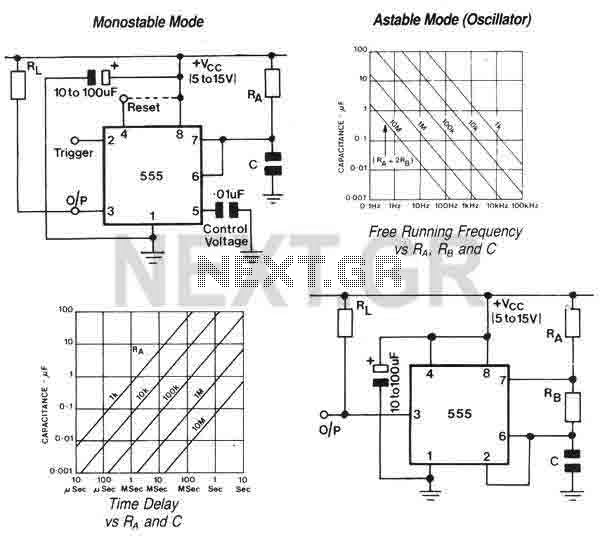
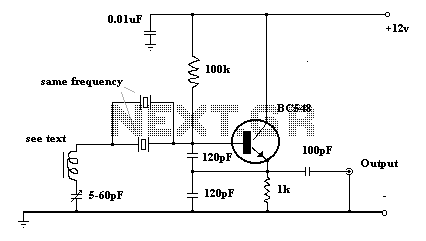
Oscillator circuits
The Clapp oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator constructed from a transistor or vacuum tube and a positive feedback network. The Meissner oscillator circuit is a harmonic oscillator that consists of an active electronic element, such as a transistor or electronic tube, an LC resonant circuit, and a positive feedback system. According to the Barkhausen criteria, oscillation in a positive feedback system occurs when the loop gain, which is the product of forward gain and feedback gain, has a phase shift of zero (or 180 degrees for negative feedback systems) and a magnitude of unity. Various types of sine wave oscillators include the Wien Bridge Oscillator, Crystal Oscillators, Tuned-Gate Oscillators, Armstrong oscillator, Hartley oscillator, and Clapp oscillator. Additionally, a variable-frequency, three-phase sine-wave generator circuit can generate three symmetrical square-wave voltages with a precise 120-degree phase difference, each square wave containing only odd harmonics.
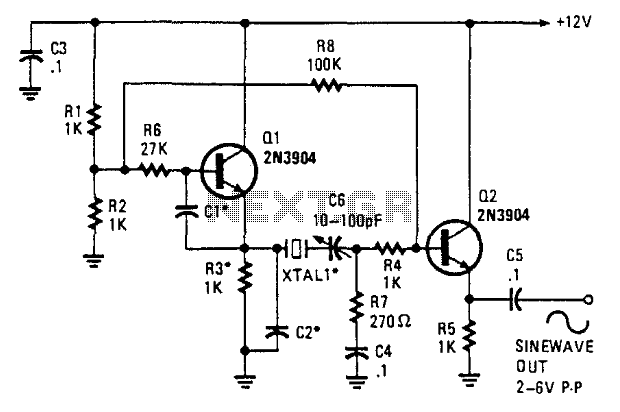
The Clapp oscillator is a notable variant of the LC oscillator family, characterized by its ability to produce stable sine wave outputs. It utilizes a combination of a transistor or vacuum tube and a feedback network that includes an inductor and a capacitor arranged in a specific configuration. This oscillator is particularly valued for its frequency stability, which is enhanced by the inclusion of a variable capacitor that allows fine-tuning of the output frequency.
