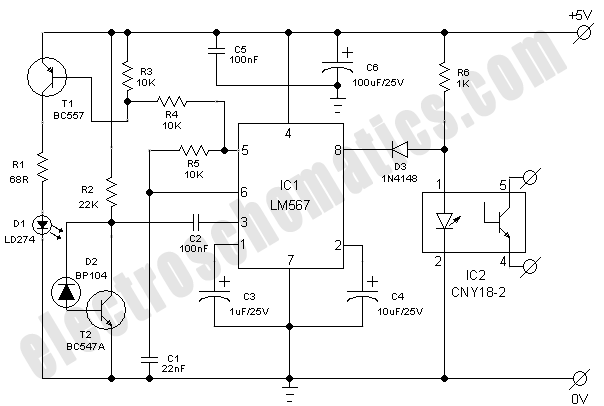
Optically isolated RS485 circuit diagram of a typical
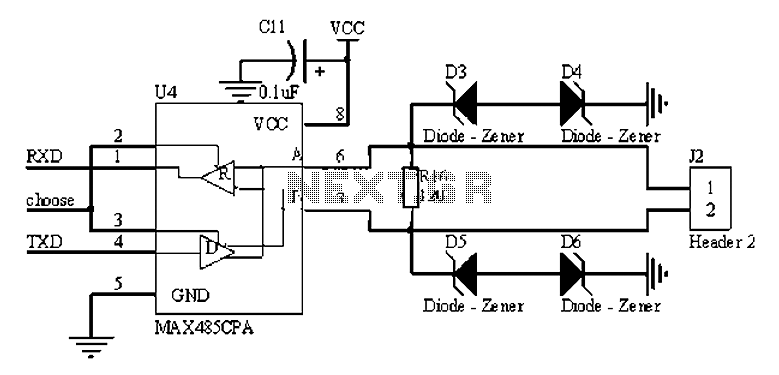
The RS485 bus is a widely used serial bus standard that employs balanced differential transmission and reception techniques, enabling it to effectively suppress common mode interference. It is particularly advantageous for communication distances ranging from tens of meters to several kilometers, making it a popular choice for multi-node systems. The RS485 bus can be categorized into isolated and non-isolated circuits. Isolated circuits generally offer superior performance in terms of interference resistance and system stability, although non-isolated configurations may be suitable in certain scenarios. A typical non-isolated RS485 circuit can be established by directly connecting an RS485 chip to the serial communication port of a microcontroller (MCU) and an I/O control port. In such a configuration, a pull-down bias resistor of 4.7K is added to line B. A matching resistor, typically 120 ohms, is placed in the middle of the circuit, although the exact value may vary depending on the specific transmission cables used. The matching resistor is crucial for ensuring the stability of the entire communication system, and it is common practice to include matching resistors at both the first and last nodes of the communication line. Field personnel can determine whether to use these resistors based on the system's configuration. Additionally, a Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) diode, typically rated at 6.8V, is employed for protection against voltage spikes.
The RS485 bus circuit is designed to facilitate robust communication in environments where electrical noise and interference may be present. The differential signaling used in RS485 allows for the detection of signals even in the presence of common mode noise, making it suitable for long-distance communication. The isolated RS485 circuit configuration includes isolation components such as opto-isolators or isolators that provide electrical separation between the communicating devices, enhancing system reliability and safety.
In practical applications, the selection of components such as the RS485 transceiver, termination resistors, and biasing resistors must be made carefully to optimize performance. The RS485 transceiver is responsible for converting the serial data from the MCU into differential signals suitable for transmission over the bus. Proper termination with the matching resistor minimizes signal reflections, which can degrade communication integrity. The pull-down bias resistor on line B ensures that the line remains in a defined state when no devices are actively transmitting, preventing false triggering of receivers.
Additionally, the layout of the circuit board should consider factors such as trace length, impedance matching, and grounding to further reduce noise and enhance signal integrity. When implementing an RS485 bus system, attention to these details will lead to improved performance and reliability in various industrial and commercial applications, including automation systems, data acquisition, and remote monitoring.A, RS485 bus Introduction RS485 bus is a common serial bus standard, using balanced differential transmit and receive mode, and therefore has the ability to suppress common mod e interference. In some of the requirements on the communication distance of tens of meters to kilometers when, RS485 bus is a bus most widely used. But also in the operation of the system of multi-node also has a wide range of applications. Two, RS485 bus describes a typical circuit It can be divided into isolated and non-isolated RS485 circuit as a whole.
Isolated than non-isolated in interference, system stability and other aspects of better performance, but there are some situations you can also use non-isolated. We speak about non-typical circuit isolated and non-isolated circuit is very simple, just a RS485 chip directly with MCU serial communication port and an I/O control port connection can be.
As shown in Figure 1: in line B plus a pull-down bias resistors of 4.7K. Matching resistor R16 is in the middle, typically 120, of course, this depends on your specific transmission cables. (Matching resistor: 485 entire communication system for transmission system stability, we will normally be the first node and last node plus matching resistance so we are generally in the design, you will have a set at each node jumper 120 resistance, as to use or not, by the field staff to set.
of course, specifically how to distinguish between the first node is the last node, have to be on-site experts to answer Oh.) TVS we generally use 6.8V and this we will further explain later.
The RS485 bus circuit is designed to facilitate robust communication in environments where electrical noise and interference may be present. The differential signaling used in RS485 allows for the detection of signals even in the presence of common mode noise, making it suitable for long-distance communication. The isolated RS485 circuit configuration includes isolation components such as opto-isolators or isolators that provide electrical separation between the communicating devices, enhancing system reliability and safety.
In practical applications, the selection of components such as the RS485 transceiver, termination resistors, and biasing resistors must be made carefully to optimize performance. The RS485 transceiver is responsible for converting the serial data from the MCU into differential signals suitable for transmission over the bus. Proper termination with the matching resistor minimizes signal reflections, which can degrade communication integrity. The pull-down bias resistor on line B ensures that the line remains in a defined state when no devices are actively transmitting, preventing false triggering of receivers.
Additionally, the layout of the circuit board should consider factors such as trace length, impedance matching, and grounding to further reduce noise and enhance signal integrity. When implementing an RS485 bus system, attention to these details will lead to improved performance and reliability in various industrial and commercial applications, including automation systems, data acquisition, and remote monitoring.A, RS485 bus Introduction RS485 bus is a common serial bus standard, using balanced differential transmit and receive mode, and therefore has the ability to suppress common mod e interference. In some of the requirements on the communication distance of tens of meters to kilometers when, RS485 bus is a bus most widely used. But also in the operation of the system of multi-node also has a wide range of applications. Two, RS485 bus describes a typical circuit It can be divided into isolated and non-isolated RS485 circuit as a whole.
Isolated than non-isolated in interference, system stability and other aspects of better performance, but there are some situations you can also use non-isolated. We speak about non-typical circuit isolated and non-isolated circuit is very simple, just a RS485 chip directly with MCU serial communication port and an I/O control port connection can be.
As shown in Figure 1: in line B plus a pull-down bias resistors of 4.7K. Matching resistor R16 is in the middle, typically 120, of course, this depends on your specific transmission cables. (Matching resistor: 485 entire communication system for transmission system stability, we will normally be the first node and last node plus matching resistance so we are generally in the design, you will have a set at each node jumper 120 resistance, as to use or not, by the field staff to set.
of course, specifically how to distinguish between the first node is the last node, have to be on-site experts to answer Oh.) TVS we generally use 6.8V and this we will further explain later.