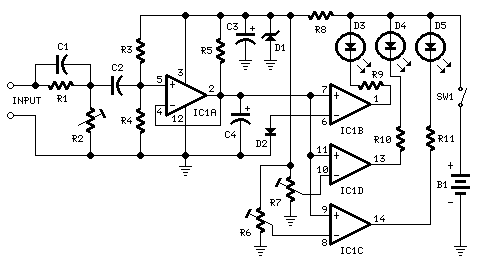
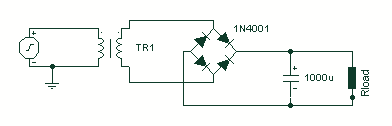
Reducing Relay Power Consumption
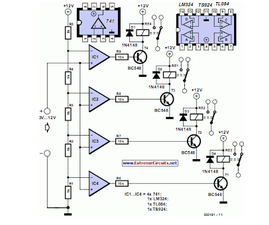
This circuit demonstrates that microprocessors, personal computers, and the latest ultra-accurate digital-to-analog converters (DACs) are excessive for the task of sequentially controlling four relays.
The circuit utilizes a simple microcontroller or a basic timer IC to manage the operation of four relays in a predetermined sequence. The design incorporates a series of output pins from the microcontroller, which are connected to the relay control inputs. Each relay can be activated or deactivated based on the logic levels provided by the microcontroller.
For instance, a 555 timer configured in astable mode can generate a square wave signal, which can be fed into the microcontroller. The microcontroller can be programmed to respond to this signal by turning on each relay in succession, with a defined delay between each activation. This sequence can be easily modified through software, allowing for flexibility in operation.
The relays used in the circuit should be rated appropriately for the load they will control, ensuring they can handle the required voltage and current without failure. Additionally, flyback diodes should be placed across the relay coils to protect the microcontroller from voltage spikes generated when the relays are de-energized.
Power supply considerations are also crucial. The circuit should be powered by a stable voltage source that meets the requirements of the microcontroller and relays. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included to minimize noise and ensure reliable operation.
This design highlights the efficiency of using a microcontroller or timer IC for simple relay control tasks, demonstrating that complex systems are unnecessary for straightforward applications.This circuit proves that microcoprocessors, PCs and the latest ultra-accurate DACs are overkill when it comes to controlling four relays in sequence in re.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a simple microcontroller or a basic timer IC to manage the operation of four relays in a predetermined sequence. The design incorporates a series of output pins from the microcontroller, which are connected to the relay control inputs. Each relay can be activated or deactivated based on the logic levels provided by the microcontroller.
For instance, a 555 timer configured in astable mode can generate a square wave signal, which can be fed into the microcontroller. The microcontroller can be programmed to respond to this signal by turning on each relay in succession, with a defined delay between each activation. This sequence can be easily modified through software, allowing for flexibility in operation.
The relays used in the circuit should be rated appropriately for the load they will control, ensuring they can handle the required voltage and current without failure. Additionally, flyback diodes should be placed across the relay coils to protect the microcontroller from voltage spikes generated when the relays are de-energized.
Power supply considerations are also crucial. The circuit should be powered by a stable voltage source that meets the requirements of the microcontroller and relays. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included to minimize noise and ensure reliable operation.
This design highlights the efficiency of using a microcontroller or timer IC for simple relay control tasks, demonstrating that complex systems are unnecessary for straightforward applications.This circuit proves that microcoprocessors, PCs and the latest ultra-accurate DACs are overkill when it comes to controlling four relays in sequence in re.. 🔗 External reference