Recording signal amplifying transistor circuit
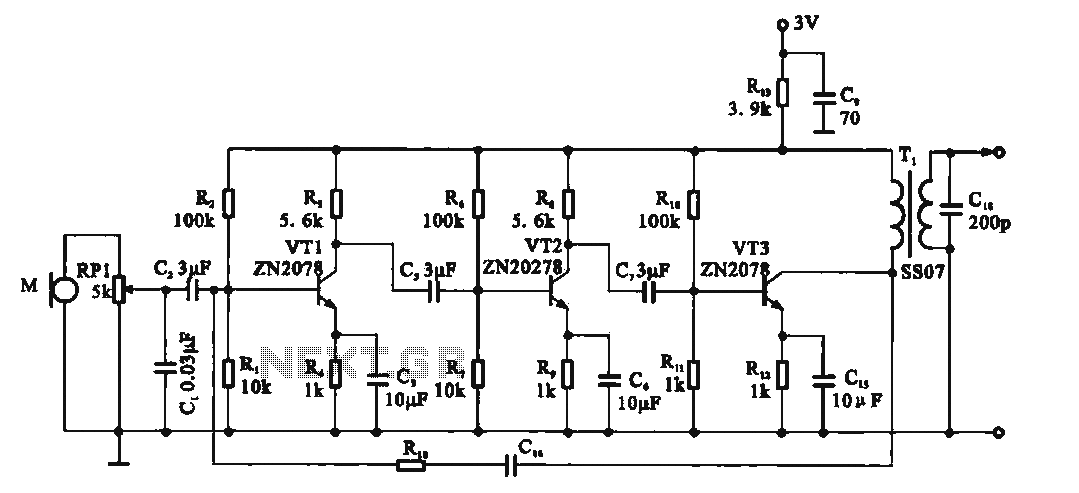
This circuit is a recording signal amplifying transistor circuit that illustrates the functioning of a microphone signal amplifier. After adjustment through potentiometer RP1, the signal is applied to the transistor VT1, which operates as a common emitter amplifier. The emitter of VT1 is connected to a negative feedback resistor, establishing a stable DC operating point. Capacitor C3 serves as a decoupling capacitor, facilitating an increase in the gain of VT1. The amplified audio signal is then applied to the primary winding of transformer T, which couples the audio signal to the recording head for the recording process. The secondary winding of the transformer, in parallel with a 200 pF capacitor, enhances high-frequency signals to compensate for losses during recording. The collector output of VT3 is connected to Rcs, while capacitor C16 and TV1 provide feedback to the base, improving the amplifier's frequency characteristics. The output of the amplifier can be adjusted in variable pressure mode to compensate for high-frequency signals. The circuit operates on a low voltage power supply of 3V, utilizing two batteries and exhibiting low power consumption characteristics.
The recording signal amplifying circuit is designed to effectively capture and enhance audio signals from a microphone. The use of a common emitter configuration for transistor VT1 allows for significant amplification of the input audio signal. The adjustment via potentiometer RP1 provides flexibility in tuning the gain to accommodate various microphone sensitivities and recording conditions.
The negative feedback resistor connected to the emitter of VT1 plays a crucial role in stabilizing the DC operating point, ensuring consistent performance across different operating temperatures and signal conditions. Capacitor C3 acts as a decoupling element, which is essential for filtering out noise and preventing oscillations that could degrade the quality of the amplified signal.
Transformer T is pivotal in this circuit, as it not only couples the amplified audio signal to the recording head but also serves to match impedance between the amplifier and the recording device. The secondary winding of the transformer, in conjunction with the 200 pF capacitor, is specifically designed to boost high-frequency response, addressing the common issue of high-frequency signal loss during the recording process.
The feedback network involving capacitor C16 and transistor TV1 is instrumental in refining the frequency response of the amplifier. This feedback mechanism allows for better control over the amplifier's gain across a range of frequencies, ensuring that the output remains clear and defined even at higher frequencies.
The circuit's design also emphasizes low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The use of a 3V power supply derived from two batteries allows for extended operation without frequent replacements, which is particularly advantageous in portable recording applications. This combination of features makes the recording signal amplifying transistor circuit a robust solution for high-quality audio recording tasks.Recording signal amplifying transistor circuit Shows the recording signal transistor amplifier, the microphone signal after adjustment by potentiometer RP1 applied to the transistor VT1, it is a common emitter amplifier, where VT1 emitter connected to the current negative feedback resistor as a stable DC operating point, C3 to decoupling capacitor so that VT1 exchange gain increase, the audio signal after amplification levels applied to the transformer T, the primary winding. By transformer coupled audio signal to the recording head for recording. Transformer secondary winding and 200 pF capacitor in parallel to enhance the high-frequency signal, the recording process to compensate high-frequency losses.
VT3 collector outputs Rcs. C16 TV1 feedback to the base, with spout improve the frequency characteristics of the amplifier. The output of the amplifier with variable pressure mode can compensate for high frequency signals. 3V low voltage power supply circuit by the use of two batteries, and has a low power consumption characteristics.
The recording signal amplifying circuit is designed to effectively capture and enhance audio signals from a microphone. The use of a common emitter configuration for transistor VT1 allows for significant amplification of the input audio signal. The adjustment via potentiometer RP1 provides flexibility in tuning the gain to accommodate various microphone sensitivities and recording conditions.
The negative feedback resistor connected to the emitter of VT1 plays a crucial role in stabilizing the DC operating point, ensuring consistent performance across different operating temperatures and signal conditions. Capacitor C3 acts as a decoupling element, which is essential for filtering out noise and preventing oscillations that could degrade the quality of the amplified signal.
Transformer T is pivotal in this circuit, as it not only couples the amplified audio signal to the recording head but also serves to match impedance between the amplifier and the recording device. The secondary winding of the transformer, in conjunction with the 200 pF capacitor, is specifically designed to boost high-frequency response, addressing the common issue of high-frequency signal loss during the recording process.
The feedback network involving capacitor C16 and transistor TV1 is instrumental in refining the frequency response of the amplifier. This feedback mechanism allows for better control over the amplifier's gain across a range of frequencies, ensuring that the output remains clear and defined even at higher frequencies.
The circuit's design also emphasizes low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The use of a 3V power supply derived from two batteries allows for extended operation without frequent replacements, which is particularly advantageous in portable recording applications. This combination of features makes the recording signal amplifying transistor circuit a robust solution for high-quality audio recording tasks.Recording signal amplifying transistor circuit Shows the recording signal transistor amplifier, the microphone signal after adjustment by potentiometer RP1 applied to the transistor VT1, it is a common emitter amplifier, where VT1 emitter connected to the current negative feedback resistor as a stable DC operating point, C3 to decoupling capacitor so that VT1 exchange gain increase, the audio signal after amplification levels applied to the transformer T, the primary winding. By transformer coupled audio signal to the recording head for recording. Transformer secondary winding and 200 pF capacitor in parallel to enhance the high-frequency signal, the recording process to compensate high-frequency losses.
VT3 collector outputs Rcs. C16 TV1 feedback to the base, with spout improve the frequency characteristics of the amplifier. The output of the amplifier with variable pressure mode can compensate for high frequency signals. 3V low voltage power supply circuit by the use of two batteries, and has a low power consumption characteristics.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713