RAPID BATTERY CHARGER FOR ICOM IC 2A
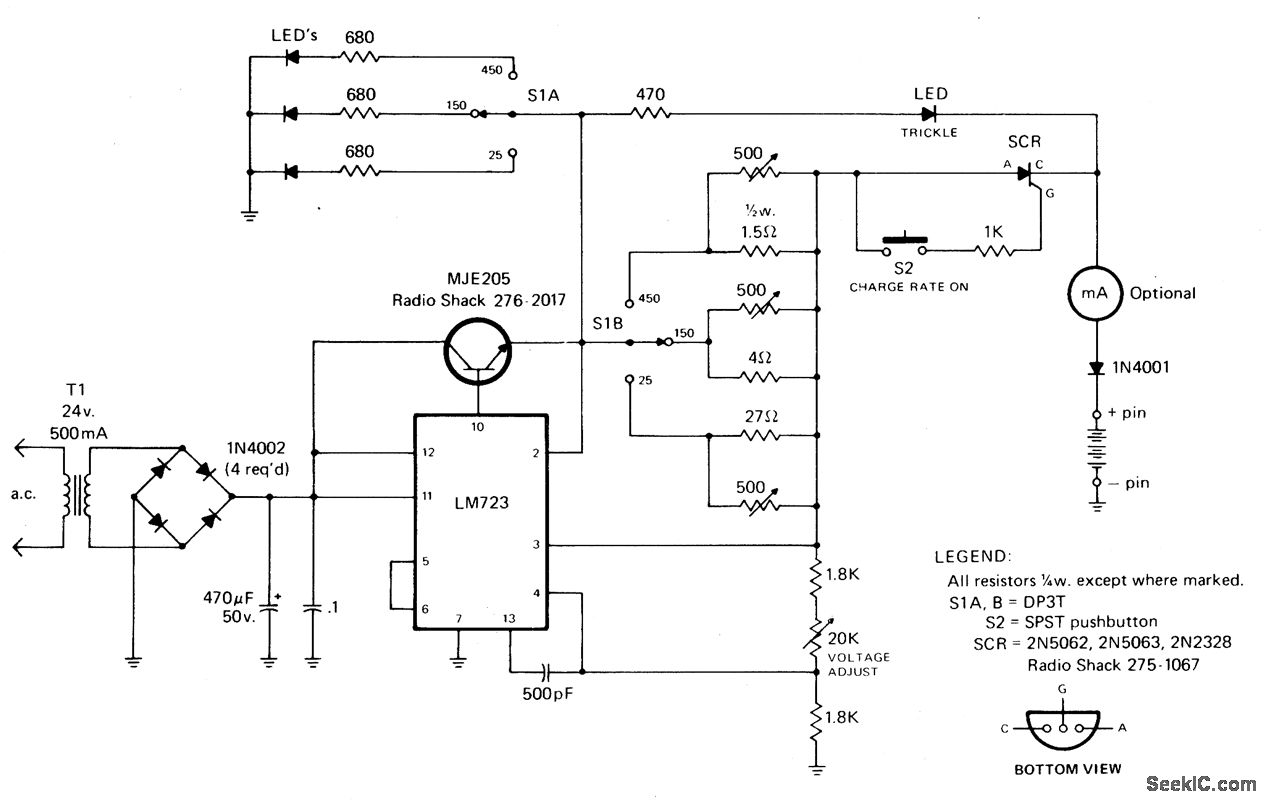
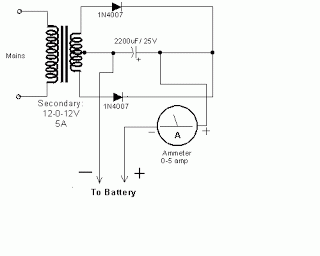
The rectified and filtered voltage from the 24 Vac transformer is applied to the LM723 voltage regulator, along with an NPN pass transistor configured for constant current supply. A 470-ohm resistor limits the trickle current until the momentary pushbutton (S2) is pressed, at which point the SCR activates and current flows through a predetermined resistor network that limits the charging current. The SCR will deactivate when the thermal cutout circuit within the battery pack opens.
