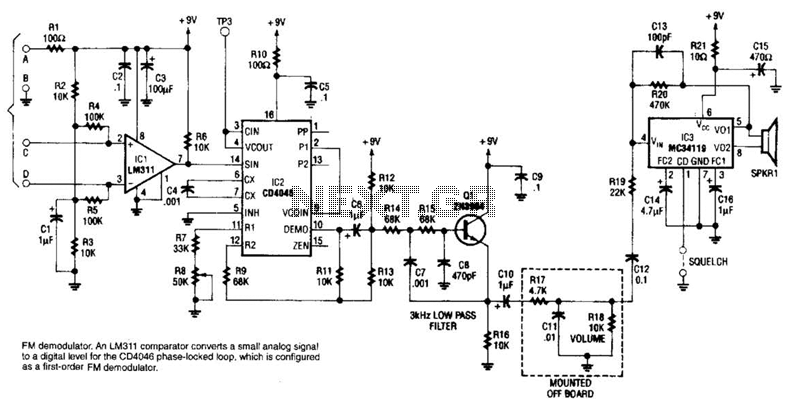
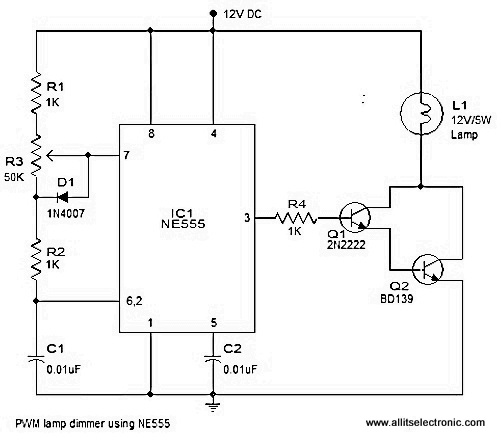
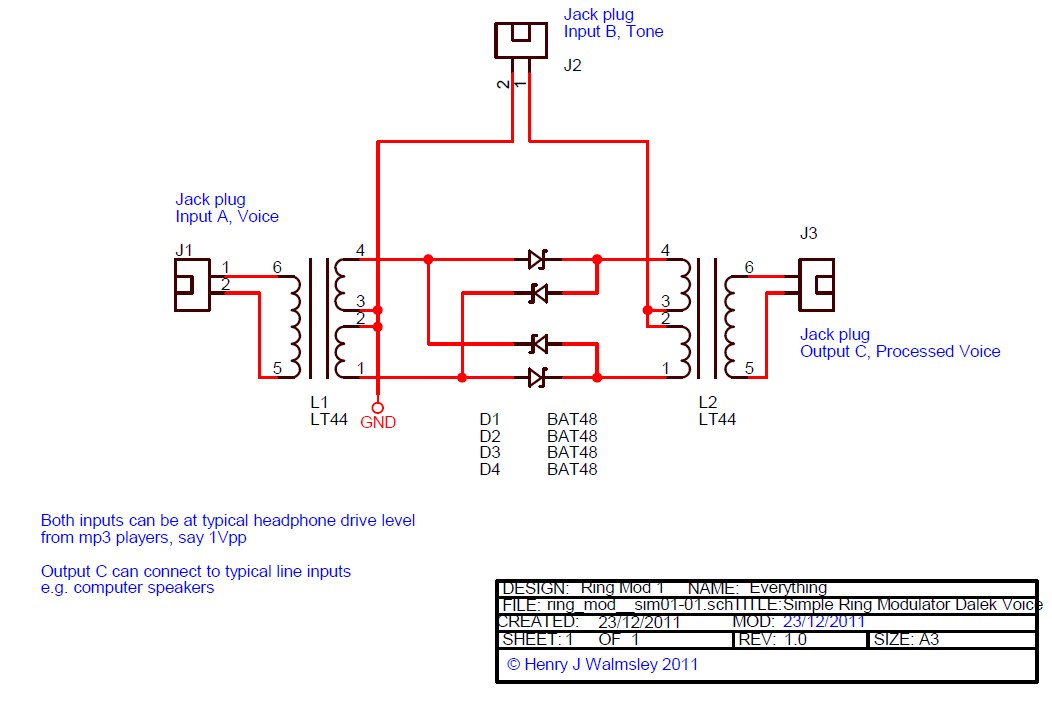
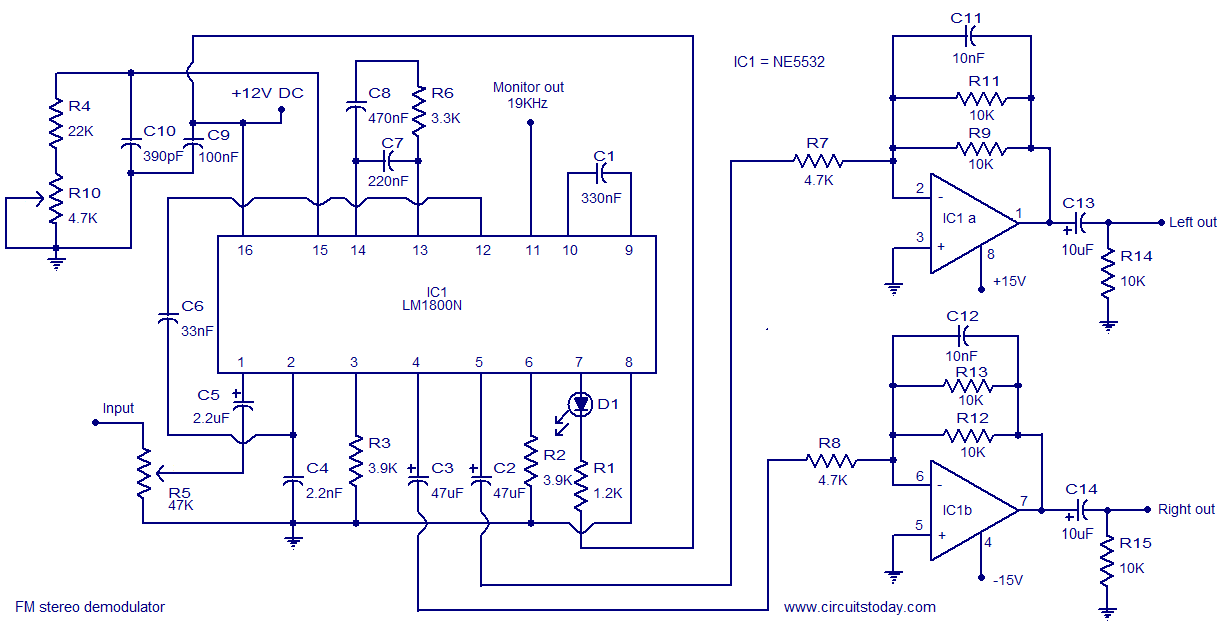
PWM Modulator

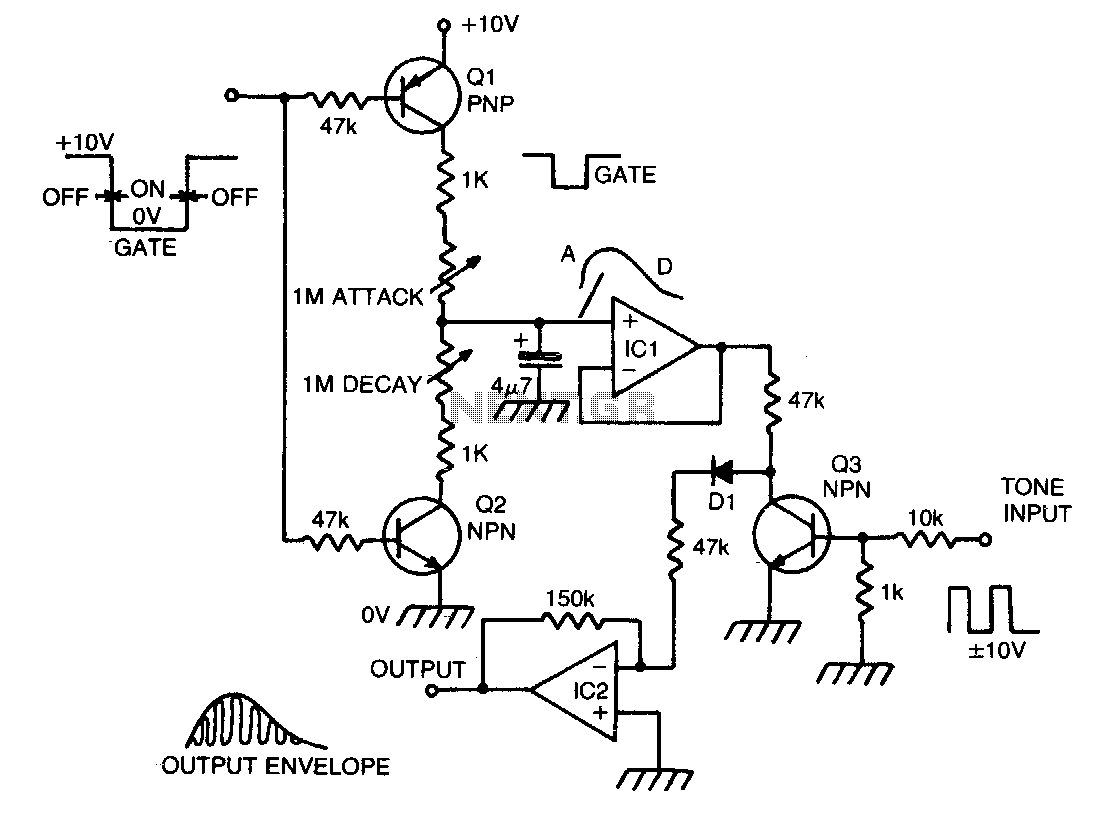
If you have considered experimenting with pulse-width modulation, this circuit serves as an excellent starting point. Simplicity has been prioritized in the design, utilizing a dual...
This circuit is designed to facilitate experimentation with pulse-width modulation (PWM), a technique widely used for controlling power delivered to electrical devices. The simplicity of the circuit allows users, especially beginners, to understand the fundamental principles of PWM without the complexity of advanced circuitry.
The core of the circuit typically involves a microcontroller or a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. This configuration generates a square wave output, which can be adjusted to vary the duty cycle. The duty cycle determines the proportion of time the signal is high compared to the total period of the waveform, effectively controlling the average power supplied to the load.
