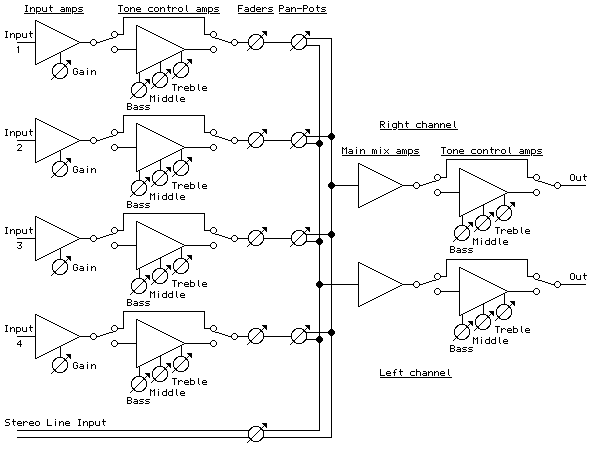
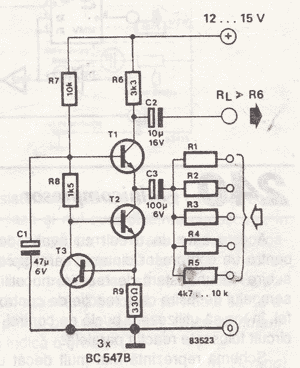
Passive mixer
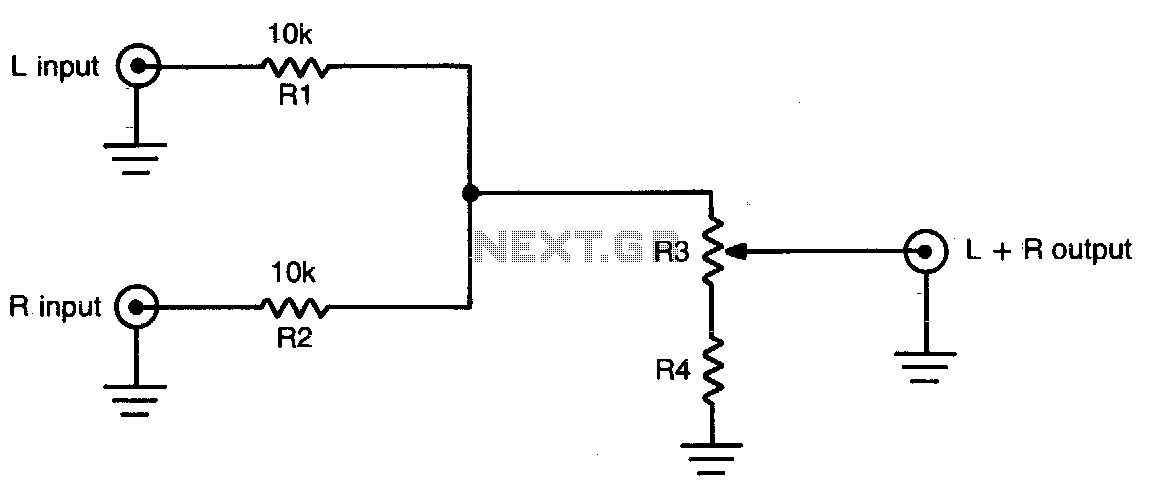
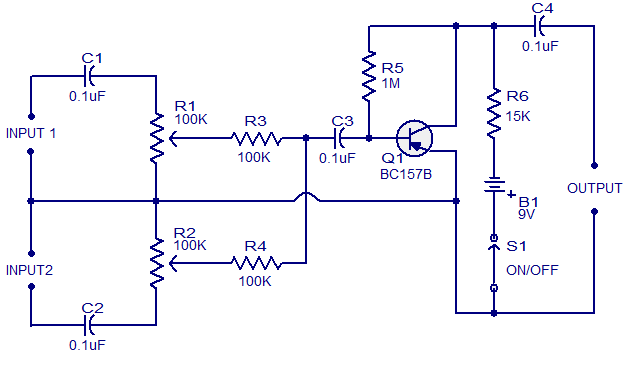
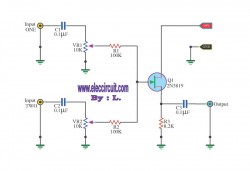
This simple circuit can be used to combine stereo signals to produce a monaural output. K1 and R2 isolate both circuits, while R3 controls the level of the combined output signal.
The circuit functions by taking two separate stereo input signals and merging them into a single monaural output. The primary components involved are the switch K1, resistors R2 and R3, and the input and output connectors.
K1 serves as a switch that isolates the left and right channels of the stereo input. When activated, it allows the signals from both channels to pass through while preventing interference between them. This isolation is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring that the final output is a true representation of the combined audio signals.
Resistor R2 is connected in such a way that it further isolates the two circuits, ensuring that any potential cross-talk or interference is minimized. This resistor plays a vital role in maintaining the quality of the audio output by reducing unwanted noise that can occur when combining signals.
Resistor R3 is used to adjust the level of the combined output signal. By varying the resistance, the amplitude of the output can be controlled, allowing for a balanced audio experience. This control is particularly important in applications where the output needs to match the input levels of other devices or systems, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
Overall, this circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for combining stereo audio signals into a single monaural output, making it suitable for various applications in audio processing and signal routing.This simple circuit can be used to combine stereo signals to produce a monaural output K1 and R2 isolate both circuits and R3 controls the level of the combined output signal. 🔗 External reference
The circuit functions by taking two separate stereo input signals and merging them into a single monaural output. The primary components involved are the switch K1, resistors R2 and R3, and the input and output connectors.
K1 serves as a switch that isolates the left and right channels of the stereo input. When activated, it allows the signals from both channels to pass through while preventing interference between them. This isolation is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring that the final output is a true representation of the combined audio signals.
Resistor R2 is connected in such a way that it further isolates the two circuits, ensuring that any potential cross-talk or interference is minimized. This resistor plays a vital role in maintaining the quality of the audio output by reducing unwanted noise that can occur when combining signals.
Resistor R3 is used to adjust the level of the combined output signal. By varying the resistance, the amplitude of the output can be controlled, allowing for a balanced audio experience. This control is particularly important in applications where the output needs to match the input levels of other devices or systems, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
Overall, this circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for combining stereo audio signals into a single monaural output, making it suitable for various applications in audio processing and signal routing.This simple circuit can be used to combine stereo signals to produce a monaural output K1 and R2 isolate both circuits and R3 controls the level of the combined output signal. 🔗 External reference