Radio Remote Control using DTMF
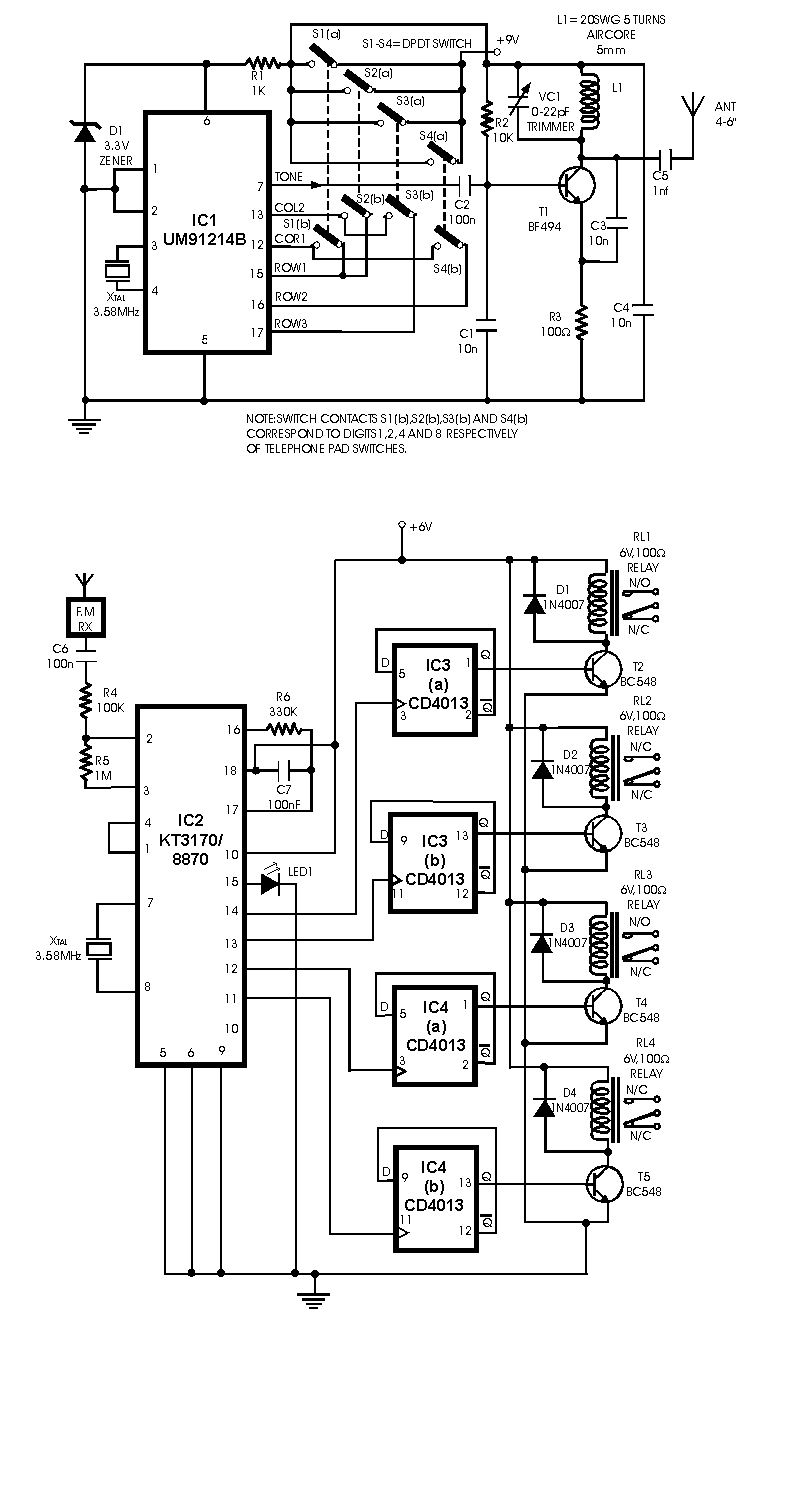
A radio remote control system utilizing DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) technology is presented. This circuit allows for the control of various electrical appliances through radio frequency signals.
The described radio remote control system employs DTMF tones, which are generated by a keypad or similar input device. Each key on the keypad corresponds to a specific frequency pair, enabling the transmission of distinct control signals. The circuit typically comprises a DTMF encoder, a radio frequency (RF) transmitter, and a receiver module.
The DTMF encoder converts the pressed key into a digital signal, which is then transmitted via an RF transmitter. The RF transmitter modulates this signal onto a carrier frequency, allowing it to be sent over the air. The design may include a microcontroller to manage the encoding process and to facilitate communication between the user interface and the RF module.
At the receiving end, an RF receiver captures the transmitted signal. The receiver demodulates the signal, converting it back into a DTMF tone. This tone is then processed by a DTMF decoder, which interprets the frequency pairs and translates them into control commands for the connected appliances. The appliances can be controlled directly through relay modules or solid-state switches, which handle the high voltage and current required for operation.
Overall, this radio remote control system offers a convenient and efficient method for managing electrical devices from a distance, utilizing widely available components and straightforward circuitry. The use of DTMF technology ensures reliable performance and ease of integration with various applications.Radio Remote Control using DTMF. Here is a circuit of a remote control unit which makes use of the radio frequency signals to control various electrical appliances. This remote control unit has. 🔗 External reference
The described radio remote control system employs DTMF tones, which are generated by a keypad or similar input device. Each key on the keypad corresponds to a specific frequency pair, enabling the transmission of distinct control signals. The circuit typically comprises a DTMF encoder, a radio frequency (RF) transmitter, and a receiver module.
The DTMF encoder converts the pressed key into a digital signal, which is then transmitted via an RF transmitter. The RF transmitter modulates this signal onto a carrier frequency, allowing it to be sent over the air. The design may include a microcontroller to manage the encoding process and to facilitate communication between the user interface and the RF module.
At the receiving end, an RF receiver captures the transmitted signal. The receiver demodulates the signal, converting it back into a DTMF tone. This tone is then processed by a DTMF decoder, which interprets the frequency pairs and translates them into control commands for the connected appliances. The appliances can be controlled directly through relay modules or solid-state switches, which handle the high voltage and current required for operation.
Overall, this radio remote control system offers a convenient and efficient method for managing electrical devices from a distance, utilizing widely available components and straightforward circuitry. The use of DTMF technology ensures reliable performance and ease of integration with various applications.Radio Remote Control using DTMF. Here is a circuit of a remote control unit which makes use of the radio frequency signals to control various electrical appliances. This remote control unit has. 🔗 External reference