Phone in use indicator by LED
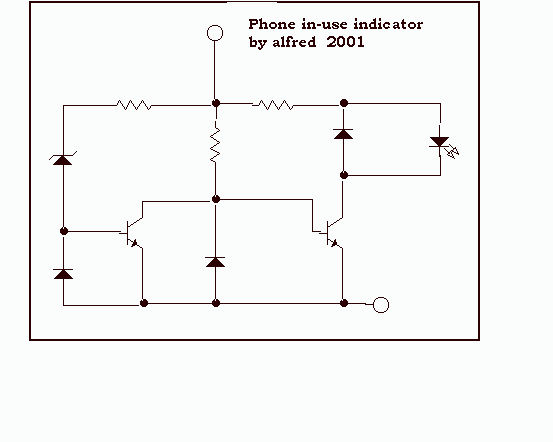
This circuit is useful to show when your line is busy. I used for this a pair of SMT transistors, the LEDs on when the voltage drops down to 40 V.
The circuit described functions as an indicator for a busy line, utilizing two surface-mount technology (SMT) transistors for its operation. The primary purpose is to illuminate LEDs when the voltage across the circuit decreases to 40 V, signaling that the line is currently in use.
In terms of components, the circuit includes two SMT transistors configured in a common-emitter arrangement. This setup allows for effective switching of the LEDs based on the voltage levels detected. When the input voltage exceeds 40 V, the transistors remain in the off state, preventing current flow through the LEDs. Conversely, as the voltage drops to 40 V or below, the transistors turn on, allowing current to flow through the LEDs, thus illuminating them.
The LED indicators provide a clear visual representation of the line status, which can be particularly useful in communication systems or other applications where line availability is critical. The choice of SMT transistors is advantageous for compactness and efficiency, allowing for a smaller circuit footprint while maintaining performance.
Additional considerations may include ensuring that the transistors are rated appropriately for the expected voltage and current levels, as well as incorporating suitable resistors in series with the LEDs to limit current and prevent damage. Proper thermal management may also be necessary to maintain the reliability of the circuit under prolonged use.This circuit is useful to show chen your line is busy. I used for this a pair of smt transistor, the leds on when the voltage drop down to 40 v. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described functions as an indicator for a busy line, utilizing two surface-mount technology (SMT) transistors for its operation. The primary purpose is to illuminate LEDs when the voltage across the circuit decreases to 40 V, signaling that the line is currently in use.
In terms of components, the circuit includes two SMT transistors configured in a common-emitter arrangement. This setup allows for effective switching of the LEDs based on the voltage levels detected. When the input voltage exceeds 40 V, the transistors remain in the off state, preventing current flow through the LEDs. Conversely, as the voltage drops to 40 V or below, the transistors turn on, allowing current to flow through the LEDs, thus illuminating them.
The LED indicators provide a clear visual representation of the line status, which can be particularly useful in communication systems or other applications where line availability is critical. The choice of SMT transistors is advantageous for compactness and efficiency, allowing for a smaller circuit footprint while maintaining performance.
Additional considerations may include ensuring that the transistors are rated appropriately for the expected voltage and current levels, as well as incorporating suitable resistors in series with the LEDs to limit current and prevent damage. Proper thermal management may also be necessary to maintain the reliability of the circuit under prolonged use.This circuit is useful to show chen your line is busy. I used for this a pair of smt transistor, the leds on when the voltage drop down to 40 v. 🔗 External reference
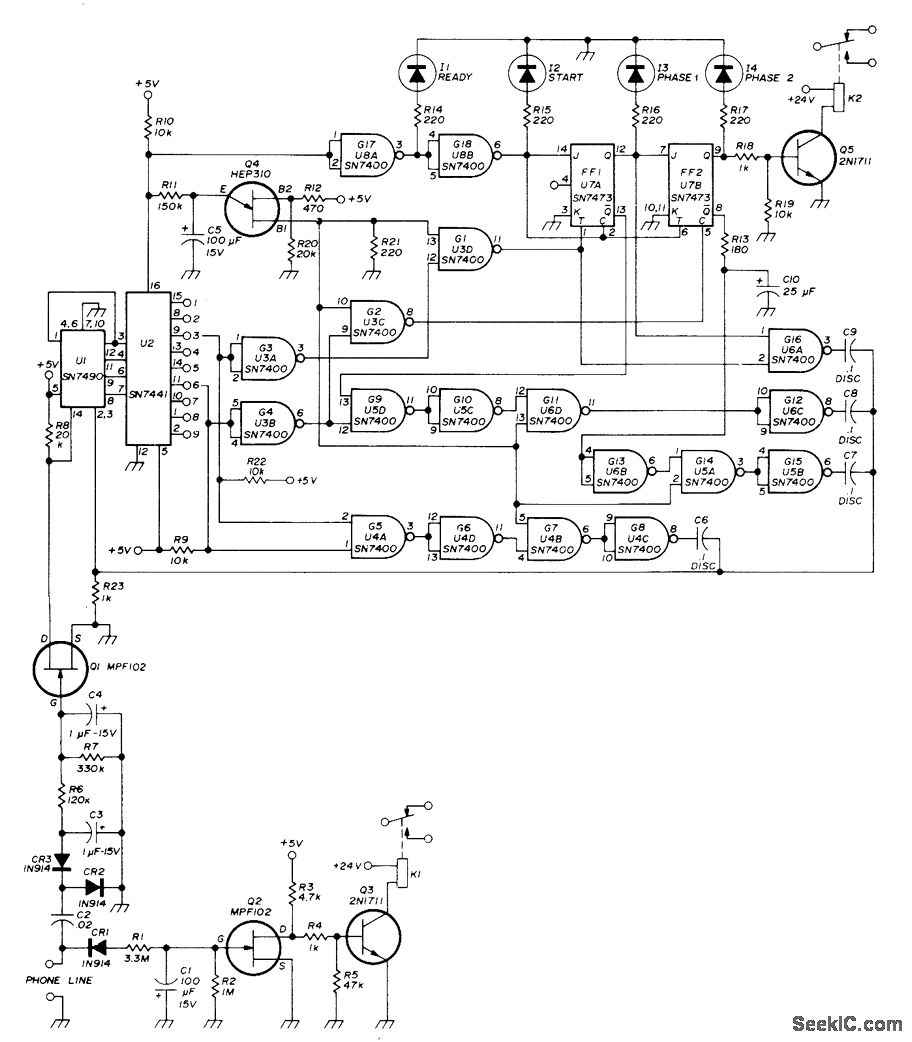
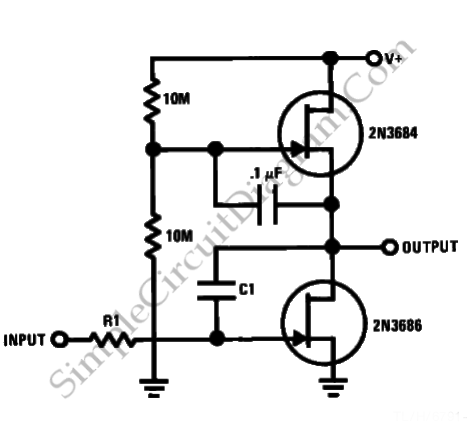
.jpg)