switch mode power supply What does frequency foldback do in a switching regulator
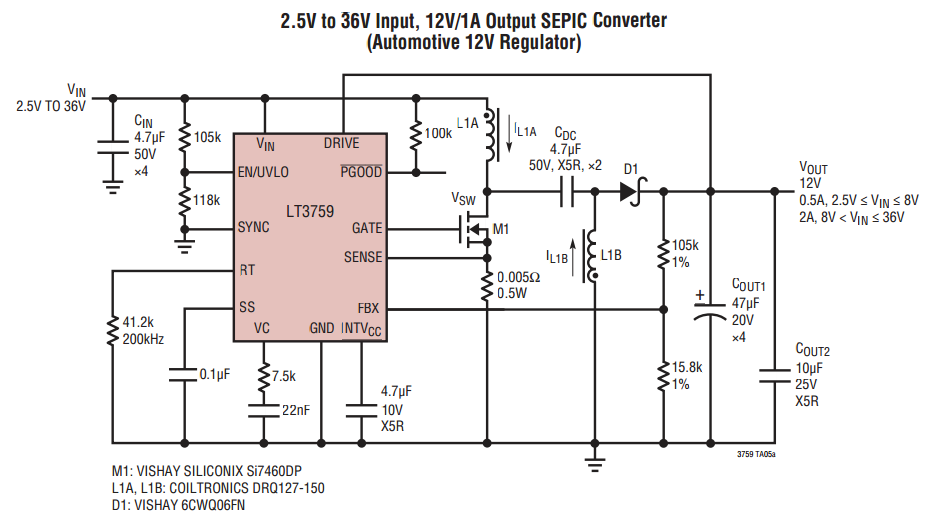
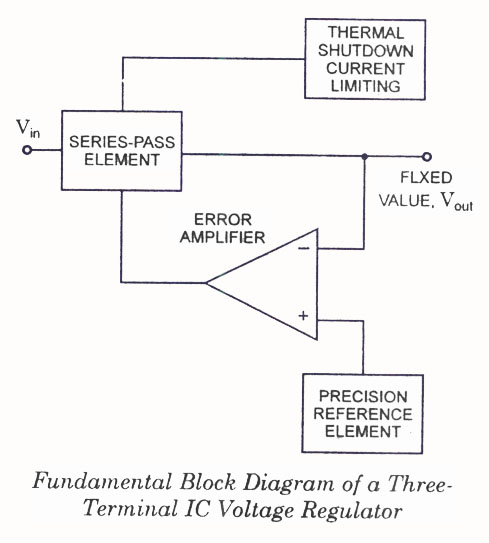
When VOUT is very low during startup or in the event of a short-circuit fault at the output, the switching regulator must operate at low duty cycles to keep the power switch current within the current limit range. This is crucial because the inductor current decay rate is significantly low during the switch-off time. The minimum on-time limitation may hinder the switcher from achieving a sufficiently low duty cycle at the programmed switching frequency. Consequently, the switch current will continue to rise with each switching cycle, surpassing the programmed current limit. To prevent the switch peak currents from exceeding the programmed value, the LT3759 incorporates a frequency foldback function that reduces the switching frequency when the FBX voltage is low. This function is illustrated in the Normalized Switching Frequency vs. FBX graph found in the Typical Performance Characteristics section. Additionally, some frequency foldback waveforms are depicted in the Typical Applications section. The frequency foldback function effectively prevents the inductor current from exceeding the programmed limits due to the minimum on-time constraint. This process differs from traditional foldback short circuit protection.
The LT3759 is a highly versatile switching regulator designed to manage power efficiently in low-output voltage scenarios, particularly during startup or fault conditions. The operational dynamics of this device are critical for maintaining the stability and reliability of the power supply system. When the output voltage (VOUT) drops significantly, the regulator is required to shift to a low duty cycle operation mode. This transition is essential to ensure that the current flowing through the power switch remains within safe limits, thereby preventing potential damage to the circuit components.
The low inductor current decay rate during switch-off periods necessitates careful control of the switching frequency. The LT3759's frequency foldback feature becomes active when the feedback voltage (FBX) falls below a certain threshold, resulting in a proportional reduction of the switching frequency. By lowering the frequency, the regulator effectively decreases the average current flowing through the inductor, which is crucial during low output conditions. This action ensures that the inductor current does not exceed the programmed limits, even in the presence of minimum on-time constraints.