In this circuit, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network is employed to set the frequency of the PWM signal. The values of the resistor and capacitor can be modified to achieve the desired frequency range. An output transistor may be included to drive larger loads, allowing the circuit to control devices such as motors or LEDs without overloading the microcontroller or timer IC.
Additionally, a feedback mechanism can be integrated to refine the PWM signal based on the load's response. This could involve using a potentiometer to adjust the duty cycle manually or employing a sensor to provide real-time feedback for automatic adjustments.
Overall, this PWM circuit serves as an effective educational tool, demonstrating the principles of signal modulation and power control while maintaining a straightforward design that is accessible to individuals with varying levels of experience in electronics.If you ever thought of experimenting with pulse-width modulation, this circuit should get you started nicely. We ve kept simplicity in mind and used a dua.. 🔗 External reference
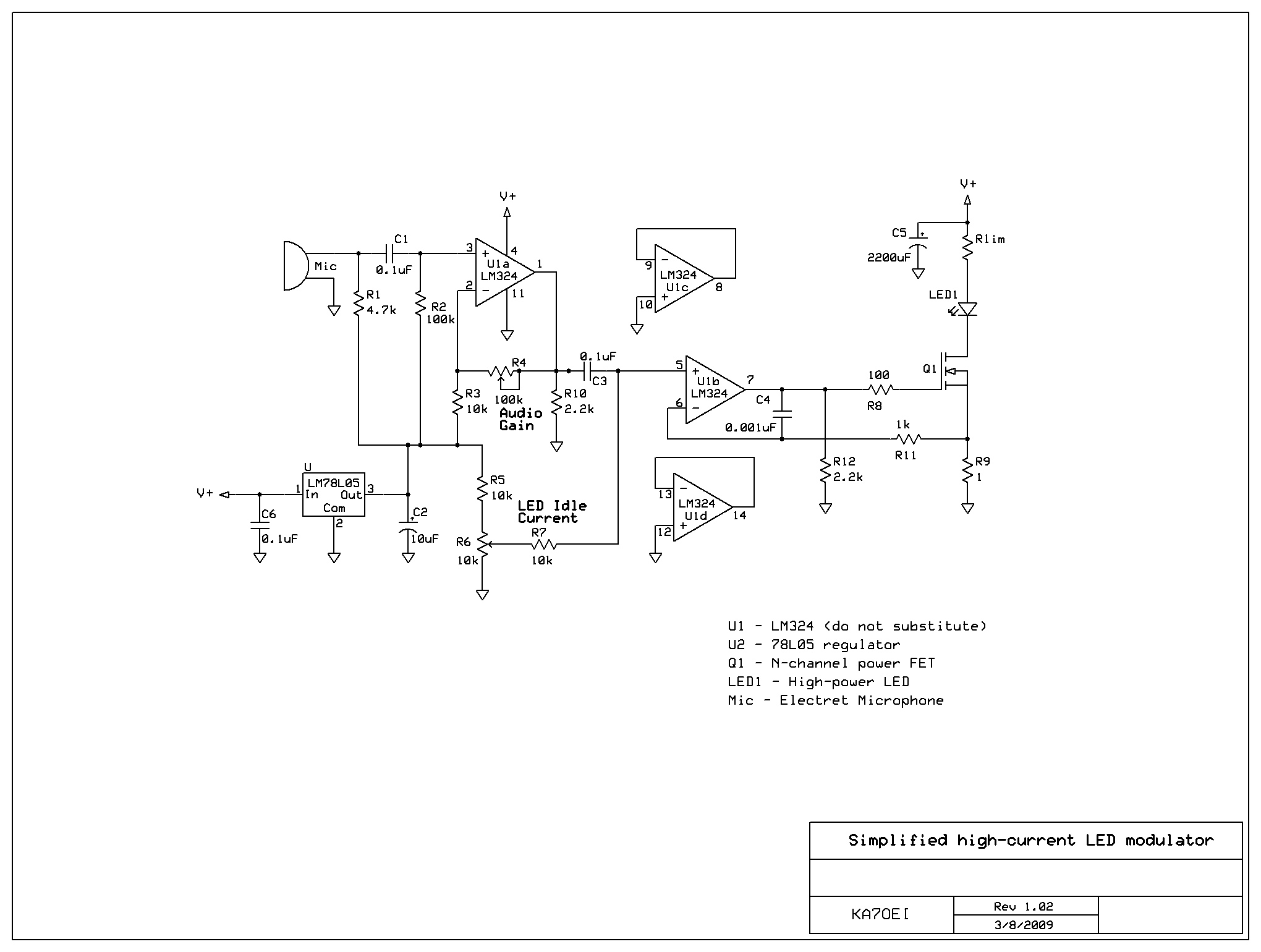
This circuit is designed to facilitate experimentation with pulse-width modulation (PWM), a technique widely used for controlling power delivered to electrical devices. The simplicity of the circuit allows users, especially beginners, to understand the fundamental principles of PWM without the complexity of advanced circuitry.
The core of the circuit typically involves a microcontroller or a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. This configuration generates a square wave output, which can be adjusted to vary the duty cycle. The duty cycle determines the proportion of time the signal is high compared to the total period of the waveform, effectively controlling the average power supplied to the load.
In this circuit, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network is employed to set the frequency of the PWM signal. The values of the resistor and capacitor can be modified to achieve the desired frequency range. An output transistor may be included to drive larger loads, allowing the circuit to control devices such as motors or LEDs without overloading the microcontroller or timer IC.
Additionally, a feedback mechanism can be integrated to refine the PWM signal based on the load's response. This could involve using a potentiometer to adjust the duty cycle manually or employing a sensor to provide real-time feedback for automatic adjustments.
Overall, this PWM circuit serves as an effective educational tool, demonstrating the principles of signal modulation and power control while maintaining a straightforward design that is accessible to individuals with varying levels of experience in electronics.If you ever thought of experimenting with pulse-width modulation, this circuit should get you started nicely. We ve kept simplicity in mind and used a dua.. 🔗 External reference