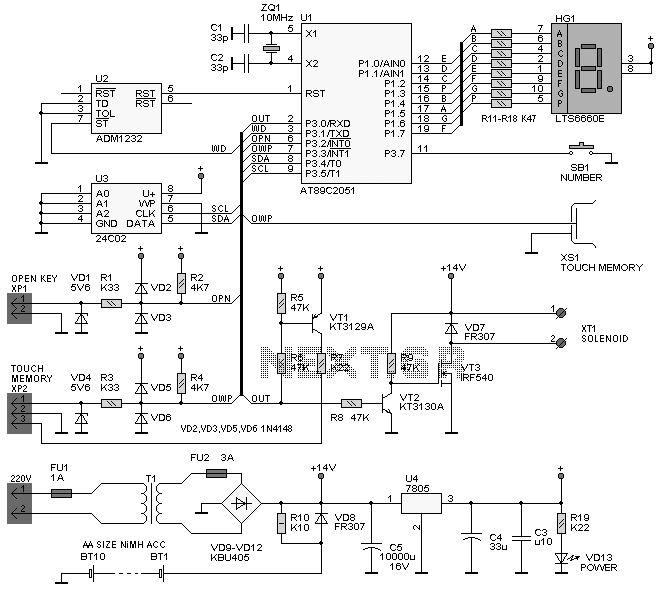
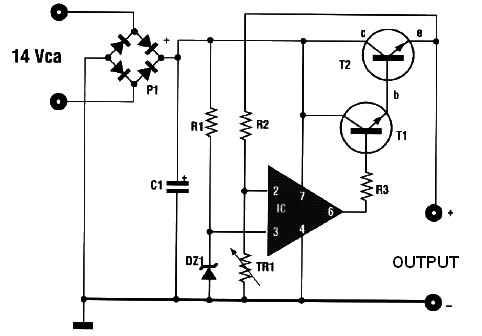
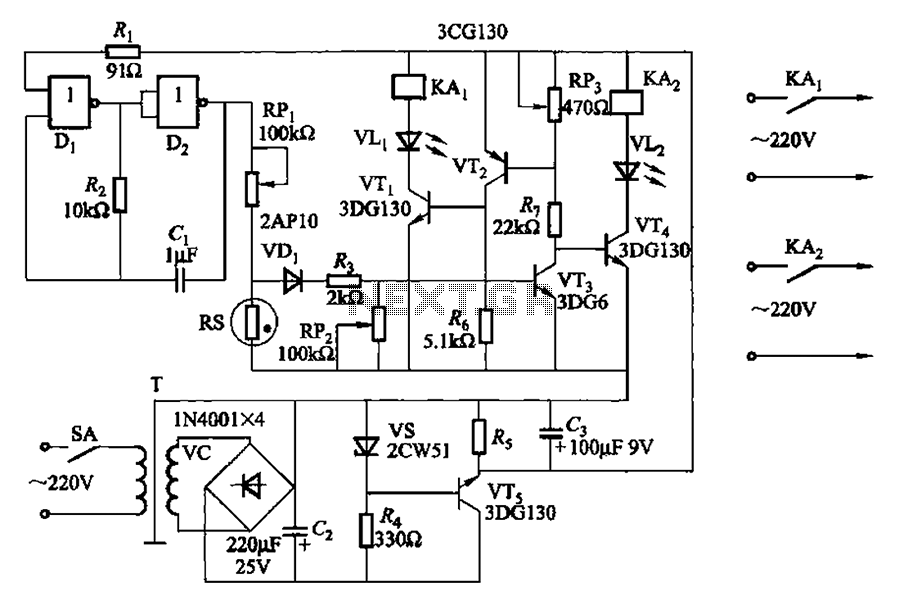
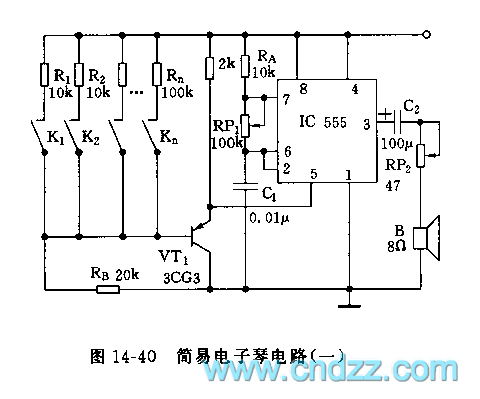
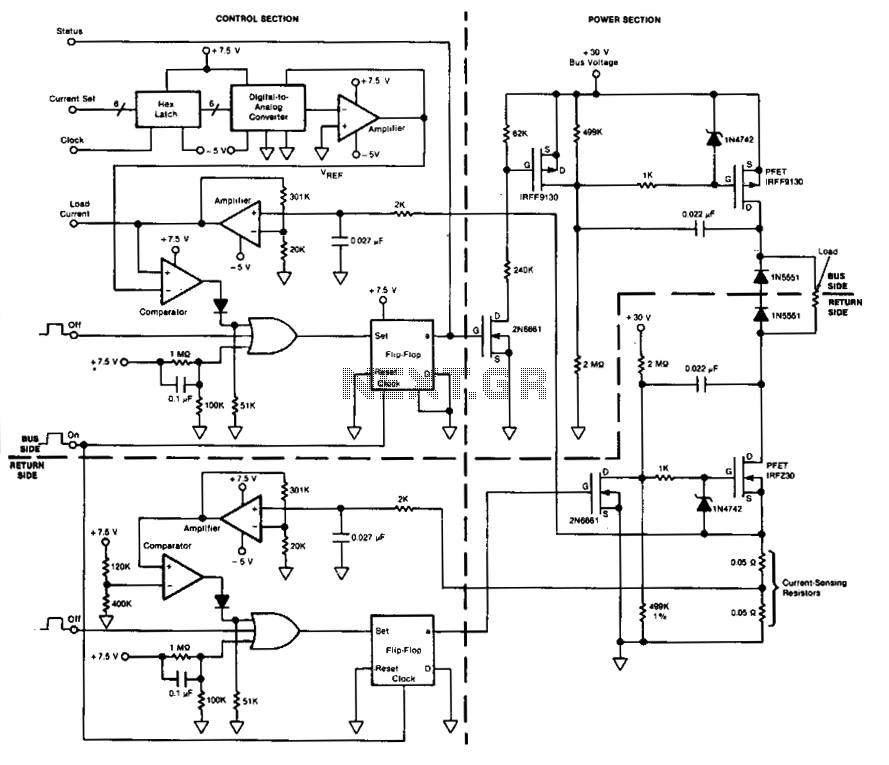
Photosensitive resistor circuit diagram of an automatic lighting
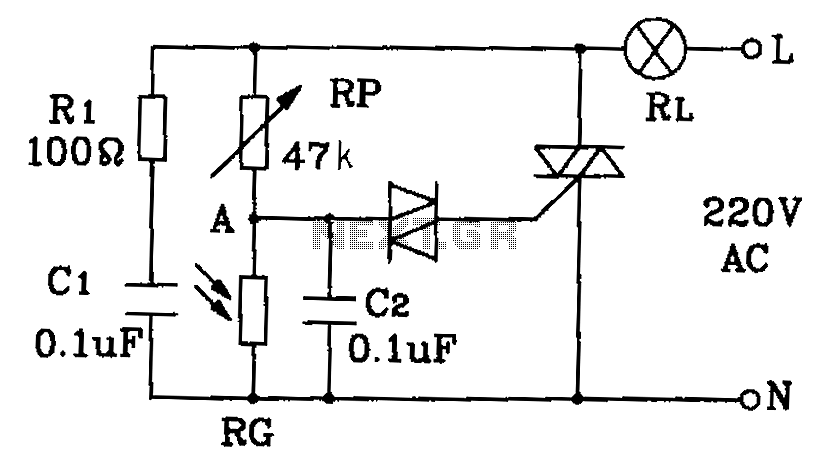
This circuit diagram illustrates an automatic lighting system designed for use in hospitals, dormitories, corridors, and public spaces. The system utilizes a photosensitive resistor to control the lighting, ensuring that lights are automatically turned off during the day and activated at night.
The automatic lighting circuit employs a photosensitive resistor (LDR) as the primary sensor, which detects ambient light levels. When the light intensity falls below a predetermined threshold, typically at dusk, the LDR's resistance increases, triggering the circuit to activate the lighting system. Conversely, during daylight hours, the increased light intensity causes the LDR's resistance to decrease, which in turn deactivates the lights.
The circuit can be designed using a simple transistor switch or a relay, depending on the required load capacity. For smaller loads, a transistor such as a NPN type can be used, where the LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The output from the divider is fed into the base of the transistor. When the resistance of the LDR increases at low light levels, sufficient base current flows, allowing the transistor to conduct and turn on the connected load, such as LED lights or fluorescent lamps.
For larger loads, a relay can be employed. The LDR and fixed resistor create a similar voltage divider, which activates a relay coil when the ambient light is low. The relay then closes its contacts, allowing mains power to flow to the lighting fixtures. This configuration provides isolation from high voltage and can handle larger currents safely.
To enhance functionality, additional components such as a timer or a microcontroller can be integrated into the circuit. This allows for more complex behaviors, such as dimming the lights or setting specific on/off schedules based on time rather than just light levels.
