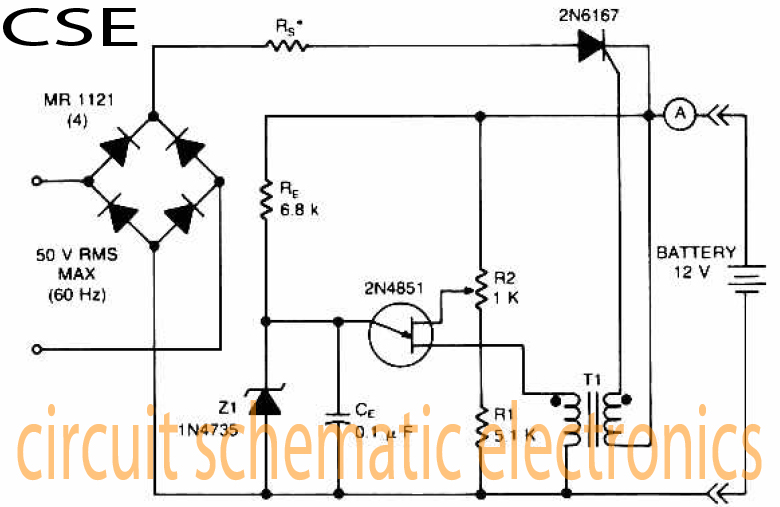
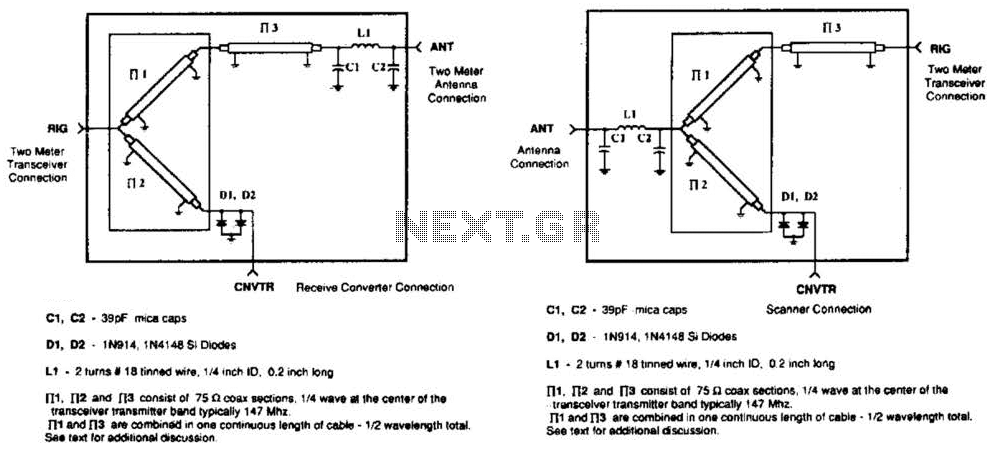
Handheld Laser Circuit
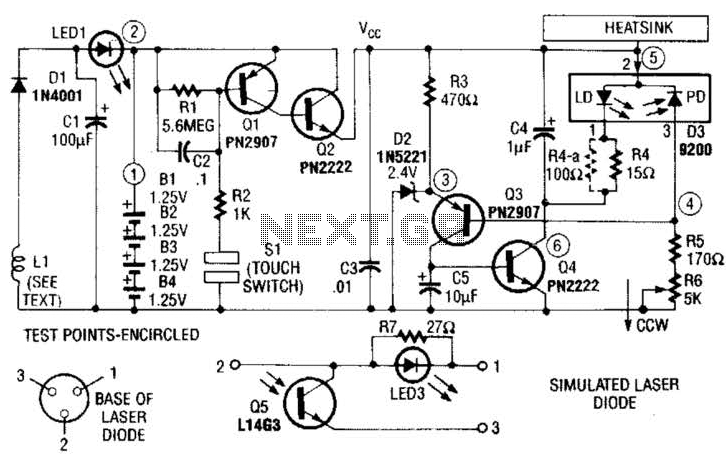
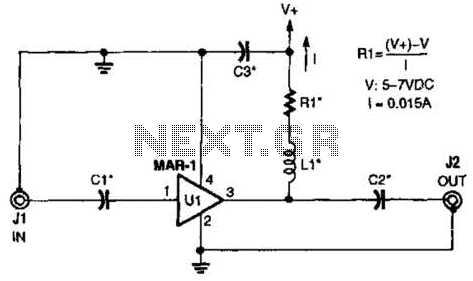
A laser diode TOLD9200 (Toshiba) serves as a source of laser light. Q3, Q2, and SI constitute a touch switch to control the laser. L1 is an RF pickup coil designed to extract energy from an RF-type battery charger. It consists of 10 turns of #18 wire wound on a Y-shaped diameter.
The circuit utilizes the TOLD9200 laser diode, which is known for its efficiency and capability to emit coherent light. The touch switch, comprising transistors Q3 and Q2 along with switch SI, enables user interaction by allowing the laser to be activated or deactivated through a simple touch, providing a user-friendly interface.
The RF pickup coil, L1, plays a crucial role in energy harvesting. By employing 10 turns of #18 gauge wire, the coil is optimized for capturing electromagnetic energy generated by an RF charger. The Y-shaped diameter of the coil enhances its inductance and efficiency, making it suitable for wireless energy transfer applications.
In the schematic, the power supply to the laser diode is controlled by the touch switch components. When the user touches the switch, a small current flows through Q2, which activates Q3, allowing current to flow to the laser diode. The operation of the laser diode can be adjusted based on the input signal from the touch switch, providing flexibility in its application.
This circuit can be applied in various applications, such as portable laser devices, where efficient power management and ease of use are essential. The integration of RF energy harvesting allows for sustainable operation, reducing the need for traditional battery replacements and enabling the device to function in a more eco-friendly manner. A laser diode TOLD9200 (Toshiba) is used as a source of laser light. Q3, Q2, and SI form a touch switch to control the.laser. LI is an RF pickup coil to pick up energy from an RF-type battery charger. It is 10 turns of #18 wire on a Y diameter. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the TOLD9200 laser diode, which is known for its efficiency and capability to emit coherent light. The touch switch, comprising transistors Q3 and Q2 along with switch SI, enables user interaction by allowing the laser to be activated or deactivated through a simple touch, providing a user-friendly interface.
The RF pickup coil, L1, plays a crucial role in energy harvesting. By employing 10 turns of #18 gauge wire, the coil is optimized for capturing electromagnetic energy generated by an RF charger. The Y-shaped diameter of the coil enhances its inductance and efficiency, making it suitable for wireless energy transfer applications.
In the schematic, the power supply to the laser diode is controlled by the touch switch components. When the user touches the switch, a small current flows through Q2, which activates Q3, allowing current to flow to the laser diode. The operation of the laser diode can be adjusted based on the input signal from the touch switch, providing flexibility in its application.
This circuit can be applied in various applications, such as portable laser devices, where efficient power management and ease of use are essential. The integration of RF energy harvesting allows for sustainable operation, reducing the need for traditional battery replacements and enabling the device to function in a more eco-friendly manner. A laser diode TOLD9200 (Toshiba) is used as a source of laser light. Q3, Q2, and SI form a touch switch to control the.laser. LI is an RF pickup coil to pick up energy from an RF-type battery charger. It is 10 turns of #18 wire on a Y diameter. 🔗 External reference