Power supply ?±18V can I just use a wall wart
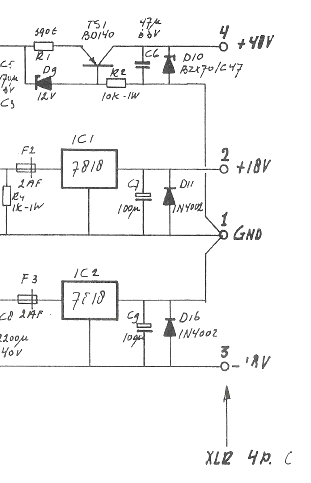
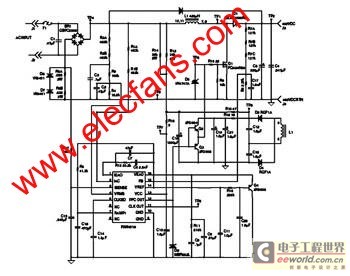
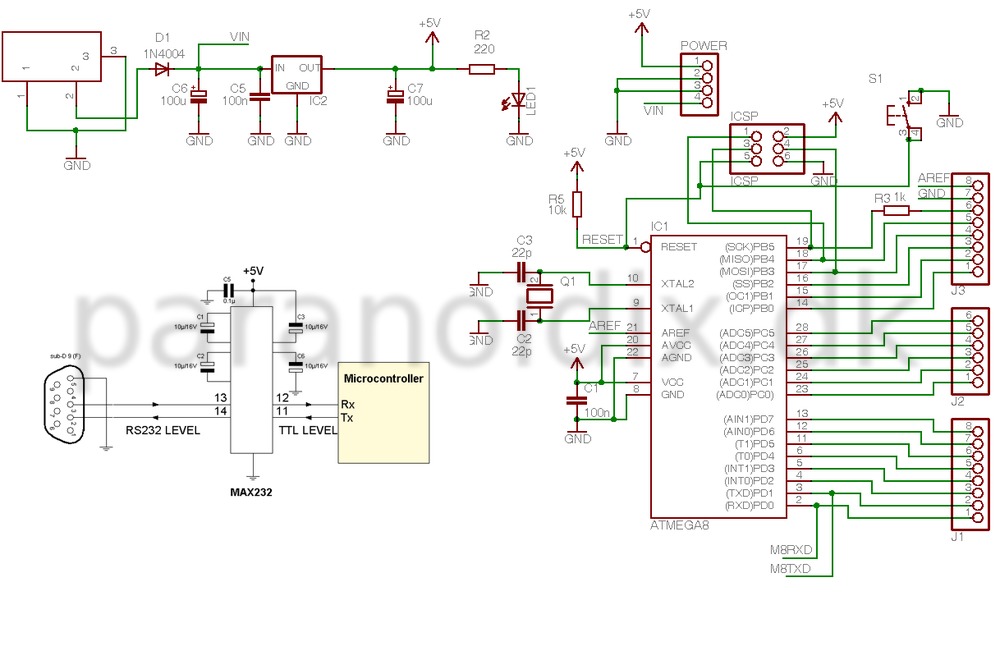
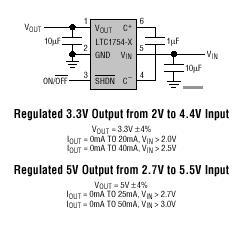
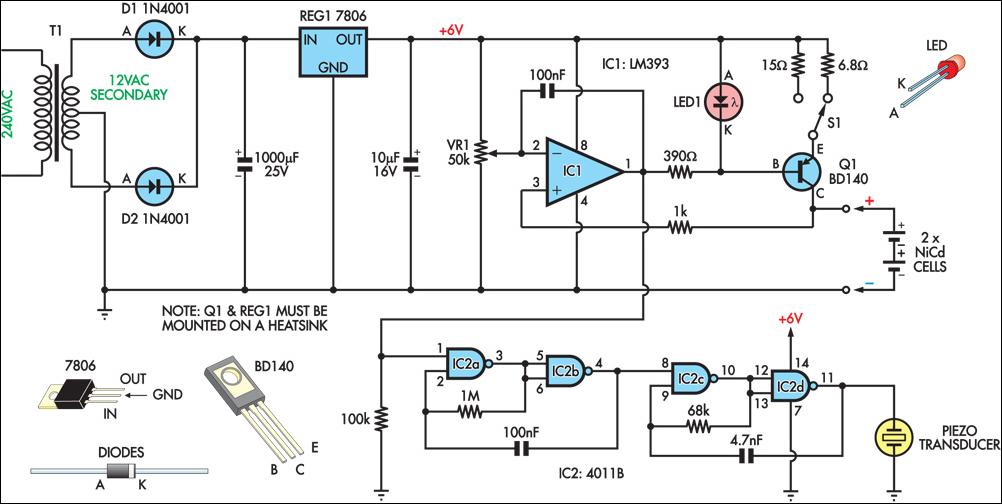
A mixer has been purchased without a power supply unit (PSU). The user does not require the 48V phantom power and is inquiring if an 18V DC wall adapter can be used instead. Additionally, the user seeks information on which pins should be connected.
