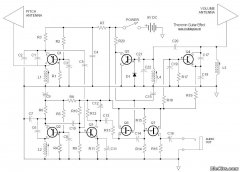
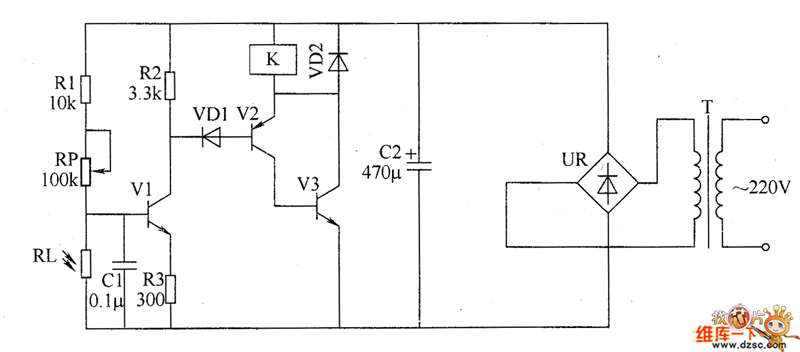
Birdie Doorbell Circuit

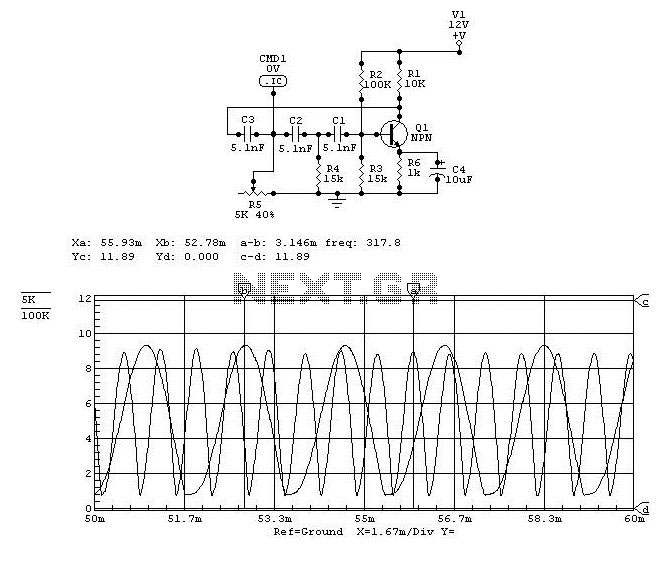
This is a circuit design for a doorbell that produces a sound resembling that of a bird. The circuit is controlled by an NPN transistor. The operation begins when P1 is set to an experimental value, starting with approximately 220 Ohms, which can be adjusted as needed. The transistor utilized is a general-purpose type, and nearly any PNP variant will suffice. L1 represents a bell transformer, which is typically already installed in residential settings. Alternatively, a 9-volt battery or wall adapter can be connected to points A and B (where A is positive). The diode (D1) is included to protect the circuit from accidental polarity reversal and is essential as a rectifier when using the bell transformer. T1 is a general-purpose PNP transistor, and any suitable alternative can be used. L2 is sourced from an old AM transistor radio and resembles a miniature transformer, often colored red or green. Experimentation with different transformers is necessary as the sound output may vary based on their specifications. The loudspeaker used is an 8 Ohm type with a power rating exceeding 200 milliwatts; a 2-watt speaker is recommended, although any speaker rated above 0.2 watts will be adequate.
The doorbell circuit operates on a simple principle of sound generation through the use of a PNP transistor and a transformer. The circuit begins its operation when the user activates the push button (P1), which allows current to flow through the base of the NPN transistor, thus turning it on. This, in turn, activates the PNP transistor (T1), allowing current to flow through the transformer (L1) or battery, generating an audio signal.
The transformer (L1) plays a crucial role in this circuit. If a bell transformer is used, it typically converts the low voltage from the power source into a higher voltage suitable for driving the speaker. In cases where a battery is used, the diode (D1) ensures that the current flows in the correct direction, preventing damage to the circuit from reverse polarity. The choice of a general-purpose PNP transistor allows for flexibility in component selection, providing ease of replacement if needed.
