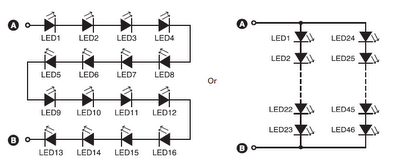
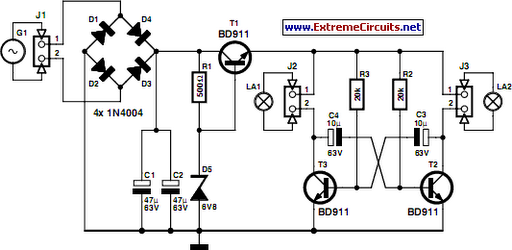
two transistor led flasher
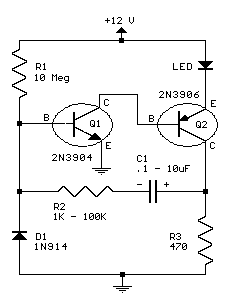
This circuit will flash a bright red LED (5000 mcd) as an attention-getting device or fake car alarm. Component values are not critical, and other transistors may be used. The flash duration is determined by R2 and C1 and is approximately three time constants (3*R2*C1). Brightness is controlled by R3, which limits the LED current to about 20 mA for specified values. R1 provides bias for the transistors, which should be low enough not to saturate Q2 with the capacitor disconnected. If the circuit does not oscillate, R1 may be too low or R2 may be too high. D1 allows for higher duty cycle operation and limits the reverse voltage at the base of Q1 to -0.7 V. D1 may be omitted for low voltage (3-9 V) and low duty cycle operation. Most parts are available at Radio Shack.
This circuit is designed to operate as a flashing LED indicator, serving as an attention-grabbing device or simulating a car alarm. The core component of the circuit is a bright red LED rated at 5000 mcd, which is responsible for the visual alert. The circuit's flashing behavior is controlled by a combination of resistors and capacitors, specifically R2 and C1, which define the timing characteristics. The flash duration is approximately calculated as three time constants, expressed mathematically as 3*R2*C1. This relationship allows for customization of the flash rate by adjusting the values of R2 and C1.
The brightness of the LED is managed by resistor R3, which limits the current flowing through the LED to approximately 20 mA. This is a critical specification, as it ensures the LED operates within safe parameters while maintaining sufficient visibility. The biasing of the transistors is achieved through R1, which must be set to a low enough value to prevent Q2 from saturating when the capacitor is disconnected, thus ensuring proper oscillation of the circuit.
In the event that the circuit fails to oscillate, adjustments may be necessary. If R1 is set too low or R2 is set too high, the circuit may not function as intended. Diode D1 plays a significant role by allowing for a higher duty cycle operation and protecting the base of transistor Q1 from reverse voltage, which is limited to -0.7 V. In applications where lower voltage operation (3-9 V) and reduced duty cycle are acceptable, D1 can be omitted, simplifying the circuit design.
The components required for this circuit are readily available from electronic suppliers, such as Radio Shack, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. Overall, this flashing LED circuit provides a straightforward and effective solution for creating a visual alert system.This circuit will flash a bright red LED (5000 mcd) as an attention getting device or fake car alarm. Component values are not critical and other transistors may be used. Flash duration is determined by R2 and C1 and is approximately 3 time constants (3*R2*C1). Brightness is controlled by R3 wich limits the LED current to about 20 mA for values li sted. R1 provides bias for the transistors which should be low enough not to saturate Q2 with the capacitor disconnected. If the circuit does not oscillate, R1 may be too low or R2 may be too high. D1 allows for higher duty cycle operation and limits the reverse voltage at the base of Q1 to -0. 7 V. D1 may be omitted for low voltage (3-9) and low duty cycle operation. Most parts available at Radio Shack. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to operate as a flashing LED indicator, serving as an attention-grabbing device or simulating a car alarm. The core component of the circuit is a bright red LED rated at 5000 mcd, which is responsible for the visual alert. The circuit's flashing behavior is controlled by a combination of resistors and capacitors, specifically R2 and C1, which define the timing characteristics. The flash duration is approximately calculated as three time constants, expressed mathematically as 3*R2*C1. This relationship allows for customization of the flash rate by adjusting the values of R2 and C1.
The brightness of the LED is managed by resistor R3, which limits the current flowing through the LED to approximately 20 mA. This is a critical specification, as it ensures the LED operates within safe parameters while maintaining sufficient visibility. The biasing of the transistors is achieved through R1, which must be set to a low enough value to prevent Q2 from saturating when the capacitor is disconnected, thus ensuring proper oscillation of the circuit.
In the event that the circuit fails to oscillate, adjustments may be necessary. If R1 is set too low or R2 is set too high, the circuit may not function as intended. Diode D1 plays a significant role by allowing for a higher duty cycle operation and protecting the base of transistor Q1 from reverse voltage, which is limited to -0.7 V. In applications where lower voltage operation (3-9 V) and reduced duty cycle are acceptable, D1 can be omitted, simplifying the circuit design.
The components required for this circuit are readily available from electronic suppliers, such as Radio Shack, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. Overall, this flashing LED circuit provides a straightforward and effective solution for creating a visual alert system.This circuit will flash a bright red LED (5000 mcd) as an attention getting device or fake car alarm. Component values are not critical and other transistors may be used. Flash duration is determined by R2 and C1 and is approximately 3 time constants (3*R2*C1). Brightness is controlled by R3 wich limits the LED current to about 20 mA for values li sted. R1 provides bias for the transistors which should be low enough not to saturate Q2 with the capacitor disconnected. If the circuit does not oscillate, R1 may be too low or R2 may be too high. D1 allows for higher duty cycle operation and limits the reverse voltage at the base of Q1 to -0. 7 V. D1 may be omitted for low voltage (3-9) and low duty cycle operation. Most parts available at Radio Shack. 🔗 External reference