Power phase sequence display circuit
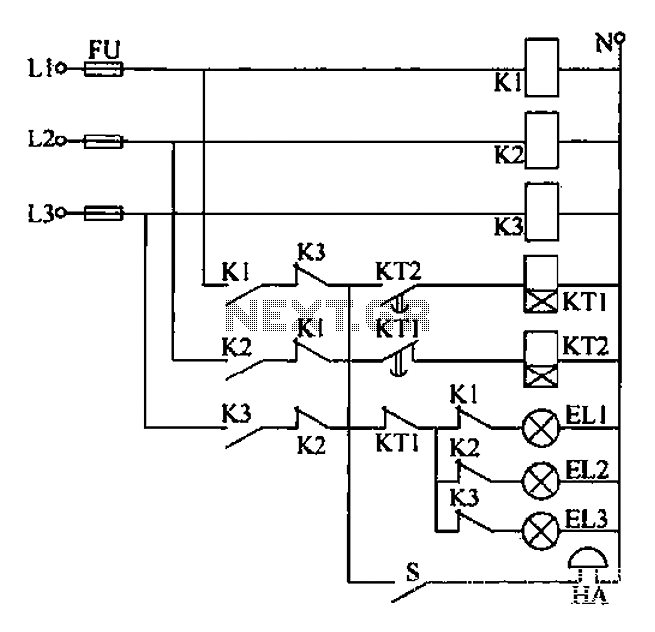
Any power supply and distribution sector should include phase sequence detection to ensure that the power supply phase sequence remains stable and unchanged. Additionally, any irreversible electromechanical product should also incorporate phase sequence detection to verify the phase sequence of the host power supply before operation begins. A three-phase power supply phase sequence indication circuit operates as follows: when the phase sequence is correct, the voltage is rectified by UR1 and charges C2 through R3 and Ri. When the voltage across C2 reaches the ignition voltage of neon bulb EL1, it lights up green. The discharge of C2 through EL1 causes the voltage to drop below a certain threshold, turning off EL1. C2 then recharges, causing EL1 to light up again, resulting in a continuous flashing green neon indication. Conversely, if the phase sequence is incorrect, the red neon bulb EL2 will flash instead. By adjusting RL, C2, and Shu, the time constant can be modified to control the flashing frequency of the neon indicators.
The described circuit for phase sequence detection in a three-phase power supply system is crucial for ensuring operational safety and reliability. The circuit employs a voltage rectifier (UR1) to convert the AC voltage from the power supply into DC voltage. This DC voltage is then used to charge capacitor C2 through resistors R3 and Ri. The neon bulb EL1, which indicates the correct phase sequence, is activated when the voltage across C2 reaches a specific threshold known as the ignition voltage.
The operation is cyclical; once EL1 lights up, it discharges C2, causing the voltage to drop. When the voltage falls below the threshold, EL1 turns off, allowing C2 to recharge again. This cycle continues, creating a visual indication of the correct phase sequence through a steady green light. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by changing the values of resistors RL and capacitors C2 and Shu, which affect the time constant of the charging and discharging process.
In contrast, if the phase sequence is reversed, the circuit is designed to activate a different neon bulb, EL2, which emits a red light to indicate an incorrect phase sequence. This dual-indicator system provides a clear visual cue for operators, enhancing safety and preventing potential damage to equipment that could arise from incorrect phase connections. The circuit is essential for any three-phase power supply system, particularly in industrial settings where the integrity of power supply phases is critical for the operation of electromechanical devices.Any power supply and distribution sector should phase sequence detection Huan Jj means to ensure stable power supply phase sequence unchanged. Any irreversible electromechanica l product itself should also have the phase sequence detection means in order to put into operation before the host power supply phase sequence is determined to meet the requirements. Three-phase power supply phase sequence indication circuit as shown when a forward phase sequence, voltage rectified by UR1 on R3, and through Ri charging C2, C2 when the voltage reaches neon EL1 Kai when the ignition voltage, EL1 lit., green.
Cz by EL1 discharge; C2 is lower than the voltage to be a certain value. EL1 off, Cz again charged, while EL1 again lit, C2 refreshing. Again and again, bright green neon EL1 constantly busy, Similarly, when the inverse when the phase sequence, only the red flashing neon EL2. Adjustment RL, C2 and Shu, G time constant, you can adjust the frequency of flashing neon.
The described circuit for phase sequence detection in a three-phase power supply system is crucial for ensuring operational safety and reliability. The circuit employs a voltage rectifier (UR1) to convert the AC voltage from the power supply into DC voltage. This DC voltage is then used to charge capacitor C2 through resistors R3 and Ri. The neon bulb EL1, which indicates the correct phase sequence, is activated when the voltage across C2 reaches a specific threshold known as the ignition voltage.
The operation is cyclical; once EL1 lights up, it discharges C2, causing the voltage to drop. When the voltage falls below the threshold, EL1 turns off, allowing C2 to recharge again. This cycle continues, creating a visual indication of the correct phase sequence through a steady green light. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by changing the values of resistors RL and capacitors C2 and Shu, which affect the time constant of the charging and discharging process.
In contrast, if the phase sequence is reversed, the circuit is designed to activate a different neon bulb, EL2, which emits a red light to indicate an incorrect phase sequence. This dual-indicator system provides a clear visual cue for operators, enhancing safety and preventing potential damage to equipment that could arise from incorrect phase connections. The circuit is essential for any three-phase power supply system, particularly in industrial settings where the integrity of power supply phases is critical for the operation of electromechanical devices.Any power supply and distribution sector should phase sequence detection Huan Jj means to ensure stable power supply phase sequence unchanged. Any irreversible electromechanica l product itself should also have the phase sequence detection means in order to put into operation before the host power supply phase sequence is determined to meet the requirements. Three-phase power supply phase sequence indication circuit as shown when a forward phase sequence, voltage rectified by UR1 on R3, and through Ri charging C2, C2 when the voltage reaches neon EL1 Kai when the ignition voltage, EL1 lit., green.
Cz by EL1 discharge; C2 is lower than the voltage to be a certain value. EL1 off, Cz again charged, while EL1 again lit, C2 refreshing. Again and again, bright green neon EL1 constantly busy, Similarly, when the inverse when the phase sequence, only the red flashing neon EL2. Adjustment RL, C2 and Shu, G time constant, you can adjust the frequency of flashing neon.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713