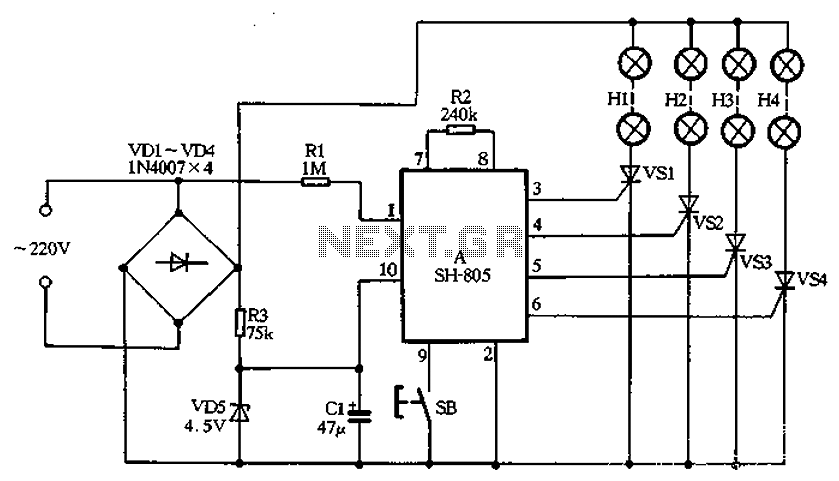
Phone light
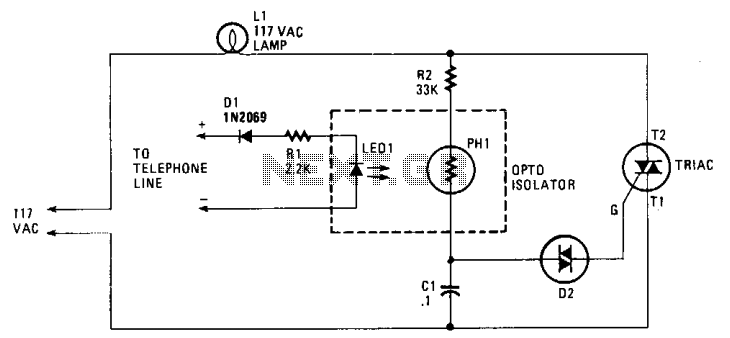
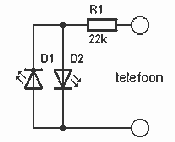
When the phone rings, the triac is activated into conduction by a signal applied to its gate (G) through a bilateral switch (diac), D2. The triac functions as a switch, conducting only when a signal is present at the gate.
The circuit involves a triac, which is a type of semiconductor device that can control power flow in AC circuits. It has three terminals: the gate (G), the anode (A1), and the cathode (A2). The gate terminal is crucial because it is where the triggering signal is applied to turn the triac on. In this scenario, the activation of the triac is initiated by a ringing signal from the phone, which is detected and passed through a diac (D2), a device that allows current to flow only after a certain threshold voltage is reached.
The diac serves as a bilateral switch, meaning it can conduct current in both directions once it is triggered. This feature is particularly useful in AC applications, as it allows the triac to be turned on regardless of the polarity of the voltage across it. When the phone rings, the signal is strong enough to exceed the diac's breakover voltage, causing it to conduct and send a triggering pulse to the gate of the triac. Once the triac is triggered, it enters a conductive state and remains on until the current flowing through it falls below a certain threshold, at which point it turns off.
In practical applications, this arrangement can be used for various purposes, such as activating a relay or another load when the phone rings, thereby enabling additional functionalities like alert systems or automated responses. The design must consider the voltage and current ratings of the components to ensure reliable operation and avoid damage. Additionally, snubber circuits may be employed across the triac to protect against voltage spikes that could occur during switching events.When the phone does ring the triac is triggered into conduction by a signal applied to its gate (G) through a bilateral switch (diac), D2. The triac acts as a switch, conducting only when a signal is present at the gate. 🔗 External reference
The circuit involves a triac, which is a type of semiconductor device that can control power flow in AC circuits. It has three terminals: the gate (G), the anode (A1), and the cathode (A2). The gate terminal is crucial because it is where the triggering signal is applied to turn the triac on. In this scenario, the activation of the triac is initiated by a ringing signal from the phone, which is detected and passed through a diac (D2), a device that allows current to flow only after a certain threshold voltage is reached.
The diac serves as a bilateral switch, meaning it can conduct current in both directions once it is triggered. This feature is particularly useful in AC applications, as it allows the triac to be turned on regardless of the polarity of the voltage across it. When the phone rings, the signal is strong enough to exceed the diac's breakover voltage, causing it to conduct and send a triggering pulse to the gate of the triac. Once the triac is triggered, it enters a conductive state and remains on until the current flowing through it falls below a certain threshold, at which point it turns off.
In practical applications, this arrangement can be used for various purposes, such as activating a relay or another load when the phone rings, thereby enabling additional functionalities like alert systems or automated responses. The design must consider the voltage and current ratings of the components to ensure reliable operation and avoid damage. Additionally, snubber circuits may be employed across the triac to protect against voltage spikes that could occur during switching events.When the phone does ring the triac is triggered into conduction by a signal applied to its gate (G) through a bilateral switch (diac), D2. The triac acts as a switch, conducting only when a signal is present at the gate. 🔗 External reference