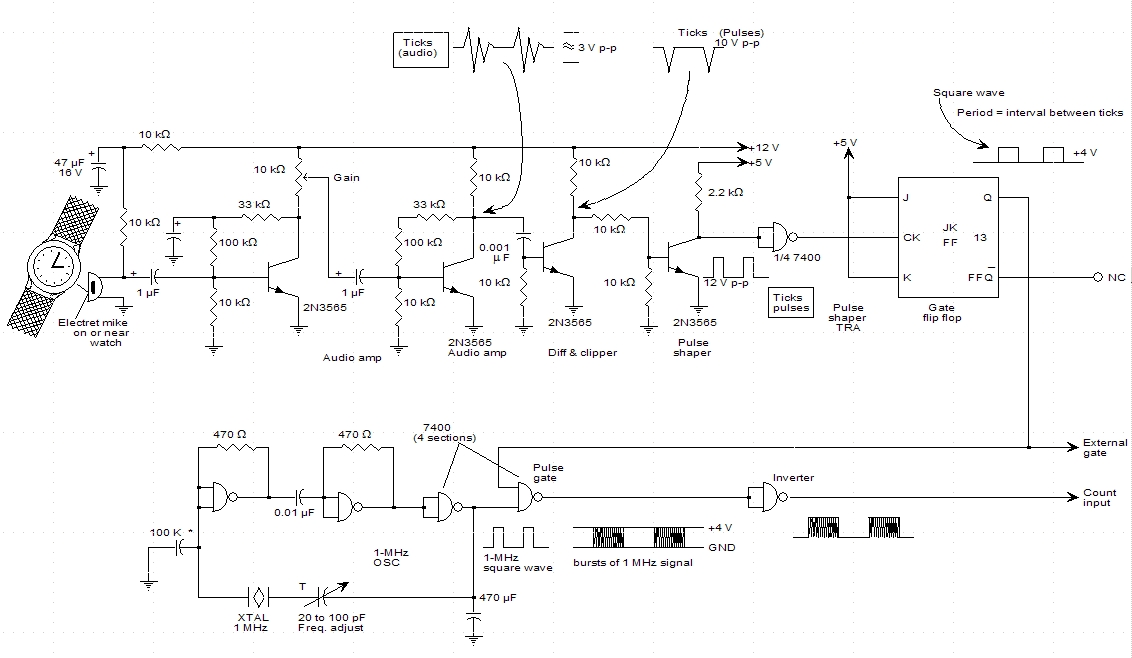
555 simple electronic keyboard circuit
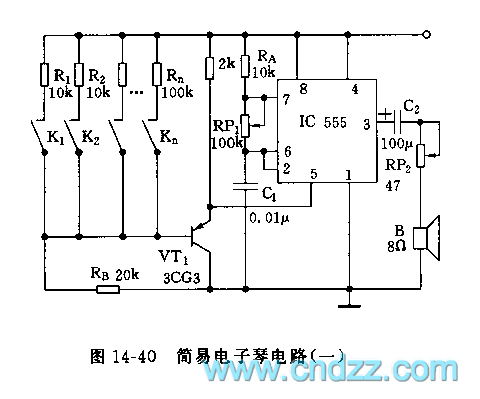
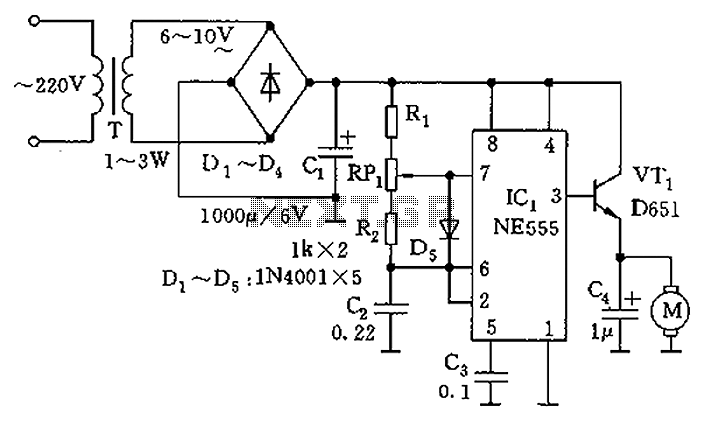
The controllable multivibrator, as illustrated in figure 14-40, consists of a 555 timer along with resistors RA, RP1, and capacitor C1. The oscillation frequency is influenced by the control voltage applied to pin 5. This control voltage is determined by the partial voltage across resistors R1 through Rn and RB, which is also dependent on the conduction state of transistor VT1. The transistor VT1 operates within its amplifier region, affecting the voltage at its collector electrode.
The controllable multivibrator circuit utilizes the 555 timer in an astable configuration, allowing it to generate a continuous square wave output. The frequency of the output waveform is primarily determined by the values of the resistors RA and RP1, as well as the capacitor C1. The control voltage at pin 5 plays a significant role in modulating the frequency of oscillation. By adjusting the voltage at this pin, the duty cycle and frequency can be altered, providing a means for external control over the timing characteristics of the circuit.
Resistors R1 to Rn and RB form a voltage divider network, influencing the voltage level seen at pin 5. The conduction state of the transistor VT1 further modifies this voltage, as it can either allow or block current flow, thereby affecting the voltage divider's output. When VT1 is in the active region, it allows the control voltage to rise or fall depending on the input signal, thereby dynamically adjusting the frequency of oscillation.
The output from the 555 timer can be used to drive various loads or can be fed into additional stages for further signal processing. This multivibrator configuration is widely used in applications such as pulse width modulation, tone generation, and timing circuits, making it a versatile component in electronic design. The careful selection of component values and the configuration of the circuit will determine the performance characteristics, such as frequency range and stability, making it essential to consider these factors during the design process.As the figure 14-40 shows, the controllable multivibrator is composed of the 555 and RA, RP1, C1, the oscillation frequency is related with the control voltage (pin-5), but the voltage of pin-5 depends on the partial voltage of R1?Rn and RB, and it is related with the conduction situation of VT1. The VT1 works in the amplifier region, voltage of electrode c.. 🔗 External reference
The controllable multivibrator circuit utilizes the 555 timer in an astable configuration, allowing it to generate a continuous square wave output. The frequency of the output waveform is primarily determined by the values of the resistors RA and RP1, as well as the capacitor C1. The control voltage at pin 5 plays a significant role in modulating the frequency of oscillation. By adjusting the voltage at this pin, the duty cycle and frequency can be altered, providing a means for external control over the timing characteristics of the circuit.
Resistors R1 to Rn and RB form a voltage divider network, influencing the voltage level seen at pin 5. The conduction state of the transistor VT1 further modifies this voltage, as it can either allow or block current flow, thereby affecting the voltage divider's output. When VT1 is in the active region, it allows the control voltage to rise or fall depending on the input signal, thereby dynamically adjusting the frequency of oscillation.
The output from the 555 timer can be used to drive various loads or can be fed into additional stages for further signal processing. This multivibrator configuration is widely used in applications such as pulse width modulation, tone generation, and timing circuits, making it a versatile component in electronic design. The careful selection of component values and the configuration of the circuit will determine the performance characteristics, such as frequency range and stability, making it essential to consider these factors during the design process.As the figure 14-40 shows, the controllable multivibrator is composed of the 555 and RA, RP1, C1, the oscillation frequency is related with the control voltage (pin-5), but the voltage of pin-5 depends on the partial voltage of R1?Rn and RB, and it is related with the conduction situation of VT1. The VT1 works in the amplifier region, voltage of electrode c.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713