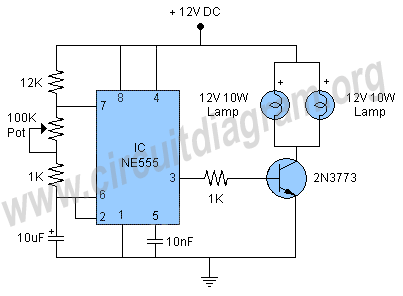
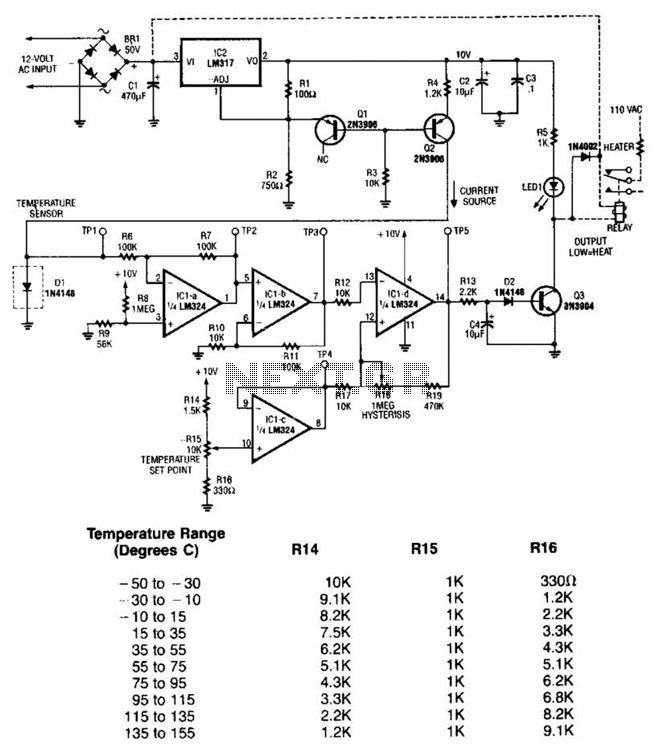
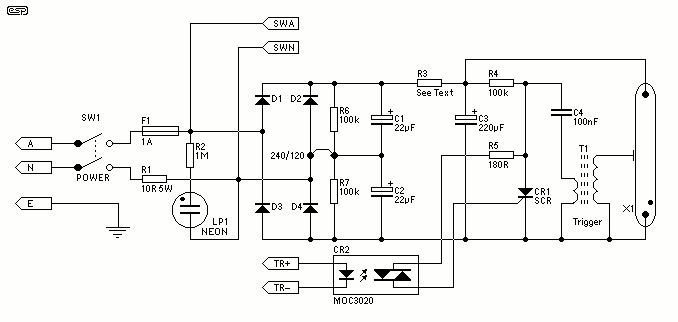
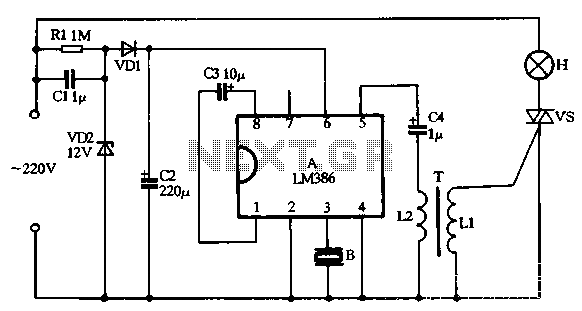
PIR Sensor Security Light & Switch
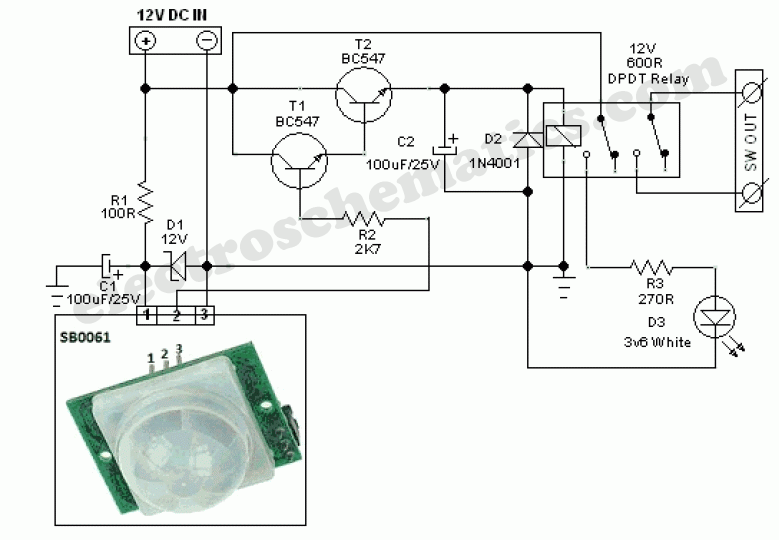
Moderately priced Passive Infrared (PIR) sensor modules are now widely available. By using these readymade and pre-configured PIR sensors, even an average electronics enthusiast can implement motion detection systems effectively.
Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors are devices that detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, typically humans or animals, within their field of view. These sensors operate based on the principle of detecting changes in infrared levels in the environment, which occur when a warm body moves across the sensor's detection zone. The typical range for these sensors is between 5 to 12 meters, depending on the specific module design and lens configuration.
A standard PIR sensor module consists of several key components: the PIR sensor itself, a Fresnel lens, a signal processing circuit, and output interfaces. The PIR sensor contains two pyroelectric elements that generate a voltage when exposed to infrared radiation. These elements are positioned in such a way that they can detect motion by comparing the infrared levels between them. The Fresnel lens focuses the incoming infrared radiation onto the sensor, enhancing its sensitivity and extending its detection range.
The signal processing circuit amplifies the output from the PIR sensor and filters it to reduce noise. This circuit typically includes a comparator that generates a digital signal when motion is detected. The output can be configured to trigger various devices, such as alarms, lights, or camera systems, depending on the application requirements.
Integration of a PIR sensor module into a circuit involves connecting the output pin to a microcontroller or a relay module, allowing for automated responses to detected motion. Power supply requirements for these modules are generally low, with most operating at 5V to 12V DC, making them suitable for battery-powered applications.
In summary, the availability of affordable PIR sensor modules has democratized the implementation of motion detection systems, enabling a wide range of applications in security, automation, and energy management. Their ease of use and effectiveness make them a popular choice among hobbyists and professionals alike.Moderately priced Passive Infrared PIR Sensor modules are now widely available. By using these readymade and pre-configured PIR sensors, even an average el.. 🔗 External reference
Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors are devices that detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, typically humans or animals, within their field of view. These sensors operate based on the principle of detecting changes in infrared levels in the environment, which occur when a warm body moves across the sensor's detection zone. The typical range for these sensors is between 5 to 12 meters, depending on the specific module design and lens configuration.
A standard PIR sensor module consists of several key components: the PIR sensor itself, a Fresnel lens, a signal processing circuit, and output interfaces. The PIR sensor contains two pyroelectric elements that generate a voltage when exposed to infrared radiation. These elements are positioned in such a way that they can detect motion by comparing the infrared levels between them. The Fresnel lens focuses the incoming infrared radiation onto the sensor, enhancing its sensitivity and extending its detection range.
The signal processing circuit amplifies the output from the PIR sensor and filters it to reduce noise. This circuit typically includes a comparator that generates a digital signal when motion is detected. The output can be configured to trigger various devices, such as alarms, lights, or camera systems, depending on the application requirements.
Integration of a PIR sensor module into a circuit involves connecting the output pin to a microcontroller or a relay module, allowing for automated responses to detected motion. Power supply requirements for these modules are generally low, with most operating at 5V to 12V DC, making them suitable for battery-powered applications.
In summary, the availability of affordable PIR sensor modules has democratized the implementation of motion detection systems, enabling a wide range of applications in security, automation, and energy management. Their ease of use and effectiveness make them a popular choice among hobbyists and professionals alike.Moderately priced Passive Infrared PIR Sensor modules are now widely available. By using these readymade and pre-configured PIR sensors, even an average el.. 🔗 External reference