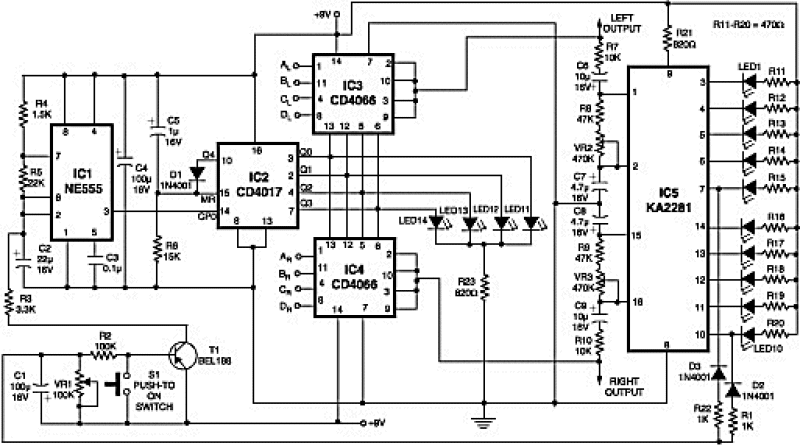
Ratiometric resistance measurement
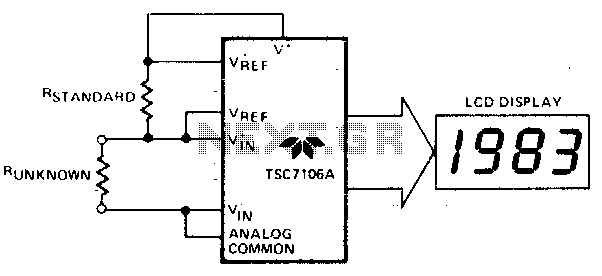
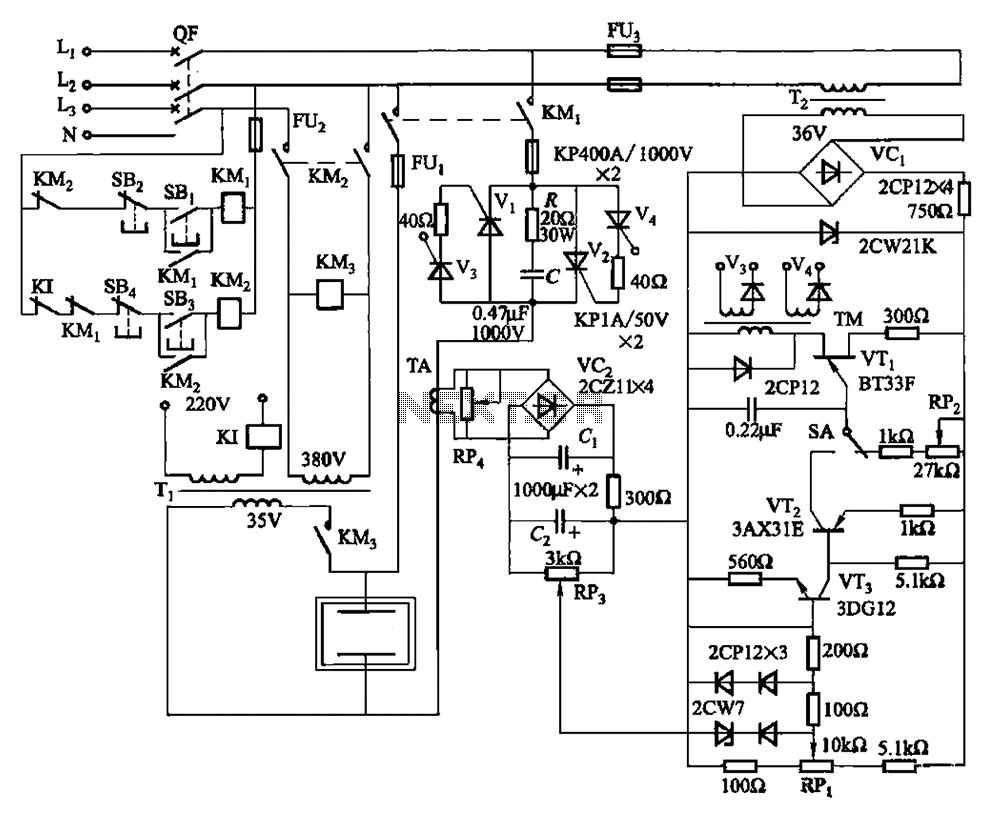
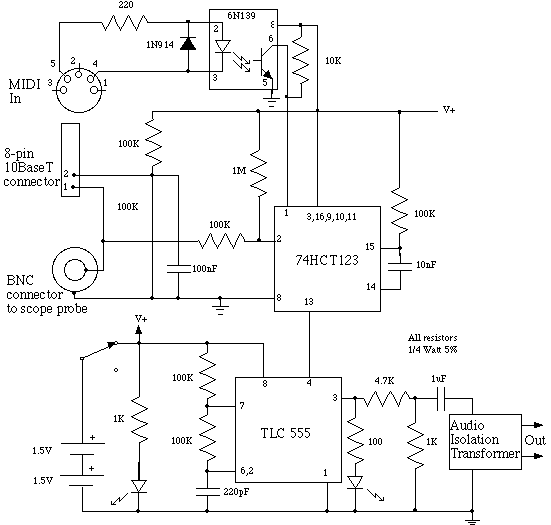
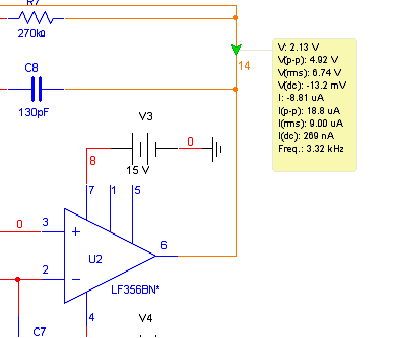
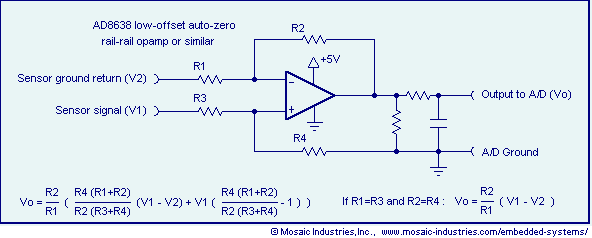
The unknown resistance is connected in series with a known standard resistor, and a current is passed through both components. The voltage developed across the unknown resistor is applied to the input, while the voltage across the known resistor is applied to the reference input. If the unknown resistance is equal to the standard resistance, the display will read 1000.
In this circuit configuration, a standard resistor with a precisely known resistance value is used as a reference to measure an unknown resistance. The arrangement involves connecting both resistors in series and passing a constant current through them. The voltage drop across the unknown resistor is measured and compared to the voltage drop across the known resistor.
To implement this circuit, a precision current source is required to ensure that the same current flows through both resistors. The voltage drop across the known resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law (V = IR), where I is the constant current and R is the resistance of the known resistor. This voltage serves as a reference point for the measurement.
A differential amplifier or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) can be utilized to measure the voltage across the unknown resistor. The output from the ADC can then be processed to determine the value of the unknown resistance. If the unknown resistance is equal to the known standard resistance, the output display will indicate a value of 1000, which serves as a calibration point for the measurement.
This type of circuit is commonly used in applications requiring precise resistance measurements, such as in laboratory settings or industrial applications where accurate component values are essential. Proper calibration and selection of components are crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurements obtained from this configuration.The unknown resistance is put in series with a known standard and a current passed through the pair. The voltage developed across the unknown is applied to the input and the voltage across the known resistor applied to the reference input If the unknown equals the standard, the display will read 1000. 🔗 External reference
In this circuit configuration, a standard resistor with a precisely known resistance value is used as a reference to measure an unknown resistance. The arrangement involves connecting both resistors in series and passing a constant current through them. The voltage drop across the unknown resistor is measured and compared to the voltage drop across the known resistor.
To implement this circuit, a precision current source is required to ensure that the same current flows through both resistors. The voltage drop across the known resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law (V = IR), where I is the constant current and R is the resistance of the known resistor. This voltage serves as a reference point for the measurement.
A differential amplifier or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) can be utilized to measure the voltage across the unknown resistor. The output from the ADC can then be processed to determine the value of the unknown resistance. If the unknown resistance is equal to the known standard resistance, the output display will indicate a value of 1000, which serves as a calibration point for the measurement.
This type of circuit is commonly used in applications requiring precise resistance measurements, such as in laboratory settings or industrial applications where accurate component values are essential. Proper calibration and selection of components are crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurements obtained from this configuration.The unknown resistance is put in series with a known standard and a current passed through the pair. The voltage developed across the unknown is applied to the input and the voltage across the known resistor applied to the reference input If the unknown equals the standard, the display will read 1000. 🔗 External reference