The circuit design begins with a 24 Vac transformer, which steps down the voltage to a manageable level suitable for rectification. The output from the transformer is then rectified using a bridge rectifier or a full-wave rectifier configuration, which converts the alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). The rectified output is smoothed using a filter capacitor to reduce ripple voltage, providing a more stable DC voltage to the next stage.
The LM723 voltage regulator is utilized to maintain a constant output voltage. This adjustable voltage regulator can be set to provide a specific output voltage by configuring external resistors. In this application, it is paired with an NPN pass transistor, which acts as a current amplifier, allowing for higher current output than the LM723 can provide alone. This configuration is particularly useful for applications requiring a stable and regulated power supply for charging batteries.
The inclusion of the 470-ohm resistor plays a critical role in controlling the initial charging current. When the system is powered on, this resistor limits the trickle charge to the connected battery, preventing damage from excessive current. The momentary pushbutton switch (S2) serves as a manual activation mechanism; when pressed, it triggers the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) to conduct, allowing a higher charging current to flow through the battery.
The SCR is a key component in this circuit, providing controlled rectification. Once triggered by the pushbutton, it allows current to flow through the resistor network, which has been designed to limit the charging current to a safe level. This network ensures that the battery charges efficiently without overheating.
Safety is further enhanced by the thermal cutout circuit integrated within the battery pack. This circuit monitors the temperature of the battery during charging. If the temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold, the thermal cutout opens, effectively turning off the SCR and halting the charging process. This feature is essential for preventing battery damage and ensuring safe operation.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines rectification, voltage regulation, and current limiting to provide a reliable charging solution for batteries, with built-in safety mechanisms to protect against overcurrent and overheating conditions.Rectifted and filtered voltage from the 24 Vac transformer is applied to the LM723 voltage regulator and the npn pass transistor set up for constant current supply. The 470 ohm resistor limits trickle current until the momentary pushbutton (S2) is depressed, the SCR turns on and current ftows through the previously determined resistor network limi
ting the charging current. The SCR will turn off when the thennal cutout circuit inside the battery pack opens up. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design begins with a 24 Vac transformer, which steps down the voltage to a manageable level suitable for rectification. The output from the transformer is then rectified using a bridge rectifier or a full-wave rectifier configuration, which converts the alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). The rectified output is smoothed using a filter capacitor to reduce ripple voltage, providing a more stable DC voltage to the next stage.
The LM723 voltage regulator is utilized to maintain a constant output voltage. This adjustable voltage regulator can be set to provide a specific output voltage by configuring external resistors. In this application, it is paired with an NPN pass transistor, which acts as a current amplifier, allowing for higher current output than the LM723 can provide alone. This configuration is particularly useful for applications requiring a stable and regulated power supply for charging batteries.
The inclusion of the 470-ohm resistor plays a critical role in controlling the initial charging current. When the system is powered on, this resistor limits the trickle charge to the connected battery, preventing damage from excessive current. The momentary pushbutton switch (S2) serves as a manual activation mechanism; when pressed, it triggers the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) to conduct, allowing a higher charging current to flow through the battery.
The SCR is a key component in this circuit, providing controlled rectification. Once triggered by the pushbutton, it allows current to flow through the resistor network, which has been designed to limit the charging current to a safe level. This network ensures that the battery charges efficiently without overheating.
Safety is further enhanced by the thermal cutout circuit integrated within the battery pack. This circuit monitors the temperature of the battery during charging. If the temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold, the thermal cutout opens, effectively turning off the SCR and halting the charging process. This feature is essential for preventing battery damage and ensuring safe operation.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines rectification, voltage regulation, and current limiting to provide a reliable charging solution for batteries, with built-in safety mechanisms to protect against overcurrent and overheating conditions.Rectifted and filtered voltage from the 24 Vac transformer is applied to the LM723 voltage regulator and the npn pass transistor set up for constant current supply. The 470 ohm resistor limits trickle current until the momentary pushbutton (S2) is depressed, the SCR turns on and current ftows through the previously determined resistor network limi
ting the charging current. The SCR will turn off when the thennal cutout circuit inside the battery pack opens up. 🔗 External reference