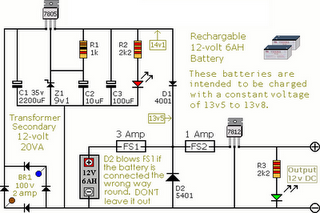
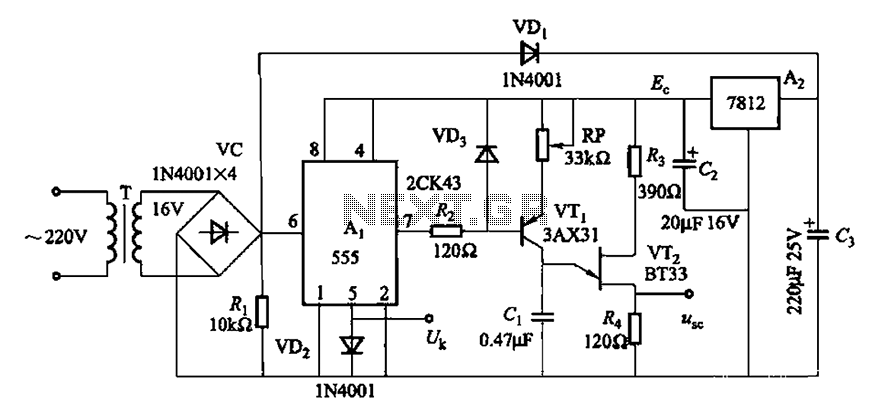
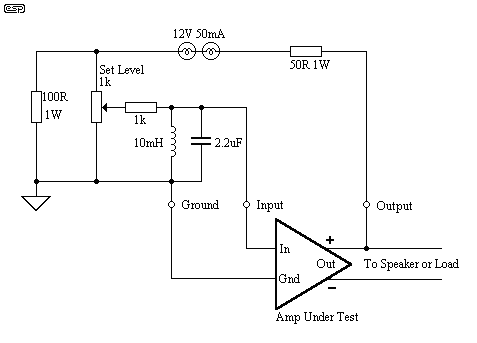
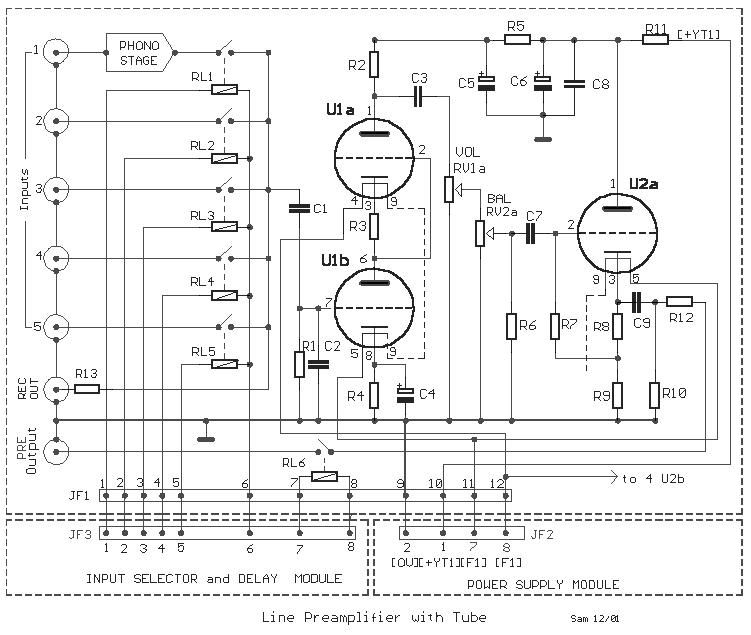
Single supply AC buffer amplifier
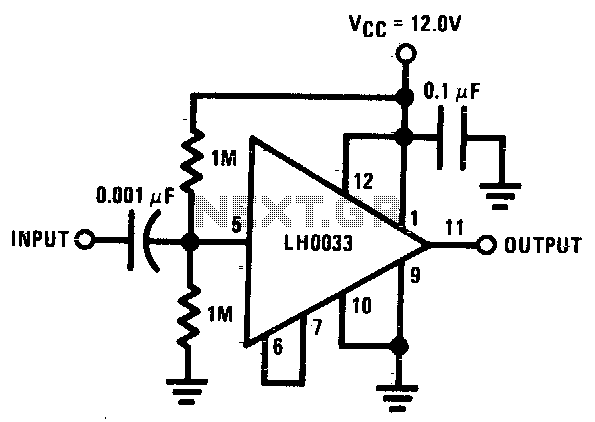
The input is DC biased to the mid-operating point and is AC coupled. Its input impedance is approximately 500K ohms at low frequencies. For DC loads referenced to ground, the quiescent current is increased by the load current set at the input DC bias voltage.
This circuit employs DC biasing to establish a stable operating point, ensuring optimal performance and linearity in signal amplification. The AC coupling indicates that the circuit is designed to block any DC component of the input signal, allowing only the AC variations to pass through. This configuration is particularly useful in audio and RF applications where it is essential to prevent DC offsets from affecting downstream circuitry.
The specified input impedance of approximately 500K ohms at low frequencies suggests that the circuit is designed to minimize loading effects on the previous stage, allowing for maximum signal transfer. High input impedance is crucial in applications where the source impedance is also high, as it prevents signal degradation.
The mention of DC loads referenced to ground indicates that the circuit can accommodate various load configurations while maintaining a stable quiescent current. The quiescent current, which is the current flowing through the circuit when no input signal is present, is adjusted based on the load current dictated by the input DC bias voltage. This characteristic is significant in ensuring that the circuit remains within its linear operating region, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the system.
In summary, this circuit design effectively balances DC and AC components, providing flexibility in load conditions while maintaining high input impedance and stable quiescent current, which are essential for high-fidelity signal processing.The input is dc biased to mid-operating point and is ac coupled. Its input impedance is 11 - OUTPUT approximately 500K at low frequencies For dc loads referenced to ground, the quiescent current is increased by the load current set at the input dc bias voltage. 🔗 External reference
This circuit employs DC biasing to establish a stable operating point, ensuring optimal performance and linearity in signal amplification. The AC coupling indicates that the circuit is designed to block any DC component of the input signal, allowing only the AC variations to pass through. This configuration is particularly useful in audio and RF applications where it is essential to prevent DC offsets from affecting downstream circuitry.
The specified input impedance of approximately 500K ohms at low frequencies suggests that the circuit is designed to minimize loading effects on the previous stage, allowing for maximum signal transfer. High input impedance is crucial in applications where the source impedance is also high, as it prevents signal degradation.
The mention of DC loads referenced to ground indicates that the circuit can accommodate various load configurations while maintaining a stable quiescent current. The quiescent current, which is the current flowing through the circuit when no input signal is present, is adjusted based on the load current dictated by the input DC bias voltage. This characteristic is significant in ensuring that the circuit remains within its linear operating region, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the system.
In summary, this circuit design effectively balances DC and AC components, providing flexibility in load conditions while maintaining high input impedance and stable quiescent current, which are essential for high-fidelity signal processing.The input is dc biased to mid-operating point and is ac coupled. Its input impedance is 11 - OUTPUT approximately 500K at low frequencies For dc loads referenced to ground, the quiescent current is increased by the load current set at the input dc bias voltage. 🔗 External reference