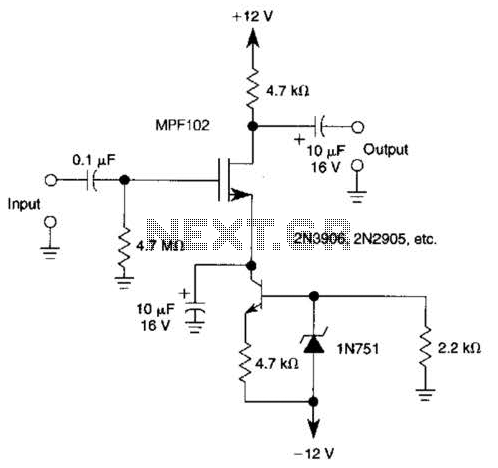
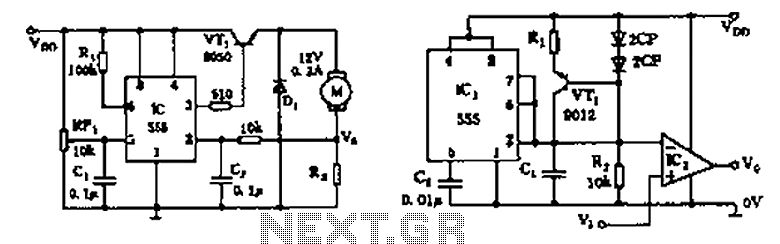
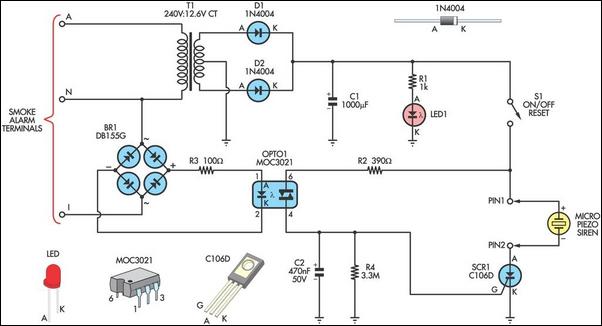
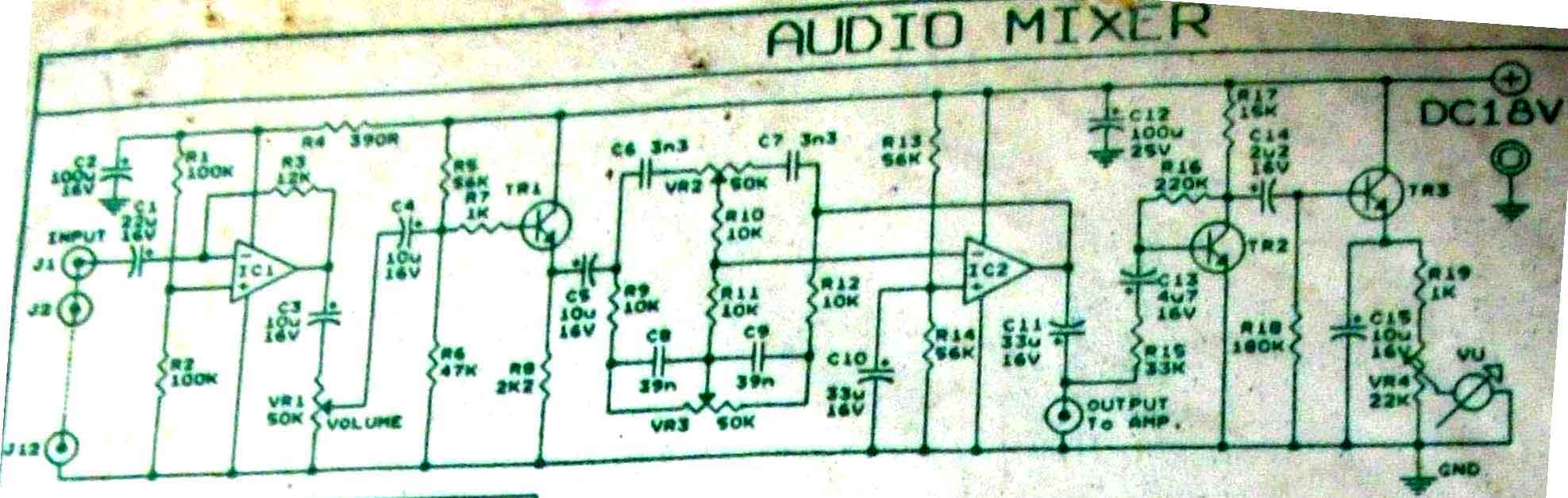
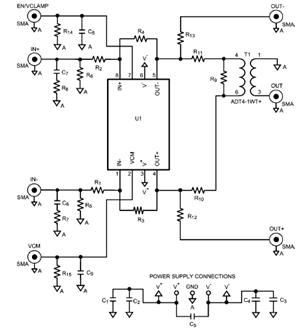
OTL transistor radio in a power amplifier circuit
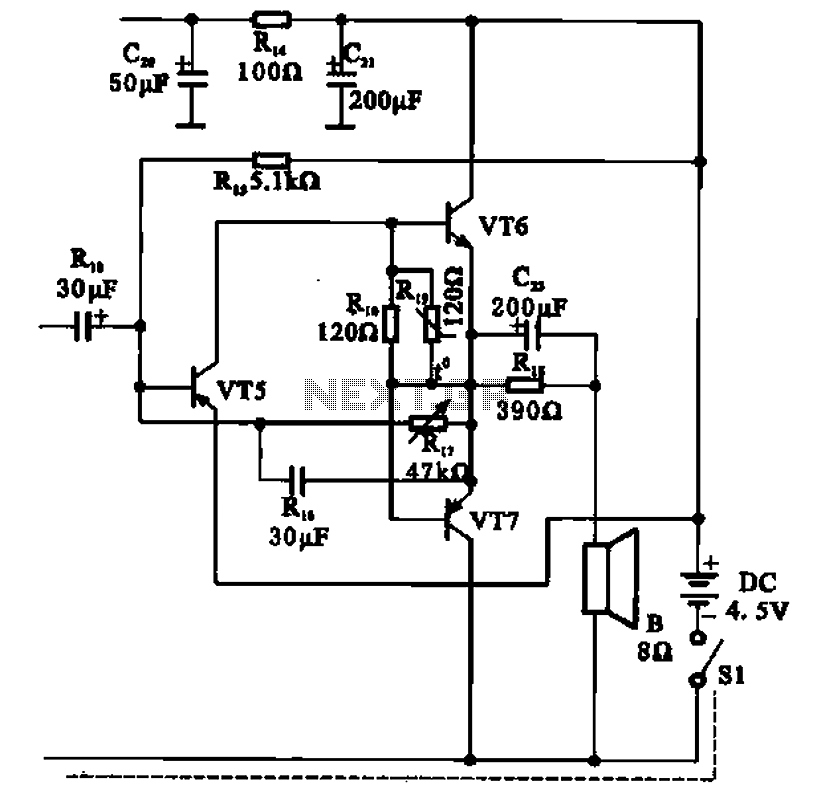
The transistor radio features a common output transformerless (OTL) power amplifier circuit. The VT5 component serves as the bias resistor for the driver stage. VT6 and VT7 form a complementary symmetry configuration, with VT6 being a germanium NPN transistor and VT7 a germanium PNP transistor. The circuit includes VT6, VT7, and the associated biasing resistor, which are characteristic of a typical OTL amplifier. The description omits details regarding the bias resistor and incentives to illustrate the circuit process.
The described circuit is a common output transformerless (OTL) power amplifier, which is designed to drive speakers directly without the need for an output transformer. This configuration is particularly beneficial in radio applications where space and weight are critical. The use of germanium transistors, such as VT6 (NPN) and VT7 (PNP), allows for lower voltage operation and improved thermal stability compared to silicon counterparts, making them suitable for low-power applications.
In this design, the driver stage is established by the VT5 bias resistor, which sets the operating point for the amplifier stages. The complementary symmetry arrangement of VT6 and VT7 ensures that both halves of the audio signal are amplified, improving linearity and reducing distortion. This is achieved by having the NPN and PNP transistors work in tandem, with VT6 amplifying the positive half of the waveform and VT7 handling the negative half.
The biasing resistor plays a crucial role in maintaining the correct biasing conditions for the transistors, ensuring that they operate in their active regions during signal amplification. The omission of certain details related to the bias resistor and incentives suggests a focus on the primary function of the circuit rather than its complete operational nuances.
