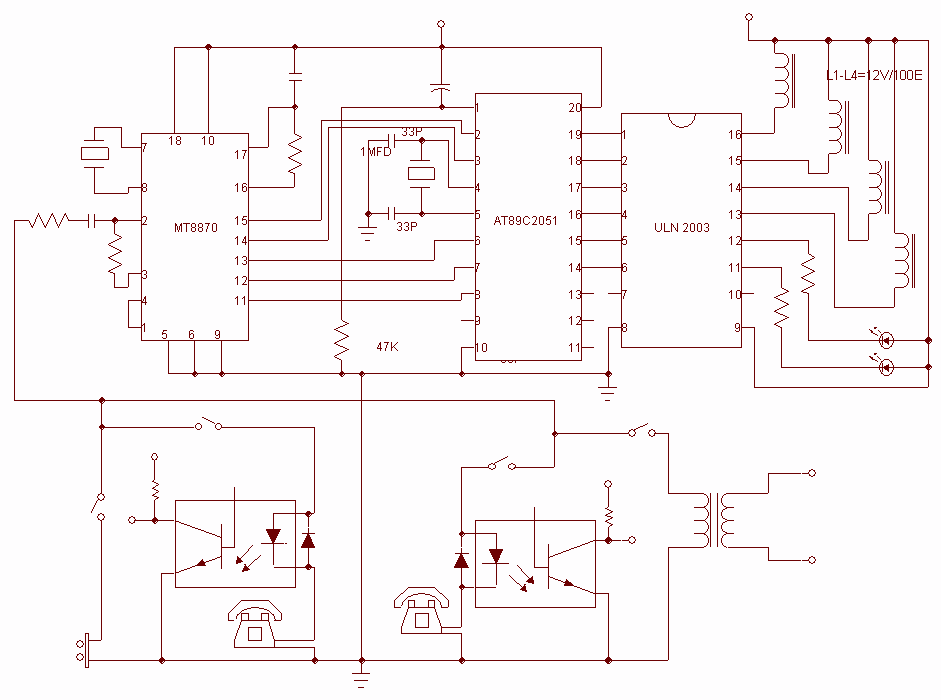
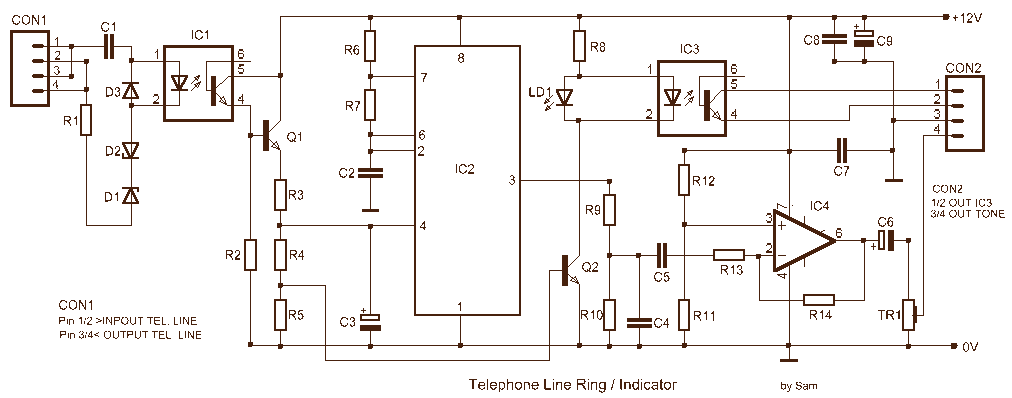
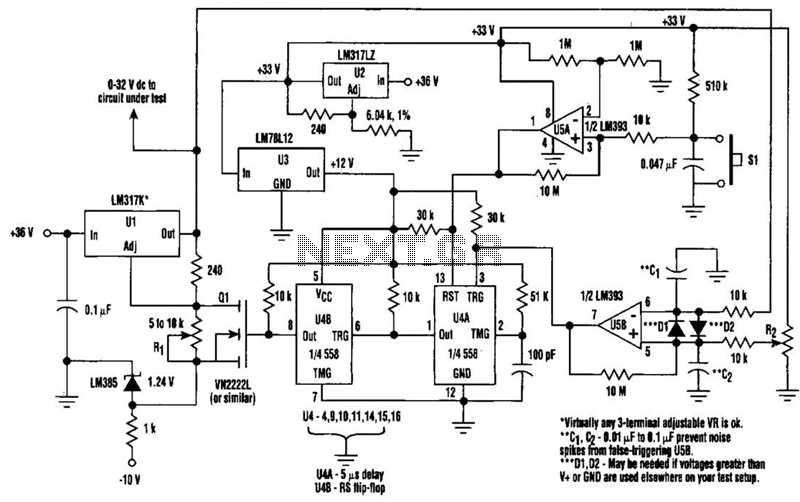
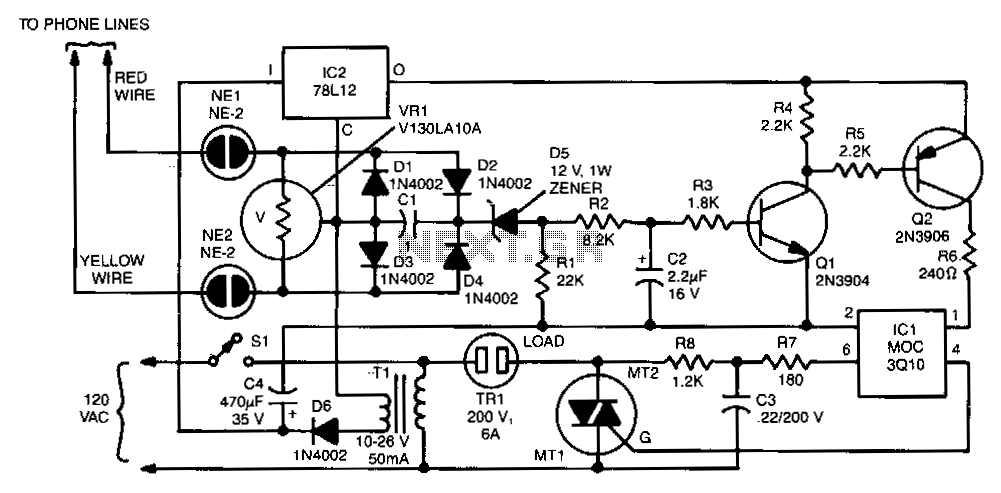
protection for telephone line
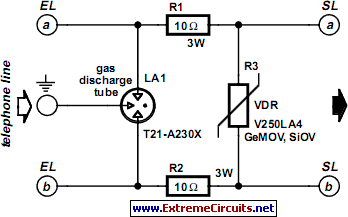
In the past, when telephones were relatively simple devices, there were minimal electrical issues to address. Telecom operators implemented surge protection for all telephone lines that were at risk from storms. Ironically, as technology has advanced and more delicate and costly equipment, such as modern telephones with complex electronics, fax machines, and DSL modems, has been introduced, this surge protection has been largely removed.
Surge protection in telecommunications is crucial for safeguarding sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes that can occur during electrical storms or due to other transient disturbances. The absence of this protection in contemporary installations poses significant risks, particularly for devices that are integral to communication and data transfer.
A comprehensive surge protection scheme involves the integration of surge protective devices (SPDs) at various points within the telephone network. These devices are designed to divert excess voltage away from sensitive equipment, ensuring that the equipment remains operational even during adverse conditions. The design typically includes both primary and secondary protection levels, with primary protection located at the entry point of the telephone line into a building and secondary protection placed closer to the devices themselves.
The primary surge protection device often consists of a combination of metal oxide varistors (MOVs) and gas discharge tubes (GDTs), which effectively clamp down high voltage surges. Secondary protection may utilize additional MOVs or transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes that provide rapid response times to voltage spikes.
For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure proper grounding of surge protection devices. A low-impedance ground connection minimizes the risk of surge energy being transmitted to the equipment. Furthermore, regular maintenance and testing of surge protection systems are recommended to ensure their reliability and effectiveness over time.
In conclusion, the reintroduction of surge protection in telecommunications is essential to protect modern electronic devices from transient voltage events. Implementing a multi-layered surge protection strategy can significantly enhance the resilience of telecommunication infrastructure against electrical surges, thereby safeguarding valuable equipment and ensuring uninterrupted service.A long time ago when telephones were so simple almost nothing could go amiss from an electrical point of view, Telecom operators installed surge protection on all telephone lines exposed to storm risks. Paradoxically, now that we are hooking up delicate and expensive equipment such as telephones filled with electronics, fax machines, (A)DSL modems, etc., this protection has disappeared..
