
PoE+ Circuit Delivers 13W to 70W for Powered Devices (PDs)
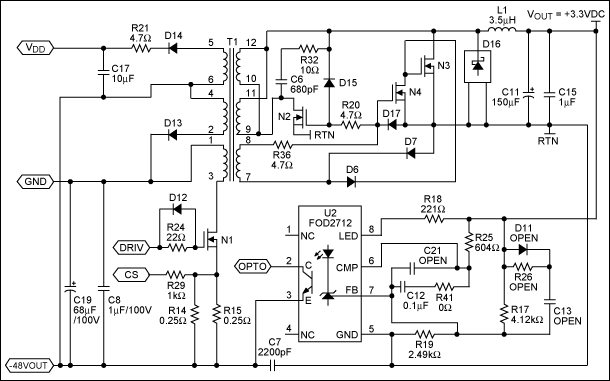
A PoE Plus power level of 30 W can be achieved by utilizing an external MOSFET along with a controller that is compatible with the older standard.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology enables the delivery of electrical power along with data over standard Ethernet cables, allowing devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points to receive power without the need for separate power supplies. The PoE Plus standard, defined by IEEE 802.3at, extends the capabilities of the original PoE standard (IEEE 802.3af) by allowing for a maximum power output of 30 W per port.
To implement a PoE Plus system capable of delivering this power level, an external MOSFET is integrated into the circuit design. The MOSFET serves as a switch that regulates the flow of power to the powered device (PD). The controller, designed for compatibility with the older PoE standard, manages the detection and classification of the powered device, ensuring that the appropriate power level is supplied.
The circuit typically includes a power sourcing equipment (PSE) component that interfaces with the Ethernet cable, supplying power through the spare pairs or the data pairs, depending on the wiring configuration. The external MOSFET is controlled by the PSE, which adjusts the gate voltage to modulate the power delivered to the PD based on its requirements.
In summary, the combination of an external MOSFET and a compatible controller allows the implementation of a PoE Plus system that meets the 30 W power requirement, enabling efficient power delivery for a variety of networked devices while adhering to the established standards.It is possible to implement a PoE Plus-required power level of 30 W, with the aid of an external MOSFET and a controller designed for the older standard.. 🔗 External reference
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology enables the delivery of electrical power along with data over standard Ethernet cables, allowing devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points to receive power without the need for separate power supplies. The PoE Plus standard, defined by IEEE 802.3at, extends the capabilities of the original PoE standard (IEEE 802.3af) by allowing for a maximum power output of 30 W per port.
To implement a PoE Plus system capable of delivering this power level, an external MOSFET is integrated into the circuit design. The MOSFET serves as a switch that regulates the flow of power to the powered device (PD). The controller, designed for compatibility with the older PoE standard, manages the detection and classification of the powered device, ensuring that the appropriate power level is supplied.
The circuit typically includes a power sourcing equipment (PSE) component that interfaces with the Ethernet cable, supplying power through the spare pairs or the data pairs, depending on the wiring configuration. The external MOSFET is controlled by the PSE, which adjusts the gate voltage to modulate the power delivered to the PD based on its requirements.
In summary, the combination of an external MOSFET and a compatible controller allows the implementation of a PoE Plus system that meets the 30 W power requirement, enabling efficient power delivery for a variety of networked devices while adhering to the established standards.It is possible to implement a PoE Plus-required power level of 30 W, with the aid of an external MOSFET and a controller designed for the older standard.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713

%2Bdecoder%2BCircuit%2Bschematic%2Busing%2BM8870.png)