Overall, this OTL amplifier circuit exemplifies an efficient and compact design suitable for portable transistor radios, where high performance and low power consumption are paramount.Transistor radio shows common OTL power amplifier circuit, VT5 bias resistor driver stage. VT6 and VT7 is a pair of complementary symmetry tube. VT6 germanium material NPN transistor, VT7 is germanium PNP transistor. VT6, VT7 and the biasing resistor composition typical OTL amplifier. To illustrate the process of the circuit, circle omitted satin bias resistor and incentives.
The described circuit is a common output transformerless (OTL) power amplifier, which is designed to drive speakers directly without the need for an output transformer. This configuration is particularly beneficial in radio applications where space and weight are critical. The use of germanium transistors, such as VT6 (NPN) and VT7 (PNP), allows for lower voltage operation and improved thermal stability compared to silicon counterparts, making them suitable for low-power applications.
In this design, the driver stage is established by the VT5 bias resistor, which sets the operating point for the amplifier stages. The complementary symmetry arrangement of VT6 and VT7 ensures that both halves of the audio signal are amplified, improving linearity and reducing distortion. This is achieved by having the NPN and PNP transistors work in tandem, with VT6 amplifying the positive half of the waveform and VT7 handling the negative half.
The biasing resistor plays a crucial role in maintaining the correct biasing conditions for the transistors, ensuring that they operate in their active regions during signal amplification. The omission of certain details related to the bias resistor and incentives suggests a focus on the primary function of the circuit rather than its complete operational nuances.
Overall, this OTL amplifier circuit exemplifies an efficient and compact design suitable for portable transistor radios, where high performance and low power consumption are paramount.Transistor radio shows common OTL power amplifier circuit, VT5 bias resistor driver stage. VT6 and VT7 is a pair of complementary symmetry tube. VT6 germanium material NPN transistor, VT7 is germanium PNP transistor. VT6, VT7 and the biasing resistor composition typical OTL amplifier. To illustrate the process of the circuit, circle omitted satin bias resistor and incentives.