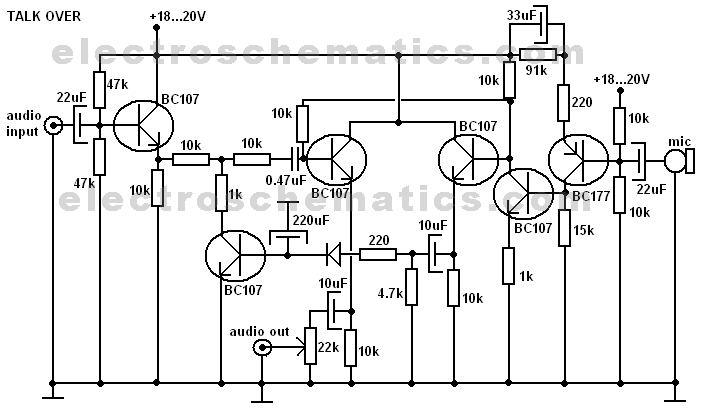
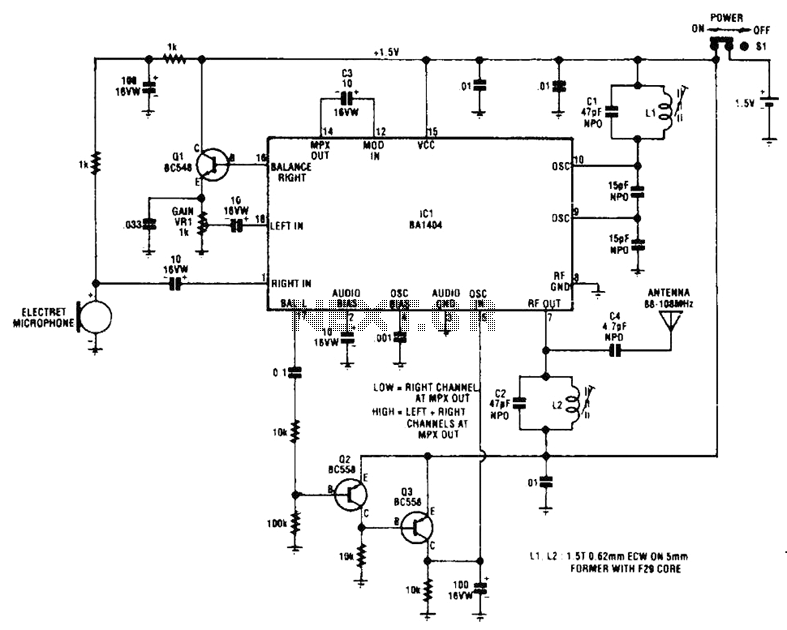
Pc Password Protection Circuit
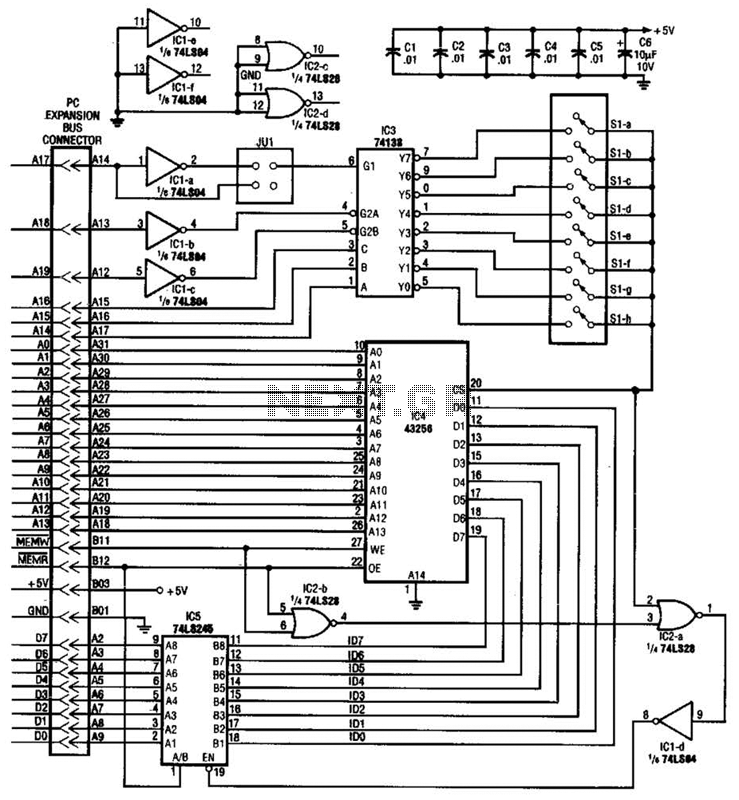
This circuit protects a PC by requiring a password to boot. After three unsuccessful attempts, the computer must undergo a cold reboot before the password can be attempted again. Software for this system is available; consult the reference for further details.
The described circuit functions as a security mechanism for personal computers, ensuring that unauthorized access is prevented during the boot process. The core of the circuit is a microcontroller or a dedicated security IC that monitors the input from a keypad or other input device where the password is entered.
Upon powering up, the circuit initializes and prompts the user for a password. The microcontroller compares the entered password against a pre-stored value in its non-volatile memory. If the correct password is entered, the circuit allows the PC to boot normally. In contrast, if the incorrect password is entered, the circuit increments a counter that tracks the number of failed attempts.
After three failed attempts, the circuit triggers a cold reboot of the PC, which can be achieved by controlling the power supply to the computer or by using a reset line. This mechanism ensures that the system is locked out temporarily, requiring the user to start the password entry process anew after the reboot.
The software component mentioned in the description is crucial for the configuration and management of the password system. It may provide functionalities such as setting the password, changing it, or even logging attempts for security auditing purposes. The software should be designed to interface seamlessly with the hardware, ensuring robust communication and minimal latency during the password verification process.
Overall, this circuit is an effective solution for enhancing the security of personal computers, particularly in environments where sensitive data is stored or accessed. With this circuit, a PC will be protected, requiring a password to boot. After three times, the computer will have to have a cold reboot and the password tried again. Software for this system is availableconsult the reference for further details. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a security mechanism for personal computers, ensuring that unauthorized access is prevented during the boot process. The core of the circuit is a microcontroller or a dedicated security IC that monitors the input from a keypad or other input device where the password is entered.
Upon powering up, the circuit initializes and prompts the user for a password. The microcontroller compares the entered password against a pre-stored value in its non-volatile memory. If the correct password is entered, the circuit allows the PC to boot normally. In contrast, if the incorrect password is entered, the circuit increments a counter that tracks the number of failed attempts.
After three failed attempts, the circuit triggers a cold reboot of the PC, which can be achieved by controlling the power supply to the computer or by using a reset line. This mechanism ensures that the system is locked out temporarily, requiring the user to start the password entry process anew after the reboot.
The software component mentioned in the description is crucial for the configuration and management of the password system. It may provide functionalities such as setting the password, changing it, or even logging attempts for security auditing purposes. The software should be designed to interface seamlessly with the hardware, ensuring robust communication and minimal latency during the password verification process.
Overall, this circuit is an effective solution for enhancing the security of personal computers, particularly in environments where sensitive data is stored or accessed. With this circuit, a PC will be protected, requiring a password to boot. After three times, the computer will have to have a cold reboot and the password tried again. Software for this system is availableconsult the reference for further details. 🔗 External reference