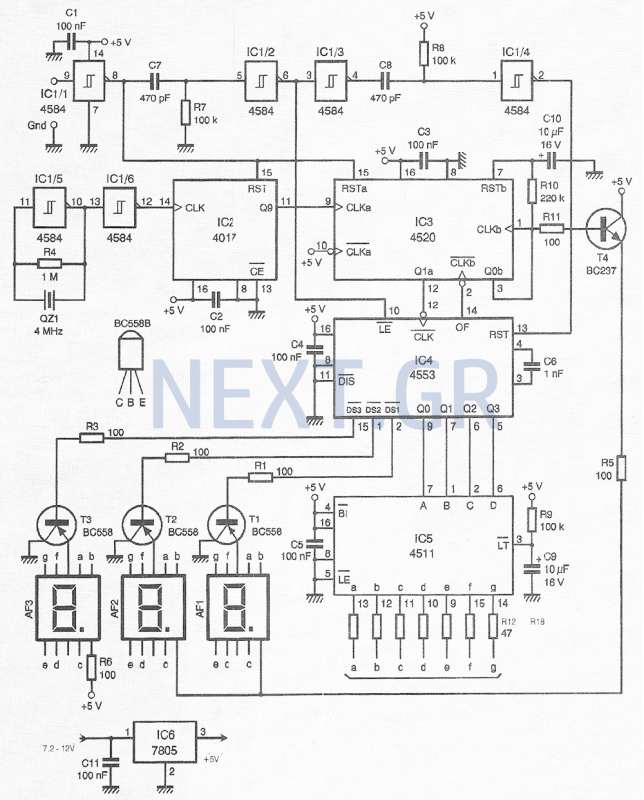
Positive Pulse Pulse Stretcher
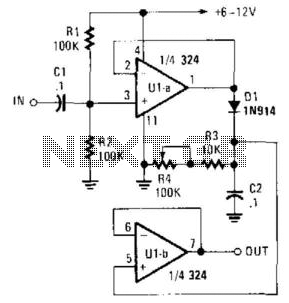
A simple pulse stretcher built with two sections of an operational amplifier uses a voltage follower U1A to drive D1 and C2. C2 charges to the peak value of the pulse voltage. Resistors R3 and R4 determine the discharge time of C2 and, consequently, the pulse stretching. U1B functions as a voltage follower. Typically, this circuit can stretch a pulse by a factor of 50. C2 can be charged to accommodate different pulse rates.
The described pulse stretcher circuit utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in two stages to achieve the desired pulse stretching effect. The first stage, comprising op-amp U1A, is configured as a voltage follower, which ensures that the output voltage follows the input voltage without any inversion or gain, thus providing high input impedance and low output impedance. This configuration is crucial for driving the diode D1 and capacitor C2 effectively.
When a pulse is applied to the input of U1A, the output voltage reaches the peak value of the input pulse, allowing capacitor C2 to charge up to this peak voltage. The charging process is rapid, enabling the capacitor to respond swiftly to changes in the input pulse amplitude. Resistors R3 and R4 are strategically placed in the circuit to control the discharge time of C2. The time constant of the discharge, which is determined by the values of R3 and R4 in conjunction with the capacitance of C2, directly influences the duration for which the output pulse is stretched.
The second stage of the circuit, comprising U1B, also operates as a voltage follower. This stage is essential for buffering the output of the pulse stretcher, ensuring that the output impedance remains low and can drive subsequent stages of the circuit without distortion or loss of signal integrity.
In practical applications, this pulse stretcher circuit is capable of stretching input pulses by a factor of up to 50 times, making it suitable for various electronic applications where pulse width modulation or timing adjustments are necessary. The ability to charge C2 to accommodate different pulse rates allows for versatility in its use, making it applicable in signal processing, communication systems, and timing circuits, where precise control over pulse duration is required. A simple pulse stretcher built with two sections of an op amp uses voltage follower U1A to drive Dl and C2. C2 charges to the peak value of pulse voltage. R3 and R4 determine the discharge time of C2 and therefore the pulse stretching. U1B acts as a voltage follower. Typically this circuit can stretch a pulse by a factor of 50. C2 can be charged to accommodate different pulse rates.
The described pulse stretcher circuit utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in two stages to achieve the desired pulse stretching effect. The first stage, comprising op-amp U1A, is configured as a voltage follower, which ensures that the output voltage follows the input voltage without any inversion or gain, thus providing high input impedance and low output impedance. This configuration is crucial for driving the diode D1 and capacitor C2 effectively.
When a pulse is applied to the input of U1A, the output voltage reaches the peak value of the input pulse, allowing capacitor C2 to charge up to this peak voltage. The charging process is rapid, enabling the capacitor to respond swiftly to changes in the input pulse amplitude. Resistors R3 and R4 are strategically placed in the circuit to control the discharge time of C2. The time constant of the discharge, which is determined by the values of R3 and R4 in conjunction with the capacitance of C2, directly influences the duration for which the output pulse is stretched.
The second stage of the circuit, comprising U1B, also operates as a voltage follower. This stage is essential for buffering the output of the pulse stretcher, ensuring that the output impedance remains low and can drive subsequent stages of the circuit without distortion or loss of signal integrity.
In practical applications, this pulse stretcher circuit is capable of stretching input pulses by a factor of up to 50 times, making it suitable for various electronic applications where pulse width modulation or timing adjustments are necessary. The ability to charge C2 to accommodate different pulse rates allows for versatility in its use, making it applicable in signal processing, communication systems, and timing circuits, where precise control over pulse duration is required. A simple pulse stretcher built with two sections of an op amp uses voltage follower U1A to drive Dl and C2. C2 charges to the peak value of pulse voltage. R3 and R4 determine the discharge time of C2 and therefore the pulse stretching. U1B acts as a voltage follower. Typically this circuit can stretch a pulse by a factor of 50. C2 can be charged to accommodate different pulse rates.