receiver architectures
Various architectures of receivers have been proposed in literature, but the most popular architectures among them, such as Heterodyne, Homodyne, Wideband-IF, and Low-IF, are presented here.
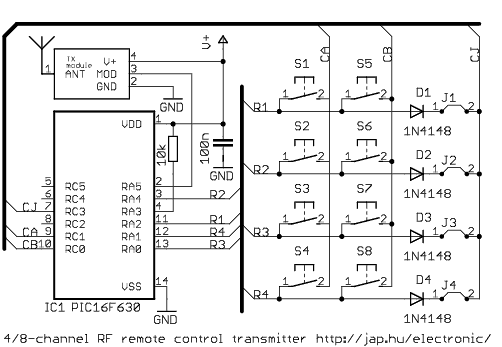
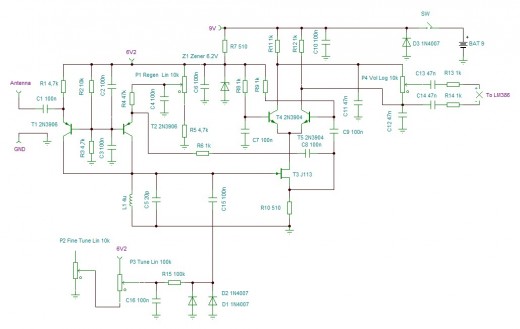
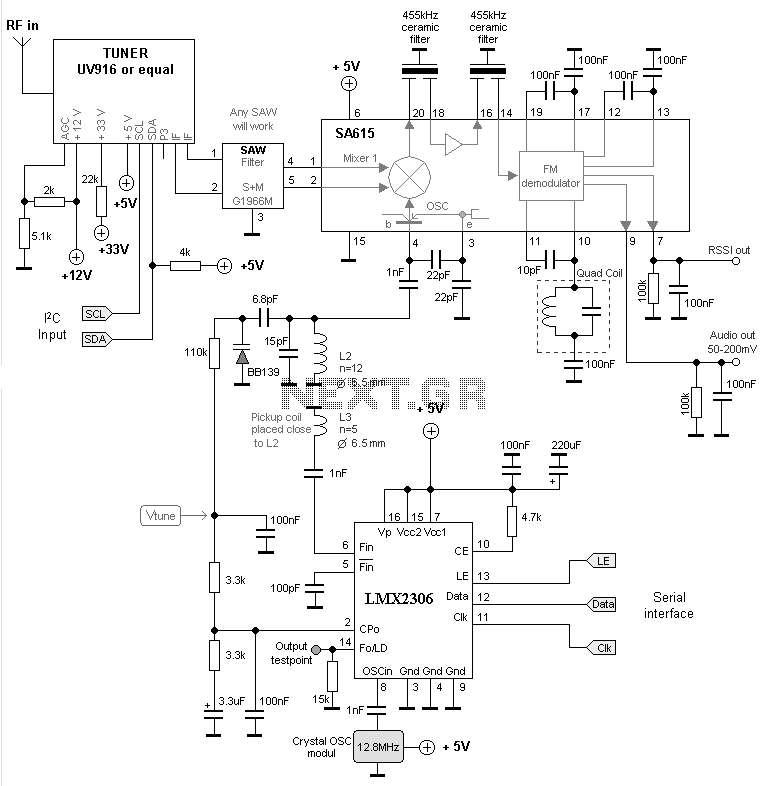
The Heterodyne receiver architecture utilizes two frequencies: the incoming radio frequency (RF) signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal. The primary function of the Heterodyne architecture is to mix these two frequencies, producing an intermediate frequency (IF) that is easier to process. This architecture is widely used due to its ability to provide high selectivity and sensitivity, making it suitable for applications in communication systems.
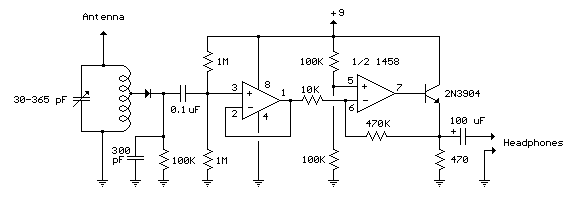
The Homodyne receiver, in contrast, employs a local oscillator that operates at the same frequency as the incoming RF signal. This architecture simplifies the design and can reduce the number of components needed. However, it can be more susceptible to phase noise, which may impact performance in high-frequency applications.
