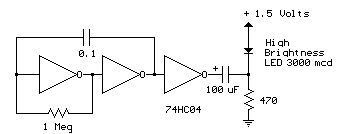
Powerful LED flasher
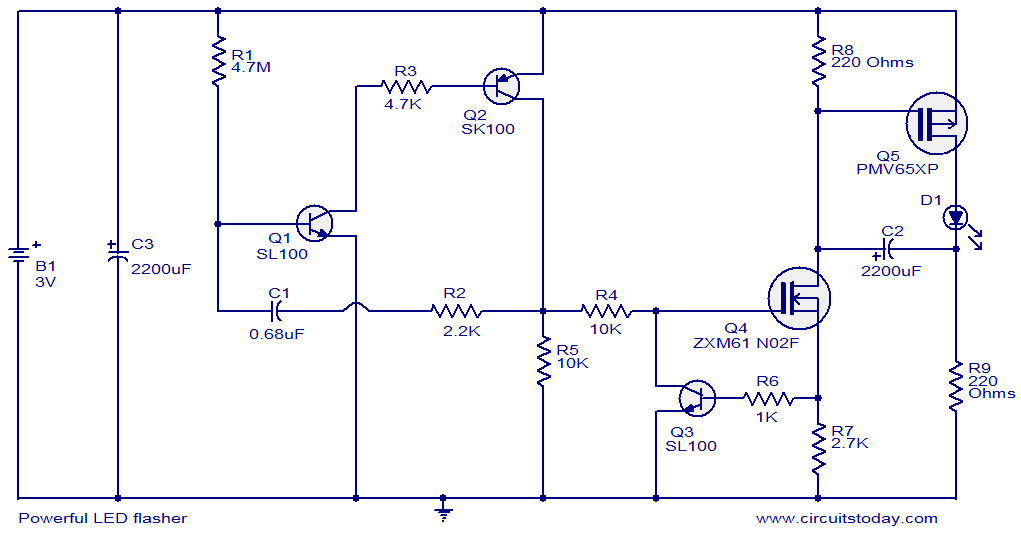
This circuit diagram illustrates a powerful LED flasher utilizing a 1W high power LED, which is widely available in the market. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are configured as an oscillator that generates positive pulses with a duration of 20 ms at a frequency of 0.5 Hz. Transistor Q3 and MOSFET Q4 invert this pulse, while MOSFET Q5 is responsible for driving the LED D1.
The circuit operates by leveraging the characteristics of transistors and MOSFETs to create a flashing effect for the LED. The oscillator formed by Q1 and Q2 generates a square wave signal, which oscillates between high and low states. The timing of this oscillation is controlled by the resistor-capacitor (RC) network connected to the base of Q1, determining the pulse width and frequency.
Transistor Q3 serves as a signal inverter, converting the output from the oscillator into a complementary signal that is suitable for driving the MOSFETs. MOSFET Q4 further processes this signal, ensuring that it can handle the power requirements necessary to drive the high power LED effectively.
MOSFET Q5 acts as a switch that allows current to flow through the LED D1 when it receives the appropriate signal from Q4. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED. The choice of a 1W high power LED allows for bright illumination, making this circuit suitable for various applications where high visibility is required.
The overall design emphasizes efficiency and reliability, making use of solid-state components to achieve the desired flashing effect. The circuit can be powered by a suitable DC voltage source, ensuring that all components operate within their specified limits. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered for the MOSFETs and the LED to maintain performance and longevity.This is the circuit diagram a powerful LED flasher. High power LEDs are very common in the market now and a 1W high power LED is used here. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are wired as an oscillator which produces positive pulses of width 20ms @ ½ Hz. Transistor Q3 and MOSFET Q4 inverts this pulse and MOSFET Q5 drives the LED D1. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by leveraging the characteristics of transistors and MOSFETs to create a flashing effect for the LED. The oscillator formed by Q1 and Q2 generates a square wave signal, which oscillates between high and low states. The timing of this oscillation is controlled by the resistor-capacitor (RC) network connected to the base of Q1, determining the pulse width and frequency.
Transistor Q3 serves as a signal inverter, converting the output from the oscillator into a complementary signal that is suitable for driving the MOSFETs. MOSFET Q4 further processes this signal, ensuring that it can handle the power requirements necessary to drive the high power LED effectively.
MOSFET Q5 acts as a switch that allows current to flow through the LED D1 when it receives the appropriate signal from Q4. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED. The choice of a 1W high power LED allows for bright illumination, making this circuit suitable for various applications where high visibility is required.
The overall design emphasizes efficiency and reliability, making use of solid-state components to achieve the desired flashing effect. The circuit can be powered by a suitable DC voltage source, ensuring that all components operate within their specified limits. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered for the MOSFETs and the LED to maintain performance and longevity.This is the circuit diagram a powerful LED flasher. High power LEDs are very common in the market now and a 1W high power LED is used here. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are wired as an oscillator which produces positive pulses of width 20ms @ ½ Hz. Transistor Q3 and MOSFET Q4 inverts this pulse and MOSFET Q5 drives the LED D1. 🔗 External reference