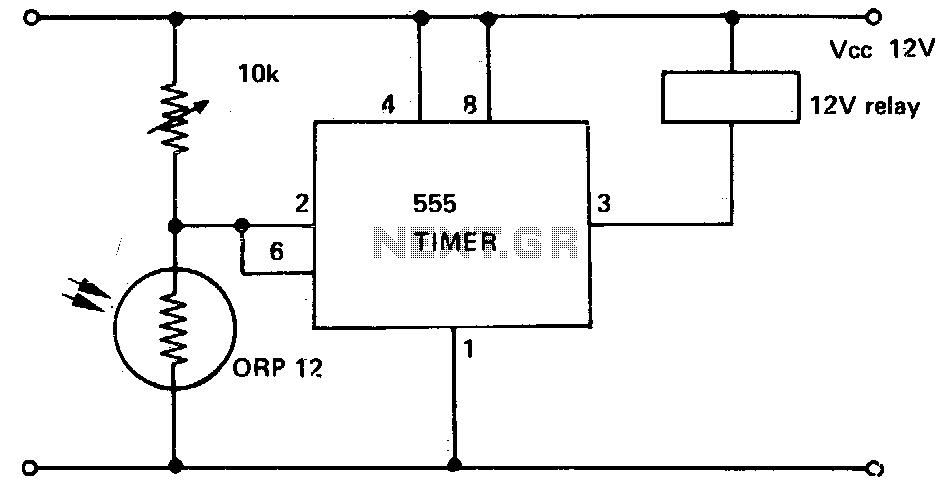
This circuit illustrates a 555 timer with its trigger and threshold inputs connected together, which is utilized to activate a relay when the light level detected by a photoconductive cell drops below a predetermined threshold. Additionally, this circuit can be employed in various applications that necessitate high input impedance and low output impedance while maintaining a minimal component count.
The described circuit employs a 555 timer in monostable mode, where the trigger and threshold inputs are tied together to create a single point of control. The photoconductive cell, or LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), acts as a light sensor, varying its resistance based on the ambient light levels. When the light intensity decreases below a specific level, the resistance of the LDR increases, causing a voltage drop across it that triggers the 555 timer.
In this configuration, the output of the 555 timer is connected to a relay, which allows the circuit to control higher power loads or devices. The relay serves as an electromechanical switch that can be activated by the low output current from the 555 timer. This is particularly useful in scenarios where it is necessary to control lights, alarms, or other devices based on light conditions.
The circuit's design ensures high input impedance, which is advantageous for interfacing with the LDR, as it minimizes the loading effect on the sensor. The low output impedance of the 555 timer ensures that it can drive the relay effectively without additional buffering components, thereby simplifying the overall design and reducing the component count.
This circuit can be adapted for various applications, such as automatic lighting systems, security alarms, or any system that requires light level monitoring and control. The minimal component count not only reduces costs but also enhances reliability and ease of assembly, making it an attractive solution for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.This circuit shows a 555 with its trigger and threshold inputs connected together used to energize a relay when the light level on a photoconductive cell falls below a preset value Circuit can be used in other applications where a high input impedance and low output impedance are required with the minimum component count. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a 555 timer in monostable mode, where the trigger and threshold inputs are tied together to create a single point of control. The photoconductive cell, or LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), acts as a light sensor, varying its resistance based on the ambient light levels. When the light intensity decreases below a specific level, the resistance of the LDR increases, causing a voltage drop across it that triggers the 555 timer.
In this configuration, the output of the 555 timer is connected to a relay, which allows the circuit to control higher power loads or devices. The relay serves as an electromechanical switch that can be activated by the low output current from the 555 timer. This is particularly useful in scenarios where it is necessary to control lights, alarms, or other devices based on light conditions.
The circuit's design ensures high input impedance, which is advantageous for interfacing with the LDR, as it minimizes the loading effect on the sensor. The low output impedance of the 555 timer ensures that it can drive the relay effectively without additional buffering components, thereby simplifying the overall design and reducing the component count.
This circuit can be adapted for various applications, such as automatic lighting systems, security alarms, or any system that requires light level monitoring and control. The minimal component count not only reduces costs but also enhances reliability and ease of assembly, making it an attractive solution for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.This circuit shows a 555 with its trigger and threshold inputs connected together used to energize a relay when the light level on a photoconductive cell falls below a preset value Circuit can be used in other applications where a high input impedance and low output impedance are required with the minimum component count. 🔗 External reference