Single-junction transistor a phase-shift trigger circuit
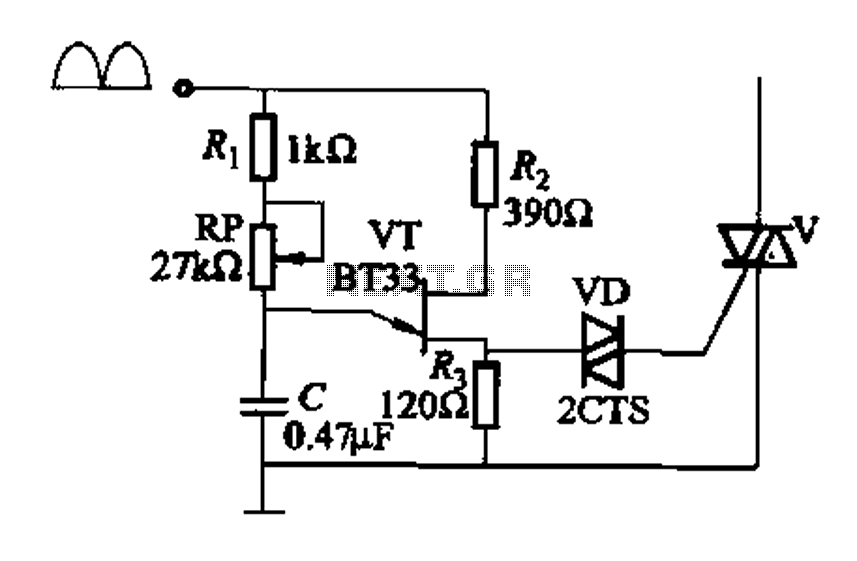
Figure 16-29 (a) illustrates the trigger output through a resistor R2, while Figure 16-29 (b) depicts the integration of a programmable unidirectional transistor (PUT) trigger circuit. The adjustable potentiometer RP can modify the conduction angle of the TRIAC to facilitate transfer press operations.
The circuit in Figure 16-29 (b) employs a programmable unidirectional transistor (PUT) as the primary triggering device for a TRIAC. The PUT is characterized by its ability to control the conduction angle, which is essential for applications requiring precise power control, such as in transfer press operations.
In this configuration, resistor R2 is critical as it helps establish the necessary trigger voltage for the PUT. The output from the circuit is connected to the gate of the TRIAC, allowing it to conduct current when the PUT is activated. The conduction angle can be adjusted using the potentiometer RP, which alters the timing of the trigger signal applied to the TRIAC.
The adjustment of the conduction angle directly influences the power delivered to the load, enabling fine-tuning of the operational characteristics of the transfer press. This feature is particularly useful in applications where varying the power level is necessary for different materials or processes. By manipulating the resistance of RP, the user can achieve optimal performance and efficiency in the operation of the transfer press, making this circuit a versatile solution in industrial settings.
Overall, the integration of the PUT in conjunction with the TRIAC and adjustable components provides a robust mechanism for controlling power in time-sensitive applications, ensuring that the system can adapt to various operational requirements.Figure 16-29 (a) of the trigger output via a resistor R2; FIG 16J29 (b) for the introduction of programmable single-junction transistor PUT trigger circuit. Adjustment potentio meter RP, can change the TRIAC conduction angle, to achieve transfer press purposes.
The circuit in Figure 16-29 (b) employs a programmable unidirectional transistor (PUT) as the primary triggering device for a TRIAC. The PUT is characterized by its ability to control the conduction angle, which is essential for applications requiring precise power control, such as in transfer press operations.
In this configuration, resistor R2 is critical as it helps establish the necessary trigger voltage for the PUT. The output from the circuit is connected to the gate of the TRIAC, allowing it to conduct current when the PUT is activated. The conduction angle can be adjusted using the potentiometer RP, which alters the timing of the trigger signal applied to the TRIAC.
The adjustment of the conduction angle directly influences the power delivered to the load, enabling fine-tuning of the operational characteristics of the transfer press. This feature is particularly useful in applications where varying the power level is necessary for different materials or processes. By manipulating the resistance of RP, the user can achieve optimal performance and efficiency in the operation of the transfer press, making this circuit a versatile solution in industrial settings.
Overall, the integration of the PUT in conjunction with the TRIAC and adjustable components provides a robust mechanism for controlling power in time-sensitive applications, ensuring that the system can adapt to various operational requirements.Figure 16-29 (a) of the trigger output via a resistor R2; FIG 16J29 (b) for the introduction of programmable single-junction transistor PUT trigger circuit. Adjustment potentio meter RP, can change the TRIAC conduction angle, to achieve transfer press purposes.