power led flasher

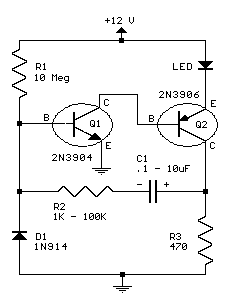
The low-cost and compact circuit presented here serves as a highly power-saving flashing LED indicator. While most LEDs typically fail to operate below 2 volts, with a forward voltage of at least 1.6 volts, this flasher can function using a single cell. The LM3909 integrated circuit incorporates nearly all the necessary triggering and pulsing circuitry that regulates the flashing rate. The only additional component utilized is capacitor C1, which determines the final flashing rate, set to approximately 1 Hz in this design. The circuit exhibits very low current consumption, around 0.3 mA, achieved through intermittent current flow in the form of brief pulses through the LED. A capacitor connected across the cell ensures the circuit remains operational even when the voltage drops below 1.2 volts, the minimum threshold.
This circuit utilizes the LM3909, a versatile integrated circuit designed specifically for LED flashing applications. The LM3909 achieves its low power consumption through the use of a pulse-width modulation technique, allowing it to generate a series of short pulses that drive the LED. The frequency of these pulses, determined by the capacitor C1 and the internal timing circuitry of the LM3909, is set to approximately 1 Hz, resulting in a visible flashing effect.
The design focuses on efficiency, making it suitable for battery-powered applications where prolonged operation is essential. The low threshold voltage requirement makes this circuit particularly advantageous for use with single-cell batteries, such as AA or AAA cells, which typically provide around 1.5 volts. The circuit's ability to function effectively down to 1.2 volts extends its operational lifespan, ensuring that the LED remains illuminated even as the battery discharges.
In practical applications, this flashing LED indicator can be employed in various settings, including low-power warning lights, status indicators, or decorative lighting. The simplicity of the circuit design allows for easy integration into existing projects, while the compact form factor ensures it can be accommodated in a wide range of enclosures. This makes the circuit not only efficient but also versatile for different uses in consumer electronics and hobbyist projects.The low cost and extremely compact circuit given here is that of a highly power saving flashing LED indicator. Whereas most LEDs fail to work below 2 volt, their forward voltage alone being 1, 6 volts minimum, this flasher can work off one single cell.
The LM3909 contains virtually all the essential trigger and pulsing circuitry which controls the f lashing rate. The only other component used is the capacitor C1 which decides the final flashing rate, which in this case is set to about 1Hz. The circuit has very low current has a very low current consumption, in the order of about 0. 3mA, which is made possible due to intermittent current flow in the form of very short pulse through the LED.
The capacitor connected across the cell ensures that the circuit continues to operate even when voltage falls below 1. 2 volt (minimum limit). 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes the LM3909, a versatile integrated circuit designed specifically for LED flashing applications. The LM3909 achieves its low power consumption through the use of a pulse-width modulation technique, allowing it to generate a series of short pulses that drive the LED. The frequency of these pulses, determined by the capacitor C1 and the internal timing circuitry of the LM3909, is set to approximately 1 Hz, resulting in a visible flashing effect.
The design focuses on efficiency, making it suitable for battery-powered applications where prolonged operation is essential. The low threshold voltage requirement makes this circuit particularly advantageous for use with single-cell batteries, such as AA or AAA cells, which typically provide around 1.5 volts. The circuit's ability to function effectively down to 1.2 volts extends its operational lifespan, ensuring that the LED remains illuminated even as the battery discharges.
In practical applications, this flashing LED indicator can be employed in various settings, including low-power warning lights, status indicators, or decorative lighting. The simplicity of the circuit design allows for easy integration into existing projects, while the compact form factor ensures it can be accommodated in a wide range of enclosures. This makes the circuit not only efficient but also versatile for different uses in consumer electronics and hobbyist projects.The low cost and extremely compact circuit given here is that of a highly power saving flashing LED indicator. Whereas most LEDs fail to work below 2 volt, their forward voltage alone being 1, 6 volts minimum, this flasher can work off one single cell.
The LM3909 contains virtually all the essential trigger and pulsing circuitry which controls the f lashing rate. The only other component used is the capacitor C1 which decides the final flashing rate, which in this case is set to about 1Hz. The circuit has very low current has a very low current consumption, in the order of about 0. 3mA, which is made possible due to intermittent current flow in the form of very short pulse through the LED.
The capacitor connected across the cell ensures that the circuit continues to operate even when voltage falls below 1. 2 volt (minimum limit). 🔗 External reference