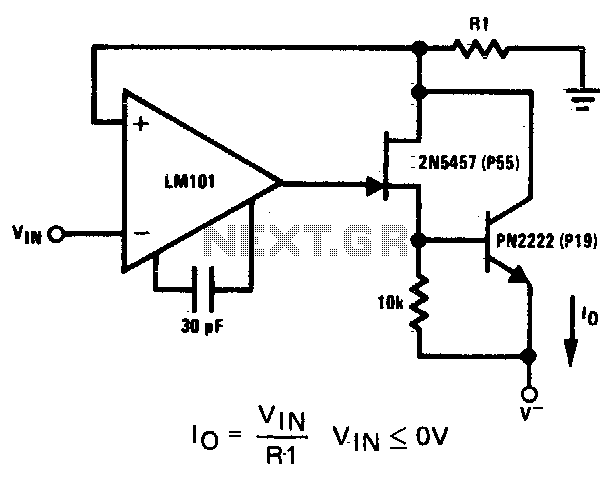
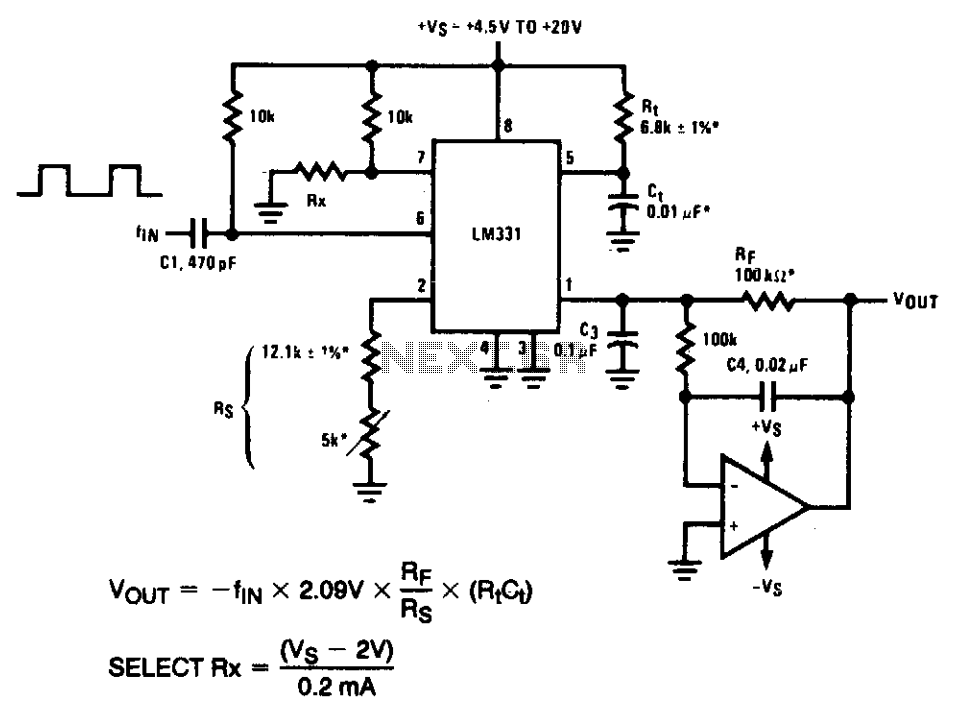
Precision Squarer
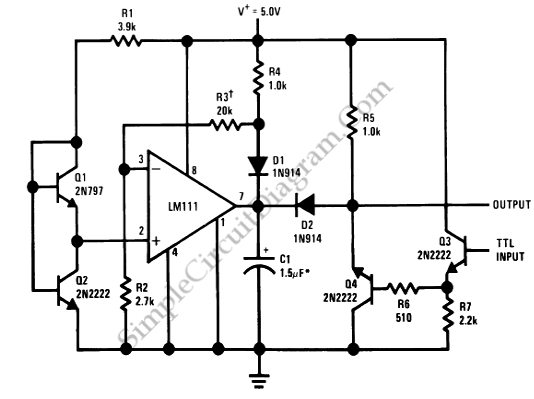
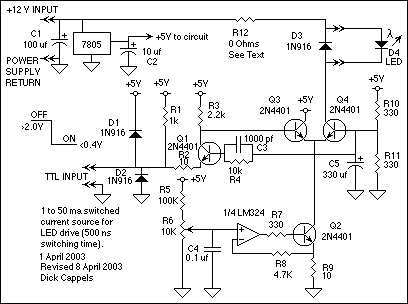
A squarer circuit is utilized to shape a signal, producing a more defined square wave. This circuit is beneficial for converting a signal to achieve a very fast rise time.
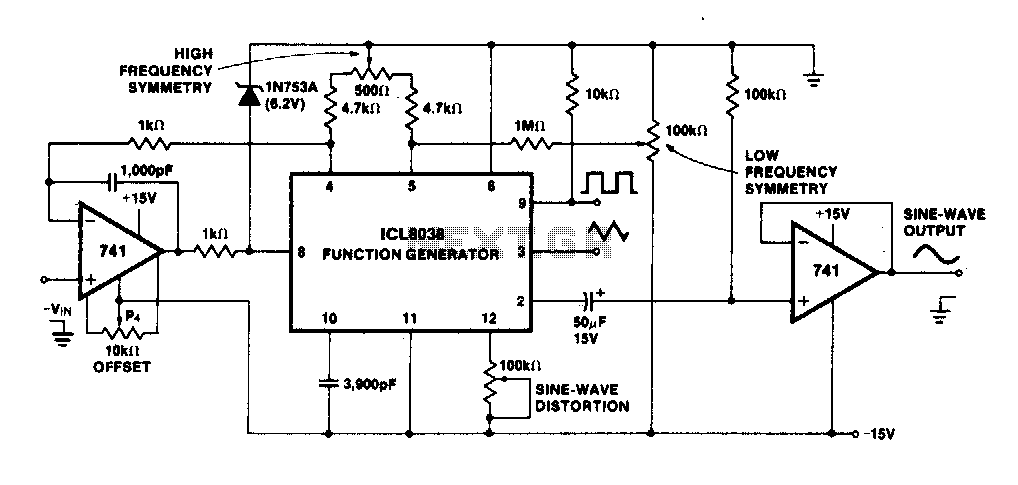
The squarer circuit is designed to convert an input signal into a square wave with a sharp transition between high and low states. It typically consists of components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors, which work together to enhance the signal's characteristics.