Overall, this automatic lighting system is efficient and practical for environments requiring reliable illumination during nighttime or low-light conditions, contributing to safety and convenience in various public and private settings. By the photosensitive resistor of this circuit is a circuit diagram of the automatic lighting for hospitals, dormitories corridor and public places. It automatically lights off during the day and at night.
The automatic lighting circuit employs a photosensitive resistor (LDR) as the primary sensor, which detects ambient light levels. When the light intensity falls below a predetermined threshold, typically at dusk, the LDR's resistance increases, triggering the circuit to activate the lighting system. Conversely, during daylight hours, the increased light intensity causes the LDR's resistance to decrease, which in turn deactivates the lights.
The circuit can be designed using a simple transistor switch or a relay, depending on the required load capacity. For smaller loads, a transistor such as a NPN type can be used, where the LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The output from the divider is fed into the base of the transistor. When the resistance of the LDR increases at low light levels, sufficient base current flows, allowing the transistor to conduct and turn on the connected load, such as LED lights or fluorescent lamps.
For larger loads, a relay can be employed. The LDR and fixed resistor create a similar voltage divider, which activates a relay coil when the ambient light is low. The relay then closes its contacts, allowing mains power to flow to the lighting fixtures. This configuration provides isolation from high voltage and can handle larger currents safely.
To enhance functionality, additional components such as a timer or a microcontroller can be integrated into the circuit. This allows for more complex behaviors, such as dimming the lights or setting specific on/off schedules based on time rather than just light levels.
Overall, this automatic lighting system is efficient and practical for environments requiring reliable illumination during nighttime or low-light conditions, contributing to safety and convenience in various public and private settings. By the photosensitive resistor of this circuit is a circuit diagram of the automatic lighting for hospitals, dormitories corridor and public places. It automatically lights off during the day and at night.