🔗 External reference
Surge protection in telecommunications is crucial for safeguarding sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes that can occur during electrical storms or due to other transient disturbances. The absence of this protection in contemporary installations poses significant risks, particularly for devices that are integral to communication and data transfer.
A comprehensive surge protection scheme involves the integration of surge protective devices (SPDs) at various points within the telephone network. These devices are designed to divert excess voltage away from sensitive equipment, ensuring that the equipment remains operational even during adverse conditions. The design typically includes both primary and secondary protection levels, with primary protection located at the entry point of the telephone line into a building and secondary protection placed closer to the devices themselves.
The primary surge protection device often consists of a combination of metal oxide varistors (MOVs) and gas discharge tubes (GDTs), which effectively clamp down high voltage surges. Secondary protection may utilize additional MOVs or transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes that provide rapid response times to voltage spikes.
For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure proper grounding of surge protection devices. A low-impedance ground connection minimizes the risk of surge energy being transmitted to the equipment. Furthermore, regular maintenance and testing of surge protection systems are recommended to ensure their reliability and effectiveness over time.
In conclusion, the reintroduction of surge protection in telecommunications is essential to protect modern electronic devices from transient voltage events. Implementing a multi-layered surge protection strategy can significantly enhance the resilience of telecommunication infrastructure against electrical surges, thereby safeguarding valuable equipment and ensuring uninterrupted service.A long time ago when telephones were so simple almost nothing could go amiss from an electrical point of view, Telecom operators installed surge protection on all telephone lines exposed to storm risks. Paradoxically, now that we are hooking up delicate and expensive equipment such as telephones filled with electronics, fax machines, (A)DSL modems, etc., this protection has disappeared..
🔗 External reference