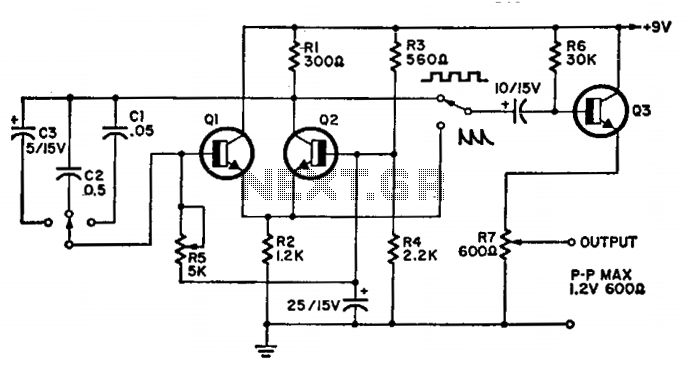
The Meissner oscillator, also known as the Armstrong oscillator, operates on similar principles but typically employs a different feedback mechanism. It consists of an active component, such as a transistor, and an LC circuit that resonates at a specific frequency. This configuration ensures that the oscillation produced is harmonic, maintaining a sinusoidal waveform that is essential for various applications, including radio frequency transmission.
The Barkhausen criteria play a critical role in the oscillation process, stipulating that for sustained oscillations to occur, the total loop gain must equal unity and the phase shift must be precisely zero or 180 degrees, depending on the feedback type. This principle underlies the design of many oscillators, ensuring that the output remains stable and consistent over time.
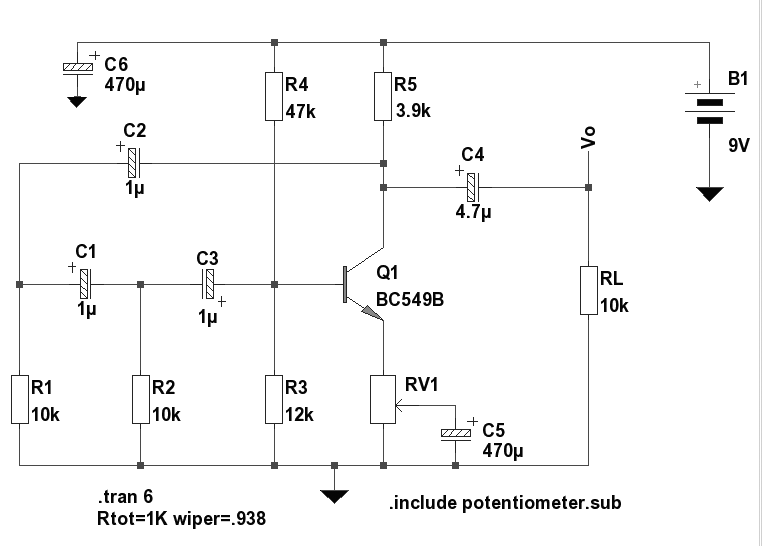
Sine wave oscillators are widely used in electronic applications, with various designs available, including the Wien Bridge Oscillator, which utilizes a bridge circuit to achieve a stable frequency, and the Phase-Shift Oscillator, which employs multiple RC networks to generate sine waves. Each type of oscillator has its unique characteristics and applications, ranging from audio signal generation to precision timing circuits.
