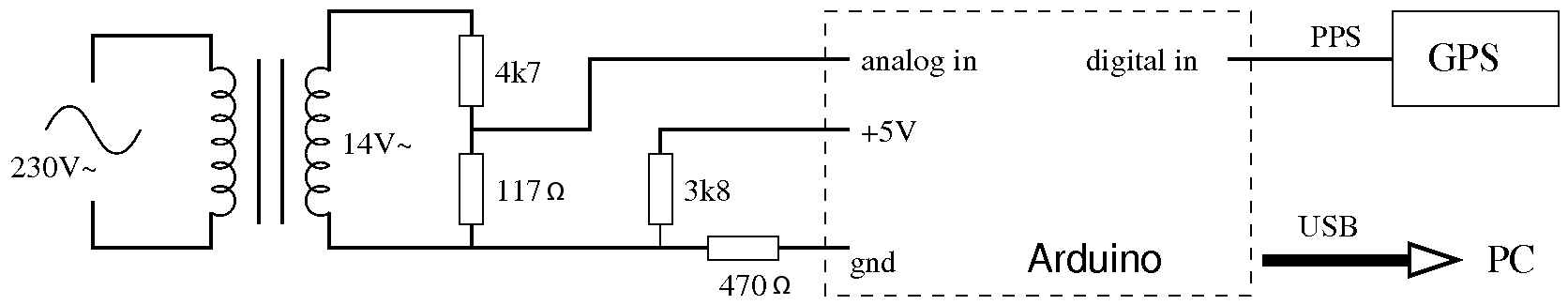
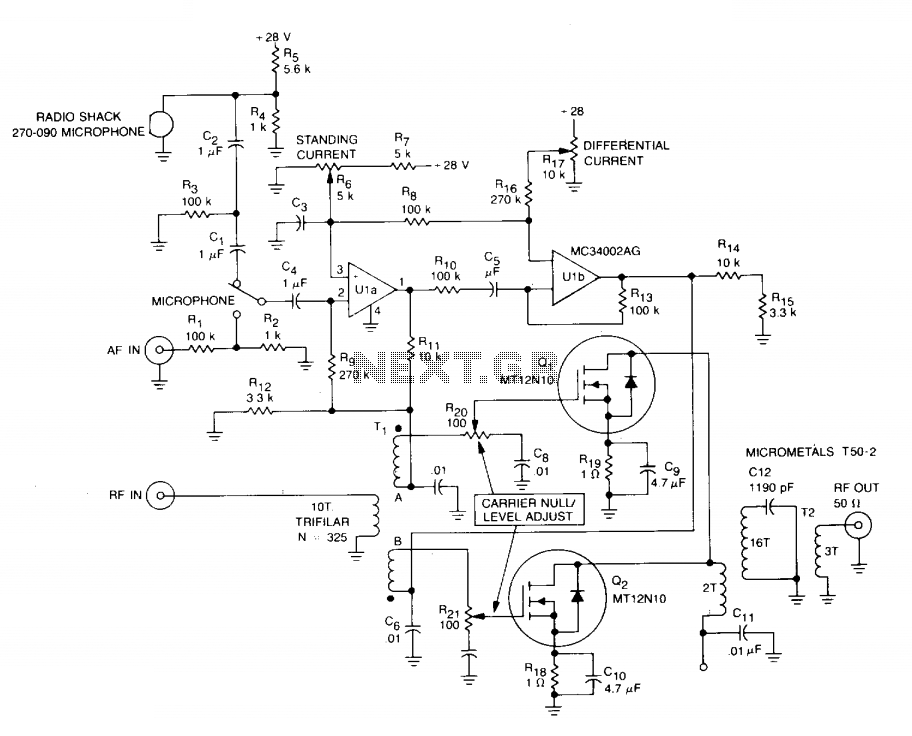
Pulse Frequency Modulator
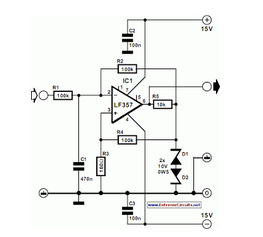
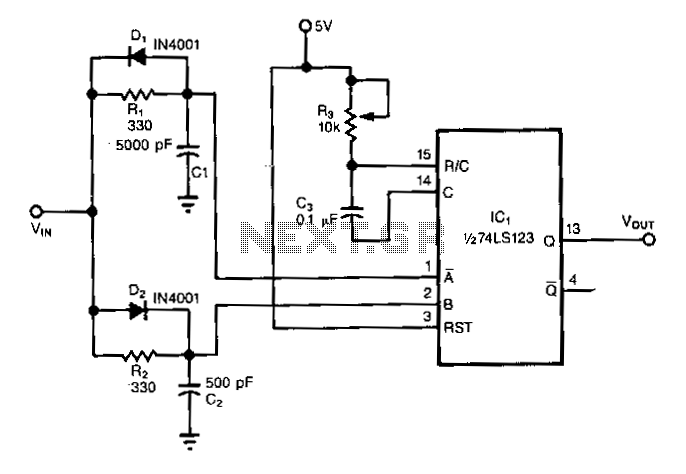
The pulse width of the compact pulse cum frequency modulator can be varied by altering the change-over point of comparator IC1 with a control voltage.
The compact pulse cum frequency modulator utilizes a comparator IC, designated as IC1, to modulate the pulse width effectively. The modulation process involves adjusting the change-over point of the comparator, which is influenced by an external control voltage. This control voltage determines the threshold at which the comparator switches states, thereby altering the duration of the output pulse.
In practical applications, the control voltage can be generated using a potentiometer or a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), allowing for precise adjustments to the pulse width. The output of the comparator can be connected to various components, such as transistors or operational amplifiers, to drive loads or further process the signal.
The design may also include filtering stages to smooth out the output waveform or to limit the frequency response, ensuring that the modulated signal meets the required specifications for its intended application. The compact nature of the modulator allows it to be integrated into various electronic systems, providing flexibility in signal processing tasks.
Overall, this circuit can be utilized in applications such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) for motor control, signal generation for communication systems, or as part of a more complex modulation scheme in RF applications.The pulse width of the compact pulse cum frequency modulator can be varied by altering the change-over point of comparator IC1 with a control voltage via.. 🔗 External reference
The compact pulse cum frequency modulator utilizes a comparator IC, designated as IC1, to modulate the pulse width effectively. The modulation process involves adjusting the change-over point of the comparator, which is influenced by an external control voltage. This control voltage determines the threshold at which the comparator switches states, thereby altering the duration of the output pulse.
In practical applications, the control voltage can be generated using a potentiometer or a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), allowing for precise adjustments to the pulse width. The output of the comparator can be connected to various components, such as transistors or operational amplifiers, to drive loads or further process the signal.
The design may also include filtering stages to smooth out the output waveform or to limit the frequency response, ensuring that the modulated signal meets the required specifications for its intended application. The compact nature of the modulator allows it to be integrated into various electronic systems, providing flexibility in signal processing tasks.
Overall, this circuit can be utilized in applications such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) for motor control, signal generation for communication systems, or as part of a more complex modulation scheme in RF applications.The pulse width of the compact pulse cum frequency modulator can be varied by altering the change-over point of comparator IC1 with a control voltage via.. 🔗 External reference