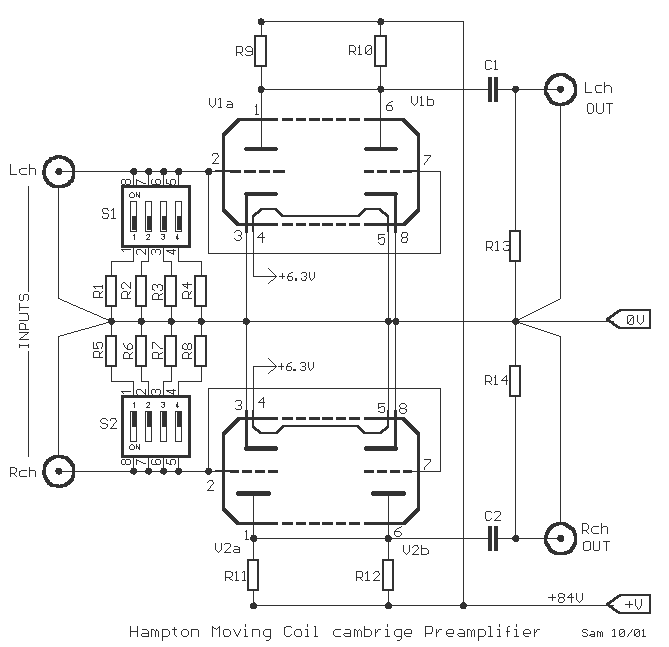
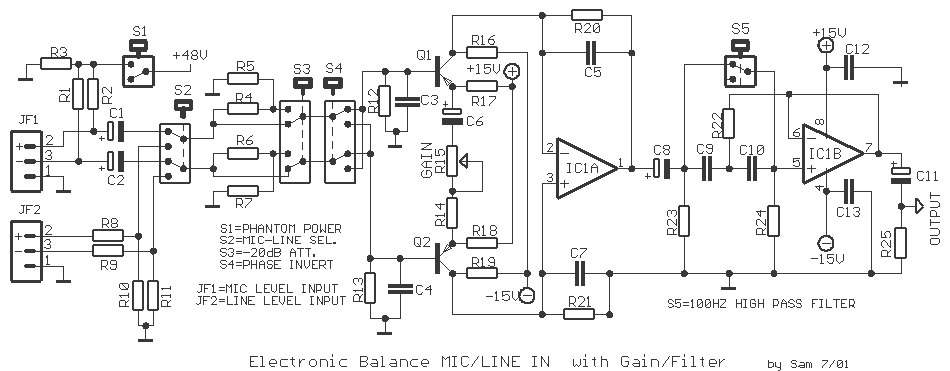
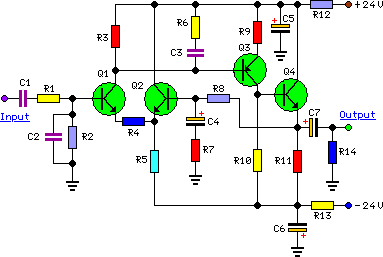
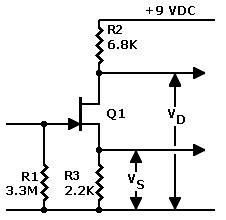
portable microphone preamplifier
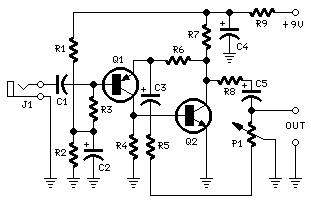
This circuit is primarily designed to offer a microphone input for standard home stereo amplifiers. Utilizing a battery supply effectively eliminates the risk of low-frequency hum interference from the mains, and simplifies the connection to the amplifier by removing the need for a mains cable and power supply.
The circuit functions by integrating a microphone preamplifier that boosts the weak audio signal from the microphone to a level suitable for input into the amplifier. The battery supply not only enhances portability but also ensures that the audio signal remains clean and free from the noise typically associated with AC mains power.
Key components of the circuit include a low-noise operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting arrangement to maximize the gain while minimizing distortion. The microphone input is connected to the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp, while feedback resistors are used to set the gain level according to the desired output.
Power management is crucial; therefore, a bypass capacitor may be included to filter any high-frequency noise from the power supply, ensuring that the audio output remains clear. Additionally, the design may incorporate a volume control potentiometer to allow for adjustment of the microphone input level before it reaches the amplifier.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective solution for integrating microphone inputs into home stereo systems, achieving high-quality audio reproduction without the complications associated with mains power supplies.This circuit is mainly intended to provide common home stereo amplifiers with a microphone input. The battery supply is a good compromise: in this manner the input circuit is free from mains low frequency hum pick-up and connection to the amplifier is more simple, due to the absence of mains cable and power supply.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit functions by integrating a microphone preamplifier that boosts the weak audio signal from the microphone to a level suitable for input into the amplifier. The battery supply not only enhances portability but also ensures that the audio signal remains clean and free from the noise typically associated with AC mains power.
Key components of the circuit include a low-noise operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting arrangement to maximize the gain while minimizing distortion. The microphone input is connected to the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp, while feedback resistors are used to set the gain level according to the desired output.
Power management is crucial; therefore, a bypass capacitor may be included to filter any high-frequency noise from the power supply, ensuring that the audio output remains clear. Additionally, the design may incorporate a volume control potentiometer to allow for adjustment of the microphone input level before it reaches the amplifier.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective solution for integrating microphone inputs into home stereo systems, achieving high-quality audio reproduction without the complications associated with mains power supplies.This circuit is mainly intended to provide common home stereo amplifiers with a microphone input. The battery supply is a good compromise: in this manner the input circuit is free from mains low frequency hum pick-up and connection to the amplifier is more simple, due to the absence of mains cable and power supply.. 🔗 External reference