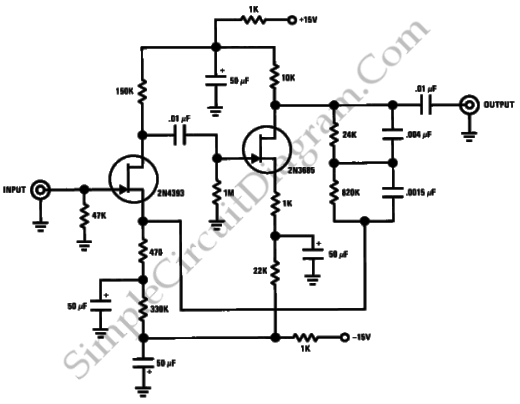
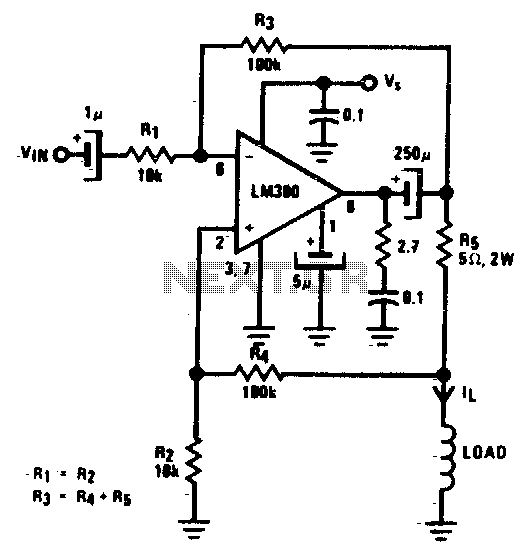
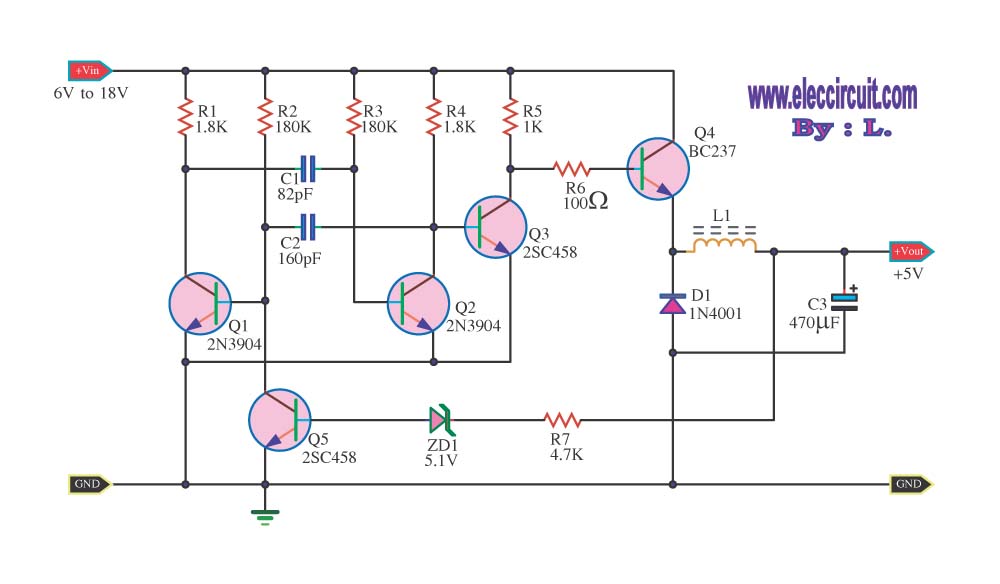
Preamplifier and high-to-low impedance converter
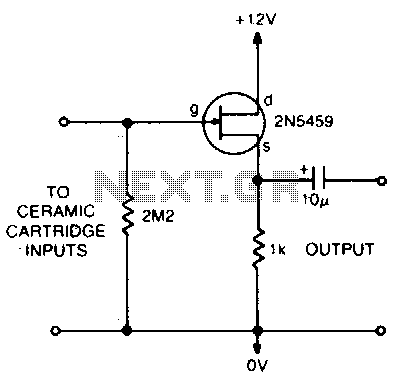
This circuit matches the very high impedance of ceramic cartridges, providing unity gain and low impedance output. By "loading" the cartridge with a 2.2MΩ input resistance, the cartridge characteristics are adjusted to closely compensate for the RIAA recording curve. The output from this preamp may be fed to a level potentiometer for mixing.
The circuit described serves as a preamplifier specifically designed for ceramic cartridges, which typically exhibit a very high output impedance. The use of a 2.2MΩ input resistance effectively "loads" the cartridge, allowing it to operate within its optimal performance range. This loading is crucial as it minimizes the effects of impedance mismatch, ensuring that the signal is accurately represented and that the frequency response aligns closely with the RIAA (Recording Industry Association of America) standard for vinyl playback.
The preamp operates at unity gain, meaning that it does not amplify the signal level but rather conditions it for further processing. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in high-fidelity audio systems. The low impedance output of the preamp facilitates easy interfacing with subsequent audio equipment, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation due to cable capacitance or other loading effects.
The output stage of the preamp is designed to feed into a level potentiometer, which allows for mixing and level adjustments before the signal is sent to additional processing stages or amplification. This flexibility is essential in audio applications where precise control over signal levels is required, enabling users to tailor the output to suit their specific needs.
In summary, the circuit effectively bridges the gap between high-impedance ceramic cartridges and standard audio equipment, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility while maintaining fidelity to the original recording.Thiscircuit matches the very high impedance of ceramic cartridges, unity gain, and low impedance output. By "loading" the cartridge with a 2M2 input resistance, the cartridge characteristics are such as to quite closely compensate for the RIAA recording curve.
The output from this preamp may be fed to a level pot for mixing.
The circuit described serves as a preamplifier specifically designed for ceramic cartridges, which typically exhibit a very high output impedance. The use of a 2.2MΩ input resistance effectively "loads" the cartridge, allowing it to operate within its optimal performance range. This loading is crucial as it minimizes the effects of impedance mismatch, ensuring that the signal is accurately represented and that the frequency response aligns closely with the RIAA (Recording Industry Association of America) standard for vinyl playback.
The preamp operates at unity gain, meaning that it does not amplify the signal level but rather conditions it for further processing. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in high-fidelity audio systems. The low impedance output of the preamp facilitates easy interfacing with subsequent audio equipment, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation due to cable capacitance or other loading effects.
The output stage of the preamp is designed to feed into a level potentiometer, which allows for mixing and level adjustments before the signal is sent to additional processing stages or amplification. This flexibility is essential in audio applications where precise control over signal levels is required, enabling users to tailor the output to suit their specific needs.
In summary, the circuit effectively bridges the gap between high-impedance ceramic cartridges and standard audio equipment, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility while maintaining fidelity to the original recording.Thiscircuit matches the very high impedance of ceramic cartridges, unity gain, and low impedance output. By "loading" the cartridge with a 2M2 input resistance, the cartridge characteristics are such as to quite closely compensate for the RIAA recording curve.
The output from this preamp may be fed to a level pot for mixing.