In addition to these oscillators, a variable-frequency three-phase sine-wave generator circuit is capable of producing three square-wave voltages that are phase-shifted by 120 degrees. This configuration is essential for applications in motor control and power electronics, where precise phase relationships are required. The generated square waves contain only odd harmonics, which is advantageous for minimizing distortion in the output signal.The Clapp oscillator is one of several types of electronic oscillator constructed from a transistor (or vacuum tube) and a positive feedback network, . Meissner (Armstrong) Oscillator The Meissner oscillator circuit is a harmonic (sinusoidal) oscillator consisting of an active electronic element (transistor, elec
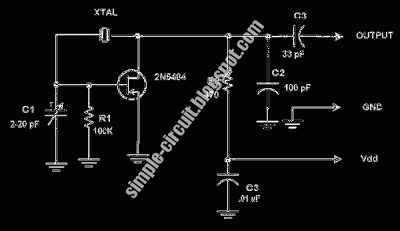
tronic tube, etc. ), an LC resonans circuit and a positive feedback Pierce Crystal Oscillator Design The Barkhausen criteria states that for a positive feedback system, oscillation will occur when the loop gain (product of forward gain and feedback gain) has a phase shift of zero (180 degrees for negative feedback systems) and a magnitude of unity Sine wave oscillators sine wave oscillators, The Wien Bridge Oscillator, Crystal Oscillators, Tuned-Gate Oscillators, Armstrong oscillator, Hartley oscillator, Clapp oscillator Sine wave oscillators Wien-Bridge Oscillator, Phase-Shift Oscillator, Single Amplifier, Phase-Shift Oscillator, Buffered, Bubba Oscillator, Quadrature Oscillator, pdf file Three phase sine wave generator a variable-frequency, three-phase, sine-wave generator circuit, Educypedia, The circuit internally generates three symmetrical square-wave voltages with precisely 120 ° phase difference, each square wave containing only odd harmonics 🔗 External reference
The Clapp oscillator is a notable variant of the LC oscillator family, characterized by its ability to produce stable sine wave outputs. It utilizes a combination of a transistor or vacuum tube and a feedback network that includes an inductor and a capacitor arranged in a specific configuration. This oscillator is particularly valued for its frequency stability, which is enhanced by the inclusion of a variable capacitor that allows fine-tuning of the output frequency.
The Meissner oscillator, also known as the Armstrong oscillator, operates on similar principles but typically employs a different feedback mechanism. It consists of an active component, such as a transistor, and an LC circuit that resonates at a specific frequency. This configuration ensures that the oscillation produced is harmonic, maintaining a sinusoidal waveform that is essential for various applications, including radio frequency transmission.
The Barkhausen criteria play a critical role in the oscillation process, stipulating that for sustained oscillations to occur, the total loop gain must equal unity and the phase shift must be precisely zero or 180 degrees, depending on the feedback type. This principle underlies the design of many oscillators, ensuring that the output remains stable and consistent over time.
Sine wave oscillators are widely used in electronic applications, with various designs available, including the Wien Bridge Oscillator, which utilizes a bridge circuit to achieve a stable frequency, and the Phase-Shift Oscillator, which employs multiple RC networks to generate sine waves. Each type of oscillator has its unique characteristics and applications, ranging from audio signal generation to precision timing circuits.
In addition to these oscillators, a variable-frequency three-phase sine-wave generator circuit is capable of producing three square-wave voltages that are phase-shifted by 120 degrees. This configuration is essential for applications in motor control and power electronics, where precise phase relationships are required. The generated square waves contain only odd harmonics, which is advantageous for minimizing distortion in the output signal.The Clapp oscillator is one of several types of electronic oscillator constructed from a transistor (or vacuum tube) and a positive feedback network, . Meissner (Armstrong) Oscillator The Meissner oscillator circuit is a harmonic (sinusoidal) oscillator consisting of an active electronic element (transistor, elec
tronic tube, etc. ), an LC resonans circuit and a positive feedback Pierce Crystal Oscillator Design The Barkhausen criteria states that for a positive feedback system, oscillation will occur when the loop gain (product of forward gain and feedback gain) has a phase shift of zero (180 degrees for negative feedback systems) and a magnitude of unity Sine wave oscillators sine wave oscillators, The Wien Bridge Oscillator, Crystal Oscillators, Tuned-Gate Oscillators, Armstrong oscillator, Hartley oscillator, Clapp oscillator Sine wave oscillators Wien-Bridge Oscillator, Phase-Shift Oscillator, Single Amplifier, Phase-Shift Oscillator, Buffered, Bubba Oscillator, Quadrature Oscillator, pdf file Three phase sine wave generator a variable-frequency, three-phase, sine-wave generator circuit, Educypedia, The circuit internally generates three symmetrical square-wave voltages with precisely 120 ° phase difference, each square wave containing only odd harmonics 🔗 External reference