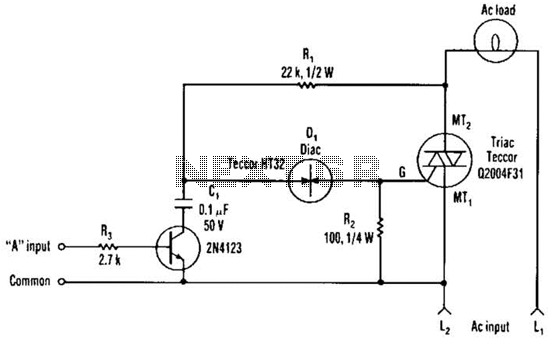
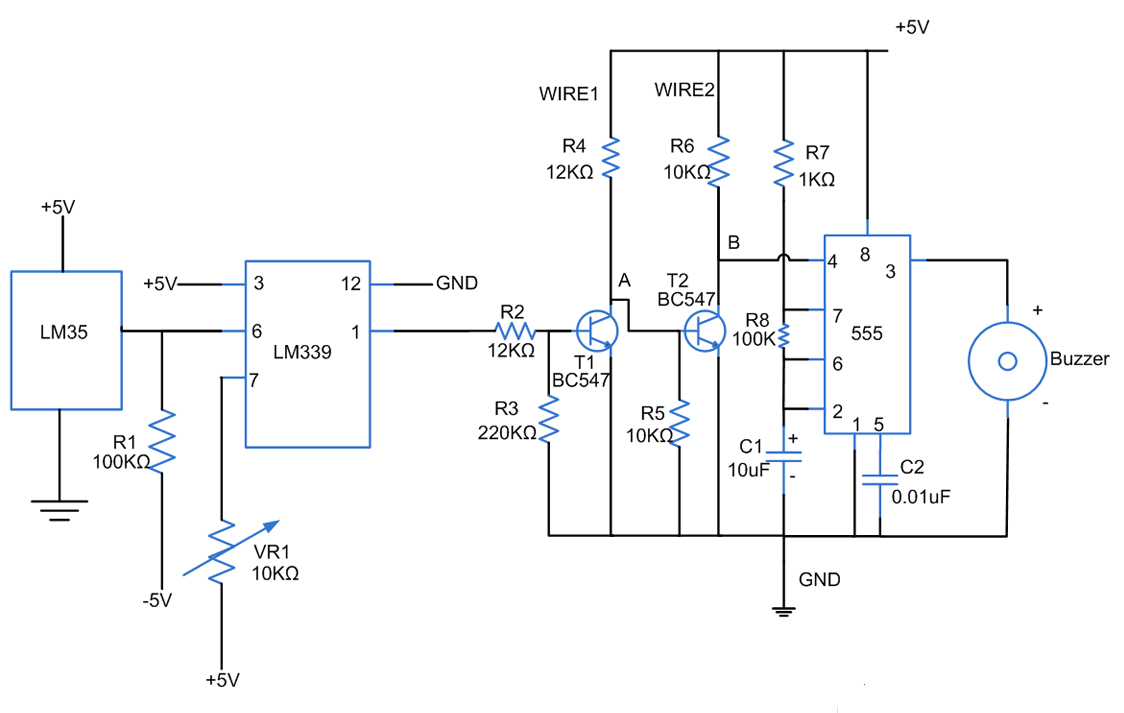
Simple mixer circuit
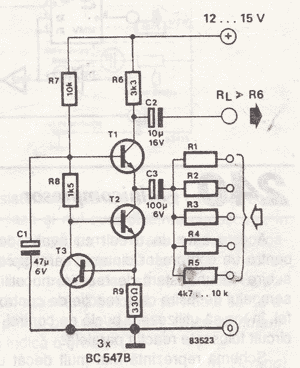
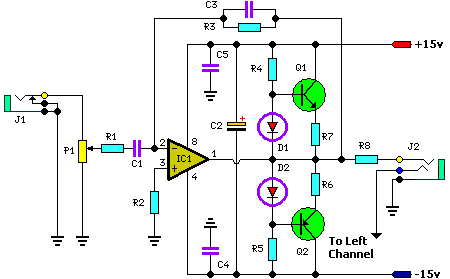
The simple mixer schematic is based on the common base principle, where input voltages are transformed into alternating currents that are summed to form the output.
The simple mixer circuit utilizes the common base configuration of a transistor, which is characterized by its ability to handle high-frequency signals and provide low output impedance. In this configuration, the emitter terminal serves as the input, while the collector terminal is the output. The base terminal is typically grounded or connected to a reference voltage, allowing the input signals to be applied directly to the emitter.
In operation, two or more input voltage signals are fed into the emitter of the transistor. These signals are transformed into alternating currents, which are then combined or summed at the collector. The summing process effectively allows for the mixing of different frequencies, making it suitable for applications in audio processing, radio frequency (RF) communications, and other signal processing tasks.
The output from the collector can be further processed or amplified, depending on the requirements of the application. The choice of transistor, along with the biasing resistors and coupling capacitors, plays a crucial role in determining the performance characteristics of the mixer, including gain, bandwidth, and distortion levels.
In summary, the simple mixer schematic based on the common base principle provides a straightforward yet effective method for combining multiple input signals into a single output, making it a valuable component in various electronic systems.The simple mixer schematic is built on common base principle, where input voltages are transformed in alternative currents wich are summed to form the alte. 🔗 External reference
The simple mixer circuit utilizes the common base configuration of a transistor, which is characterized by its ability to handle high-frequency signals and provide low output impedance. In this configuration, the emitter terminal serves as the input, while the collector terminal is the output. The base terminal is typically grounded or connected to a reference voltage, allowing the input signals to be applied directly to the emitter.
In operation, two or more input voltage signals are fed into the emitter of the transistor. These signals are transformed into alternating currents, which are then combined or summed at the collector. The summing process effectively allows for the mixing of different frequencies, making it suitable for applications in audio processing, radio frequency (RF) communications, and other signal processing tasks.
The output from the collector can be further processed or amplified, depending on the requirements of the application. The choice of transistor, along with the biasing resistors and coupling capacitors, plays a crucial role in determining the performance characteristics of the mixer, including gain, bandwidth, and distortion levels.
In summary, the simple mixer schematic based on the common base principle provides a straightforward yet effective method for combining multiple input signals into a single output, making it a valuable component in various electronic systems.The simple mixer schematic is built on common base principle, where input voltages are transformed in alternative currents wich are summed to form the alte. 🔗 External reference