Power Supply for P.A. Class40
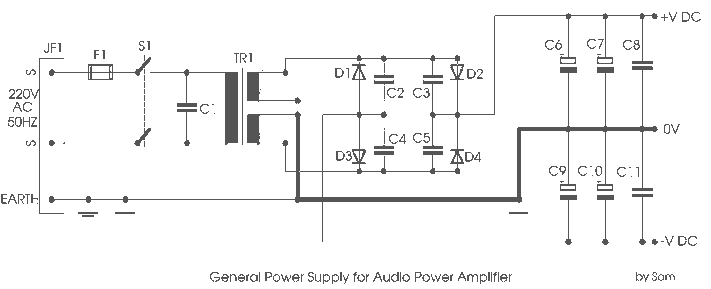
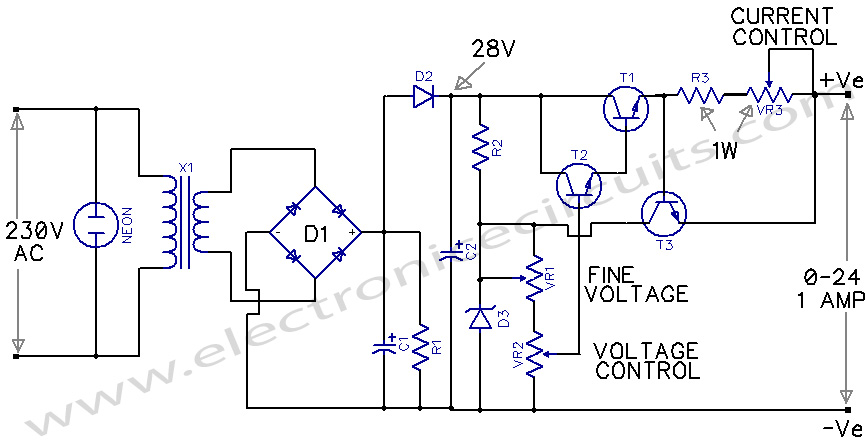
For its maximum result, the final stage of the amplifier should have the proper power supply, as the flowing currents are very high. A Class A amplifier requires attention. These are the rules for the power supply for the Class A audio amplifier. The transformer must be able to provide the required current at any time. The amplifier requires high current at standby; the filtering capacitors have enough capacity so they can supply enough current whenever we need it.
The design of a Class A audio amplifier necessitates a robust power supply capable of delivering substantial current consistently. The power supply circuit typically includes a transformer, rectifier, filtering capacitors, and voltage regulation components.
The transformer is a critical component that must be selected based on the voltage and current requirements of the amplifier. It should have a secondary voltage rating that matches the amplifier's needs while providing sufficient current to handle peak demands. The transformer should also be rated for continuous operation to prevent overheating and ensure reliability.
After the transformer, the rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC. A full-wave bridge rectifier is commonly used in these applications to maximize the efficiency of power conversion. The rectifier's diodes must be rated for the peak inverse voltage (PIV) and the expected current to avoid failure during operation.
Following rectification, filtering capacitors are employed to smooth the output voltage. These capacitors must have a high capacitance value to maintain a stable voltage during periods of high current demand, especially during standby and transient conditions. The capacitors should also have a voltage rating significantly higher than the peak DC voltage to ensure safe operation.
In addition to these components, it is important to consider the inclusion of voltage regulation circuits. These circuits can help maintain a stable output voltage under varying load conditions, which is essential for the consistent performance of the Class A amplifier.
Proper attention to the layout and wiring of the power supply is crucial to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the amplifier's performance. Adequate heat dissipation measures should also be implemented to ensure that all components operate within their specified temperature ranges, enhancing the overall reliability and longevity of the amplifier.For it`s maximum result, the final stage of the amplifier should have the proper power supply, as the flowing, currents are very high. An Class A amplifier, requires attention. These are the rules for the power supply for the Class A audio amplifier. The transformer must be able to provide the required current at any time. The amplifier requires high current at stand by, the filtering capacitors have enough capacity, so they can supply enough capacity, so they can supply enough current whenever we need it.
🔗 External reference
The design of a Class A audio amplifier necessitates a robust power supply capable of delivering substantial current consistently. The power supply circuit typically includes a transformer, rectifier, filtering capacitors, and voltage regulation components.
The transformer is a critical component that must be selected based on the voltage and current requirements of the amplifier. It should have a secondary voltage rating that matches the amplifier's needs while providing sufficient current to handle peak demands. The transformer should also be rated for continuous operation to prevent overheating and ensure reliability.
After the transformer, the rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC. A full-wave bridge rectifier is commonly used in these applications to maximize the efficiency of power conversion. The rectifier's diodes must be rated for the peak inverse voltage (PIV) and the expected current to avoid failure during operation.
Following rectification, filtering capacitors are employed to smooth the output voltage. These capacitors must have a high capacitance value to maintain a stable voltage during periods of high current demand, especially during standby and transient conditions. The capacitors should also have a voltage rating significantly higher than the peak DC voltage to ensure safe operation.
In addition to these components, it is important to consider the inclusion of voltage regulation circuits. These circuits can help maintain a stable output voltage under varying load conditions, which is essential for the consistent performance of the Class A amplifier.
Proper attention to the layout and wiring of the power supply is crucial to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the amplifier's performance. Adequate heat dissipation measures should also be implemented to ensure that all components operate within their specified temperature ranges, enhancing the overall reliability and longevity of the amplifier.For it`s maximum result, the final stage of the amplifier should have the proper power supply, as the flowing, currents are very high. An Class A amplifier, requires attention. These are the rules for the power supply for the Class A audio amplifier. The transformer must be able to provide the required current at any time. The amplifier requires high current at stand by, the filtering capacitors have enough capacity, so they can supply enough capacity, so they can supply enough current whenever we need it.
🔗 External reference