passive low pass filter remove RF
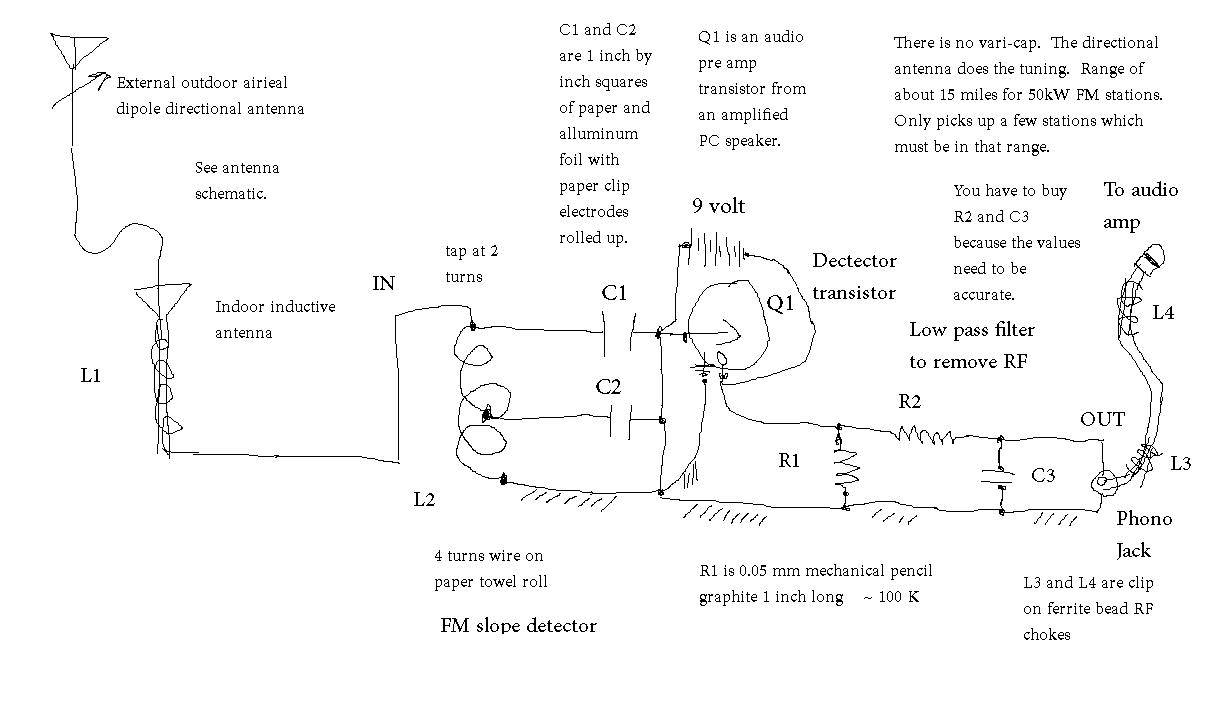
Seeking the appropriate resistor and capacitor values for a low-pass filter designed to eliminate radio frequency (RF) interference. The application focuses on filtering out unwanted untuned RF signals from a crystal radio set.
A low-pass filter is an essential component in radio frequency applications, particularly for crystal sets, where it is crucial to remove unwanted high-frequency signals that can interfere with the desired audio output. The design of a low-pass filter typically involves selecting resistor (R) and capacitor (C) values that determine the cutoff frequency (fc) of the filter.
The cutoff frequency is defined by the formula:
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
Where:
- fc is the cutoff frequency in Hertz (Hz),
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω),
- C is the capacitance in farads (F).
To effectively remove RF interference, the cutoff frequency should be set below the frequency of the undesired RF signals while allowing the desired audio frequencies to pass through. For instance, if the target audio frequencies range from 300 Hz to 3 kHz, the cutoff frequency may be set around 3 kHz to ensure that the filter attenuates higher RF frequencies while preserving the audio signal.
To select appropriate resistor and capacitor values, one can rearrange the cutoff frequency formula. For example, if a capacitor value of 10 nF (10 x 10^-9 F) is chosen, the resistor value can be calculated as follows:
R = 1 / (2πfcC)
Assuming a cutoff frequency of 3 kHz:
R = 1 / (2π(3000)(10 x 10^-9)) ≈ 5.3 kΩ
Alternatively, if a standard resistor value of 4.7 kΩ is selected, the corresponding capacitor value can be calculated:
C = 1 / (2πRfc)
Using R = 4.7 kΩ and fc = 3 kHz:
C = 1 / (2π(4700)(3000)) ≈ 11.3 nF
The selection of resistor and capacitor values can thus be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the application, ensuring optimal performance of the low-pass filter in removing unwanted RF signals from the crystal set. It is also advisable to consider the tolerances and power ratings of the components to ensure reliability and efficiency in the circuit design.Looking for resistor value and capacitor value for low pass filter to remove RF. The application is removing undesired untuned RF from the crystal set .. 🔗 External reference
A low-pass filter is an essential component in radio frequency applications, particularly for crystal sets, where it is crucial to remove unwanted high-frequency signals that can interfere with the desired audio output. The design of a low-pass filter typically involves selecting resistor (R) and capacitor (C) values that determine the cutoff frequency (fc) of the filter.
The cutoff frequency is defined by the formula:
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
Where:
- fc is the cutoff frequency in Hertz (Hz),
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω),
- C is the capacitance in farads (F).
To effectively remove RF interference, the cutoff frequency should be set below the frequency of the undesired RF signals while allowing the desired audio frequencies to pass through. For instance, if the target audio frequencies range from 300 Hz to 3 kHz, the cutoff frequency may be set around 3 kHz to ensure that the filter attenuates higher RF frequencies while preserving the audio signal.
To select appropriate resistor and capacitor values, one can rearrange the cutoff frequency formula. For example, if a capacitor value of 10 nF (10 x 10^-9 F) is chosen, the resistor value can be calculated as follows:
R = 1 / (2πfcC)
Assuming a cutoff frequency of 3 kHz:
R = 1 / (2π(3000)(10 x 10^-9)) ≈ 5.3 kΩ
Alternatively, if a standard resistor value of 4.7 kΩ is selected, the corresponding capacitor value can be calculated:
C = 1 / (2πRfc)
Using R = 4.7 kΩ and fc = 3 kHz:
C = 1 / (2π(4700)(3000)) ≈ 11.3 nF
The selection of resistor and capacitor values can thus be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the application, ensuring optimal performance of the low-pass filter in removing unwanted RF signals from the crystal set. It is also advisable to consider the tolerances and power ratings of the components to ensure reliability and efficiency in the circuit design.Looking for resistor value and capacitor value for low pass filter to remove RF. The application is removing undesired untuned RF from the crystal set .. 🔗 External reference