Plant Watering Watcher Circuit Schematic
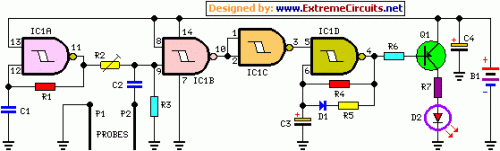
This circuit is designed to indicate when a plant requires watering. An LED blinks at a low frequency when the soil in the flower pot is excessively dry, turning off as the moisture level rises. The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted using resistor R2 to accommodate various soil types, pot sizes, and probe configurations.
The circuit utilizes a moisture sensor that detects the water content in the soil. When the soil moisture drops below a predetermined threshold, the sensor triggers a comparator circuit. This comparator is typically configured with a reference voltage that corresponds to the desired moisture level. The output of the comparator is connected to a microcontroller or a simple transistor switch that controls the LED.
In this setup, the LED serves as a visual indicator of the soil's moisture condition. The blinking rate of the LED can be influenced by the design of the timing circuit, which may include components like capacitors and additional resistors. The adjustment of R2 allows for fine-tuning of the sensitivity, ensuring that the circuit can effectively respond to different environmental conditions and soil compositions.
For optimal performance, the moisture sensor should be positioned at an appropriate depth within the soil, ensuring accurate readings. The circuit may also benefit from additional features such as a power-saving mode to prolong battery life or the incorporation of a buzzer for audible alerts. Overall, this moisture-sensing circuit is a practical solution for plant care, providing timely notifications to users regarding the watering needs of their plants.This circuit is intended to signal when a plant needs water. A LED flashes at a low rate when the ground in the flower-pot is too dry, turning off when the moisture level is increasing. Adjusting R2 will allow the user to adapt the sensitivity of the circuit for different grounds, pots and probe types
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a moisture sensor that detects the water content in the soil. When the soil moisture drops below a predetermined threshold, the sensor triggers a comparator circuit. This comparator is typically configured with a reference voltage that corresponds to the desired moisture level. The output of the comparator is connected to a microcontroller or a simple transistor switch that controls the LED.
In this setup, the LED serves as a visual indicator of the soil's moisture condition. The blinking rate of the LED can be influenced by the design of the timing circuit, which may include components like capacitors and additional resistors. The adjustment of R2 allows for fine-tuning of the sensitivity, ensuring that the circuit can effectively respond to different environmental conditions and soil compositions.
For optimal performance, the moisture sensor should be positioned at an appropriate depth within the soil, ensuring accurate readings. The circuit may also benefit from additional features such as a power-saving mode to prolong battery life or the incorporation of a buzzer for audible alerts. Overall, this moisture-sensing circuit is a practical solution for plant care, providing timely notifications to users regarding the watering needs of their plants.This circuit is intended to signal when a plant needs water. A LED flashes at a low rate when the ground in the flower-pot is too dry, turning off when the moisture level is increasing. Adjusting R2 will allow the user to adapt the sensitivity of the circuit for different grounds, pots and probe types
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713