Using an 18V DC wall adapter instead of a dedicated power supply for a mixer may be feasible, depending on the specific requirements of the mixer model. Most audio mixers that require phantom power typically operate at 48V for microphone inputs, which is essential for powering condenser microphones. If the mixer does not need the phantom power feature, the possibility of using a lower voltage power supply, such as 18V, depends on the internal voltage regulation of the mixer.
It is crucial to verify the voltage specifications and pin configuration of the mixer. The mixer’s datasheet or user manual should provide detailed information regarding the acceptable input voltage range and the pin assignments for power connections. If the mixer is designed to accommodate a range of input voltages, an 18V supply may be acceptable. However, using a voltage that is significantly lower than required may result in improper operation or failure to power on.
In terms of pin connections, the power input pins must be identified accurately. Typically, mixers will have designated pins for positive and negative voltage connections. It is essential to ensure correct polarity when connecting the power supply to avoid damage to the mixer. If the mixer has a dedicated power connector, the pinout will be specified in the documentation. If no documentation is available, it may be necessary to use a multimeter to trace the connections or consult with the manufacturer for guidance.
In conclusion, while it may be possible to operate the mixer with an 18V DC wall adapter, it is imperative to confirm compatibility with the mixer’s specifications and ensure correct pin connections to prevent any potential damage.I`ve just bought a mixer without a PSU. I don`t really need the 48V phantom, so can I just use an 18V DC wall wart type PSU? If yes, which pins should.. 🔗 External reference
Using an 18V DC wall adapter instead of a dedicated power supply for a mixer may be feasible, depending on the specific requirements of the mixer model. Most audio mixers that require phantom power typically operate at 48V for microphone inputs, which is essential for powering condenser microphones. If the mixer does not need the phantom power feature, the possibility of using a lower voltage power supply, such as 18V, depends on the internal voltage regulation of the mixer.
It is crucial to verify the voltage specifications and pin configuration of the mixer. The mixer’s datasheet or user manual should provide detailed information regarding the acceptable input voltage range and the pin assignments for power connections. If the mixer is designed to accommodate a range of input voltages, an 18V supply may be acceptable. However, using a voltage that is significantly lower than required may result in improper operation or failure to power on.
In terms of pin connections, the power input pins must be identified accurately. Typically, mixers will have designated pins for positive and negative voltage connections. It is essential to ensure correct polarity when connecting the power supply to avoid damage to the mixer. If the mixer has a dedicated power connector, the pinout will be specified in the documentation. If no documentation is available, it may be necessary to use a multimeter to trace the connections or consult with the manufacturer for guidance.
In conclusion, while it may be possible to operate the mixer with an 18V DC wall adapter, it is imperative to confirm compatibility with the mixer’s specifications and ensure correct pin connections to prevent any potential damage.I`ve just bought a mixer without a PSU. I don`t really need the 48V phantom, so can I just use an 18V DC wall wart type PSU? If yes, which pins should.. 🔗 External reference