The audio output is influenced significantly by the transformer (L2) sourced from an old AM radio. The characteristics of this transformer determine the frequency response and overall sound quality produced by the loudspeaker. Adjusting the values and types of transformers can lead to different sound outputs, allowing for customization based on user preference.
The loudspeaker must be capable of handling the power output of the circuit. An 8 Ohm speaker rated for at least 200 milliwatts ensures sufficient sound output without distortion. For optimal performance, a speaker rated at 2 watts is recommended, as it provides a better safety margin and improved sound quality.
In summary, this doorbell circuit design offers an innovative way to produce a bird-like sound using a combination of basic electronic components. The flexibility in component selection and the ability to customize sound output make it an engaging project for those interested in electronics.This is a design circuit for a doorbell. This circuit can produces a sound like bird sound. This circuit controlled by transistor NPN. This is the figure of the circuit. The operation of the circuit is beginning when P1 is of experimental value. Start with 220 Ohms or so and modify to suit your needs. The transistor is a general purpose kind and i s not critical, almost any PNP type will work. L1 is a bell-transformer which is usually already present in the house. If you wish, you could use a battery instead of the bell transformer. Just hookup a 9-volt battery (or wall adapter)to points `A` and `B` (A=+) the diode (D1) is to protect the circuit from accidental polarity reversal and is optional, but required as a rectifier for use with the bell transformer. T1 is a General Purpose PNP transistor and probably anything will work. L2 comes out of an old am transistor radio. They look like miniature transformers and are usually colored red or green. You have to fiddle with different transformers as the sound can vary depending on the value. The loudspeaker is a 8 Ohm type and must be larger than 200milli-Watt. I used a 2Watt type, but anything over 0. 2W will do. 🔗 External reference
The doorbell circuit operates on a simple principle of sound generation through the use of a PNP transistor and a transformer. The circuit begins its operation when the user activates the push button (P1), which allows current to flow through the base of the NPN transistor, thus turning it on. This, in turn, activates the PNP transistor (T1), allowing current to flow through the transformer (L1) or battery, generating an audio signal.
The transformer (L1) plays a crucial role in this circuit. If a bell transformer is used, it typically converts the low voltage from the power source into a higher voltage suitable for driving the speaker. In cases where a battery is used, the diode (D1) ensures that the current flows in the correct direction, preventing damage to the circuit from reverse polarity. The choice of a general-purpose PNP transistor allows for flexibility in component selection, providing ease of replacement if needed.
The audio output is influenced significantly by the transformer (L2) sourced from an old AM radio. The characteristics of this transformer determine the frequency response and overall sound quality produced by the loudspeaker. Adjusting the values and types of transformers can lead to different sound outputs, allowing for customization based on user preference.
The loudspeaker must be capable of handling the power output of the circuit. An 8 Ohm speaker rated for at least 200 milliwatts ensures sufficient sound output without distortion. For optimal performance, a speaker rated at 2 watts is recommended, as it provides a better safety margin and improved sound quality.
In summary, this doorbell circuit design offers an innovative way to produce a bird-like sound using a combination of basic electronic components. The flexibility in component selection and the ability to customize sound output make it an engaging project for those interested in electronics.This is a design circuit for a doorbell. This circuit can produces a sound like bird sound. This circuit controlled by transistor NPN. This is the figure of the circuit. The operation of the circuit is beginning when P1 is of experimental value. Start with 220 Ohms or so and modify to suit your needs. The transistor is a general purpose kind and i s not critical, almost any PNP type will work. L1 is a bell-transformer which is usually already present in the house. If you wish, you could use a battery instead of the bell transformer. Just hookup a 9-volt battery (or wall adapter)to points `A` and `B` (A=+) the diode (D1) is to protect the circuit from accidental polarity reversal and is optional, but required as a rectifier for use with the bell transformer. T1 is a General Purpose PNP transistor and probably anything will work. L2 comes out of an old am transistor radio. They look like miniature transformers and are usually colored red or green. You have to fiddle with different transformers as the sound can vary depending on the value. The loudspeaker is a 8 Ohm type and must be larger than 200milli-Watt. I used a 2Watt type, but anything over 0. 2W will do. 🔗 External reference