The frequency foldback mechanism can be likened to a governor on a vehicle, which limits the speed to prevent the engine from over-revving. Just as the governor reduces engine speed when a vehicle is under heavy load, the LT3759 reduces its switching frequency to manage inductor current during low voltage conditions. Without this frequency foldback feature, the regulator would struggle to maintain safe operating conditions, leading to excessive peak currents that could compromise the integrity of the power supply system.
In graphical terms, the plot illustrating the switching frequency without frequency foldback would display a constant frequency line, which remains unchanged despite falling FBX voltage levels. In contrast, with frequency foldback implemented, the graph would show a downward slope, indicating a reduction in frequency as FBX voltage decreases. This visual representation underscores the importance of the frequency foldback function in maintaining operational stability and protecting the circuit from potential overcurrent scenarios.When VOUT is very low during start-up or a short-circuit fault on the output, the switching regulator must operate at low duty cycles to maintain the power switch current within the current limit range, since the inductor current decay rate is very low during switch off time. The minimum on-time limitation may prevent the switcher from attaining a sufficiently low duty cycle at the programmed switching frequency. So, the switch current will keep increasing through each switch cycle, exceeding the programmed current limit. To prevent the switch peak currents from exceeding the programmed value, the LT3759 contains a frequency foldback function to reduce the switching frequency when the FBX voltage is low (see the Normalized Switching Frequency vs FBX graph in the Typical Performance Characteristics section).
Some frequency foldback waveforms are shown in the Typical Applications section. The frequency foldback function prevents IL from exceeding the programmed limits because of the minimum on-time. This seems different from foldback short circuit protection. But how does frequency foldback work What would be a good analogy to its process What would the plot look like without frequency foldback
🔗 External reference
The LT3759 is a highly versatile switching regulator designed to manage power efficiently in low-output voltage scenarios, particularly during startup or fault conditions. The operational dynamics of this device are critical for maintaining the stability and reliability of the power supply system. When the output voltage (VOUT) drops significantly, the regulator is required to shift to a low duty cycle operation mode. This transition is essential to ensure that the current flowing through the power switch remains within safe limits, thereby preventing potential damage to the circuit components.
The low inductor current decay rate during switch-off periods necessitates careful control of the switching frequency. The LT3759's frequency foldback feature becomes active when the feedback voltage (FBX) falls below a certain threshold, resulting in a proportional reduction of the switching frequency. By lowering the frequency, the regulator effectively decreases the average current flowing through the inductor, which is crucial during low output conditions. This action ensures that the inductor current does not exceed the programmed limits, even in the presence of minimum on-time constraints.
The frequency foldback mechanism can be likened to a governor on a vehicle, which limits the speed to prevent the engine from over-revving. Just as the governor reduces engine speed when a vehicle is under heavy load, the LT3759 reduces its switching frequency to manage inductor current during low voltage conditions. Without this frequency foldback feature, the regulator would struggle to maintain safe operating conditions, leading to excessive peak currents that could compromise the integrity of the power supply system.
In graphical terms, the plot illustrating the switching frequency without frequency foldback would display a constant frequency line, which remains unchanged despite falling FBX voltage levels. In contrast, with frequency foldback implemented, the graph would show a downward slope, indicating a reduction in frequency as FBX voltage decreases. This visual representation underscores the importance of the frequency foldback function in maintaining operational stability and protecting the circuit from potential overcurrent scenarios.When VOUT is very low during start-up or a short-circuit fault on the output, the switching regulator must operate at low duty cycles to maintain the power switch current within the current limit range, since the inductor current decay rate is very low during switch off time. The minimum on-time limitation may prevent the switcher from attaining a sufficiently low duty cycle at the programmed switching frequency. So, the switch current will keep increasing through each switch cycle, exceeding the programmed current limit. To prevent the switch peak currents from exceeding the programmed value, the LT3759 contains a frequency foldback function to reduce the switching frequency when the FBX voltage is low (see the Normalized Switching Frequency vs FBX graph in the Typical Performance Characteristics section).
Some frequency foldback waveforms are shown in the Typical Applications section. The frequency foldback function prevents IL from exceeding the programmed limits because of the minimum on-time. This seems different from foldback short circuit protection. But how does frequency foldback work What would be a good analogy to its process What would the plot look like without frequency foldback
🔗 External reference