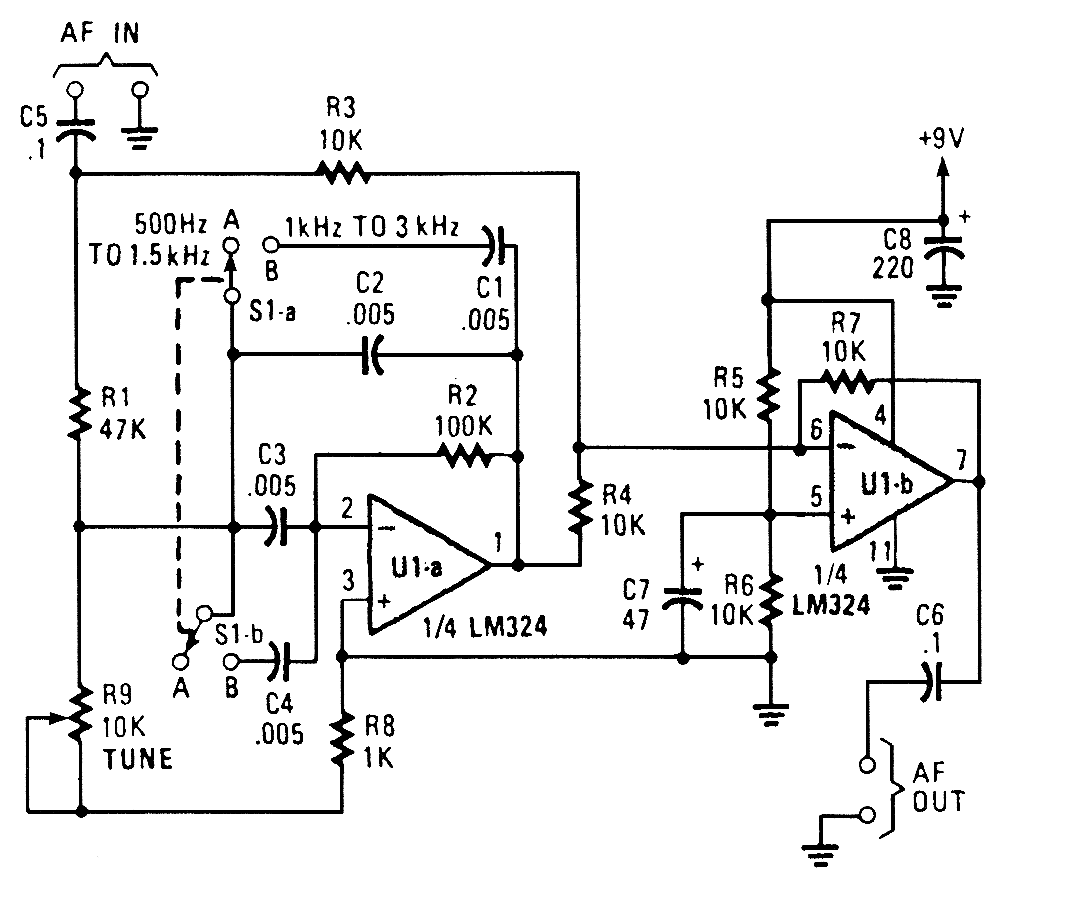
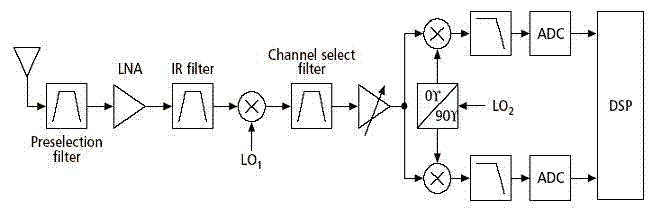
Wideband-IF receivers are designed to handle a broad range of frequencies, allowing for the simultaneous processing of multiple signals. This architecture is particularly advantageous in applications requiring the detection of various signals across a wide spectrum, such as in radar and electronic warfare systems.