The operational amplifier is often configured in a comparator mode, where it compares the input signal to a reference voltage. When the input signal exceeds the reference voltage, the output switches to the high state; conversely, when the input signal falls below the reference voltage, the output switches to the low state. This rapid transition results in a square wave output.
To ensure the squarer circuit provides a fast rise time, careful selection of components is essential. The feedback network, composed of resistors and capacitors, must be tailored to minimize propagation delay and optimize the circuit's frequency response. Additionally, the use of Schmitt trigger configurations can further enhance the circuit's performance by providing hysteresis, which prevents noise from causing unwanted oscillations in the output.
Applications of squarer circuits are prevalent in digital electronics, where clean square waves are essential for clock signals, pulse generation, and signal conditioning. The ability to produce a precise square wave from a noisy or distorted input signal makes this circuit invaluable in various electronic systems.Squarer circuit is used to shape signal, to get more defined square wave. This circuit is useful to make convert the signal so it has very fast rise time. Here.. 🔗 External reference
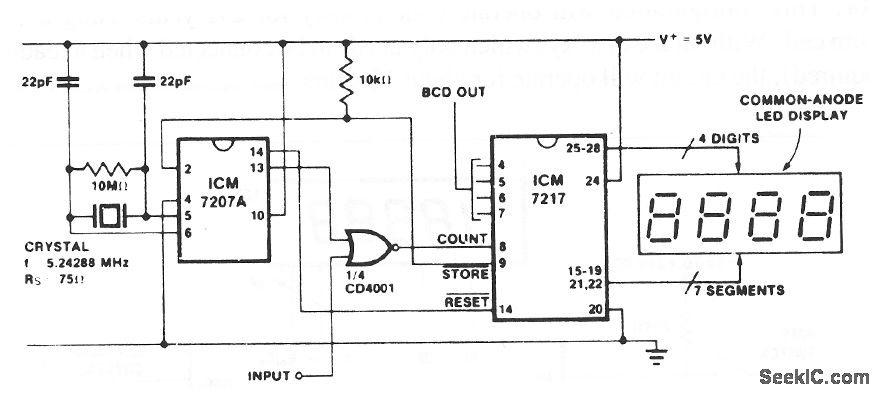
The squarer circuit is designed to convert an input signal into a square wave with a sharp transition between high and low states. It typically consists of components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors, which work together to enhance the signal's characteristics.
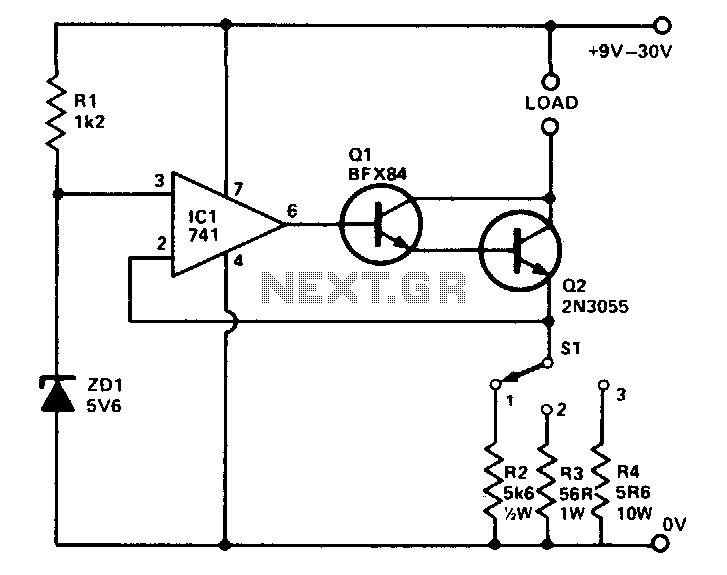
The operational amplifier is often configured in a comparator mode, where it compares the input signal to a reference voltage. When the input signal exceeds the reference voltage, the output switches to the high state; conversely, when the input signal falls below the reference voltage, the output switches to the low state. This rapid transition results in a square wave output.
To ensure the squarer circuit provides a fast rise time, careful selection of components is essential. The feedback network, composed of resistors and capacitors, must be tailored to minimize propagation delay and optimize the circuit's frequency response. Additionally, the use of Schmitt trigger configurations can further enhance the circuit's performance by providing hysteresis, which prevents noise from causing unwanted oscillations in the output.
Applications of squarer circuits are prevalent in digital electronics, where clean square waves are essential for clock signals, pulse generation, and signal conditioning. The ability to produce a precise square wave from a noisy or distorted input signal makes this circuit invaluable in various electronic systems.Squarer circuit is used to shape signal, to get more defined square wave. This circuit is useful to make convert the signal so it has very fast rise time. Here.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713