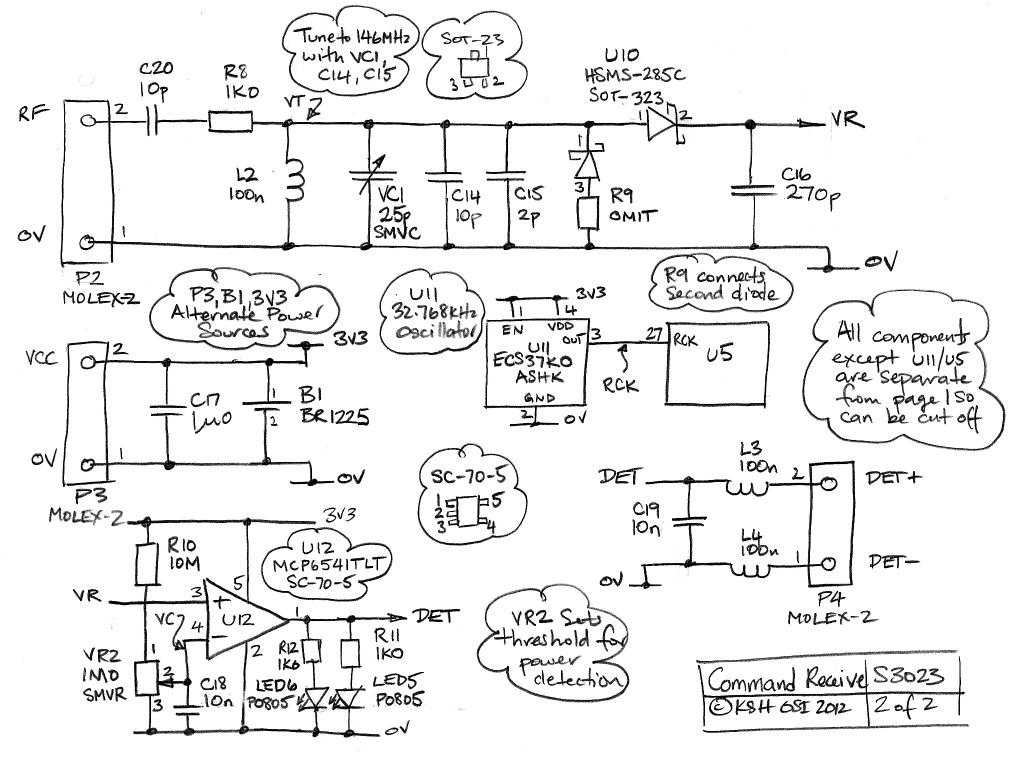
Low-IF receivers bridge the gap between traditional superheterodyne receivers and direct conversion receivers. By converting the RF signal to a low intermediate frequency, these receivers can achieve a balance between performance and complexity. They are often used in modern communication systems due to their efficiency in processing signals with lower power consumption.
Each of these architectures has distinct advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications within the field of electronic communications. Understanding the characteristics and functionalities of each receiver type is essential for designing effective communication systems.Various architectures of receivers has been proposed in literature, but most popular architectures among them like Heterodyne, Homodyne, Wideband-IF and Low-IF are presented here. Heterodyne Arch.. 🔗 External reference
The Heterodyne receiver architecture utilizes two frequencies: the incoming radio frequency (RF) signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal. The primary function of the Heterodyne architecture is to mix these two frequencies, producing an intermediate frequency (IF) that is easier to process. This architecture is widely used due to its ability to provide high selectivity and sensitivity, making it suitable for applications in communication systems.
The Homodyne receiver, in contrast, employs a local oscillator that operates at the same frequency as the incoming RF signal. This architecture simplifies the design and can reduce the number of components needed. However, it can be more susceptible to phase noise, which may impact performance in high-frequency applications.
Wideband-IF receivers are designed to handle a broad range of frequencies, allowing for the simultaneous processing of multiple signals. This architecture is particularly advantageous in applications requiring the detection of various signals across a wide spectrum, such as in radar and electronic warfare systems.
Low-IF receivers bridge the gap between traditional superheterodyne receivers and direct conversion receivers. By converting the RF signal to a low intermediate frequency, these receivers can achieve a balance between performance and complexity. They are often used in modern communication systems due to their efficiency in processing signals with lower power consumption.
Each of these architectures has distinct advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications within the field of electronic communications. Understanding the characteristics and functionalities of each receiver type is essential for designing effective communication systems.Various architectures of receivers has been proposed in literature, but most popular architectures among them like Heterodyne, Homodyne, Wideband-IF and Low-IF are presented here. Heterodyne Arch.. 🔗 External reference