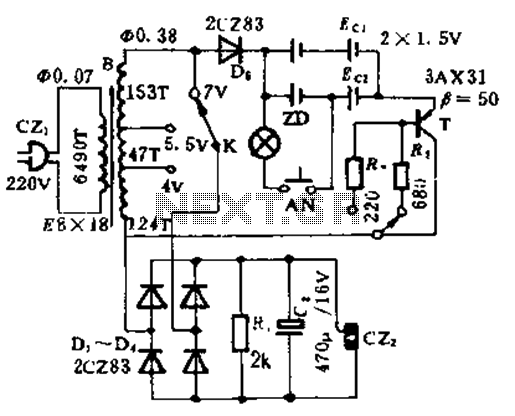
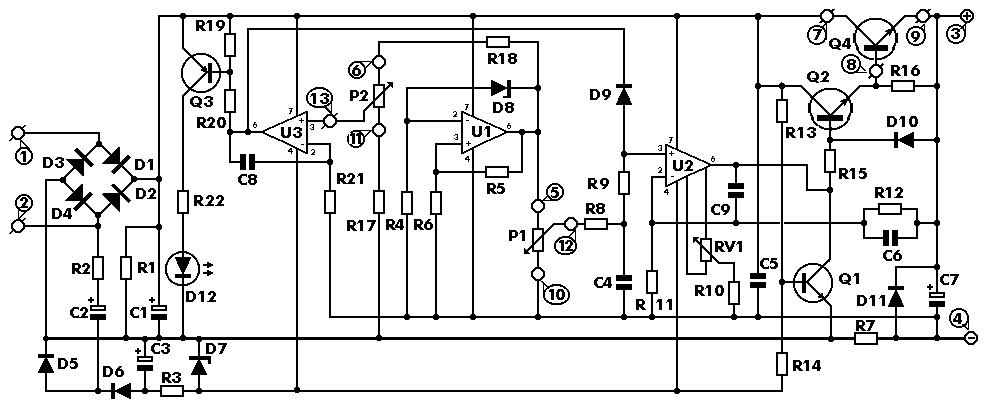
Regulated 12 Volt Supply
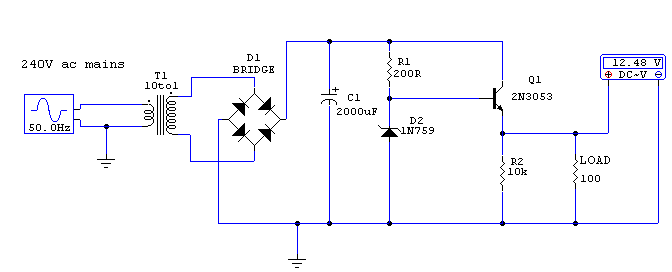
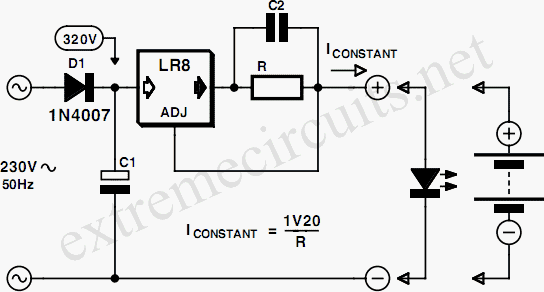
This circuit utilizes a 13-volt zener diode (D2) for voltage regulation. Approximately 0.7 volts are dropped across the base-emitter junction of the transistors, resulting in a higher current output of 12.3 volts. The circuit is capable of supplying loads up to 500 mA and is commonly referred to as an amplified zener circuit.
The amplified zener circuit is designed to provide stable output voltage regulation while allowing for higher current delivery compared to a standard zener diode configuration. The 13-volt zener diode (D2) acts as a reference voltage, ensuring that the output remains consistent despite variations in input voltage or load conditions.
The transistors in the circuit function as current amplifiers, which means they are capable of increasing the current supplied to the load while maintaining the desired voltage level. The base-emitter junction of the transistors introduces a voltage drop of approximately 0.7 volts, which is crucial for the operation of the transistors in the active region. This drop must be accounted for in the overall voltage output, leading to the effective output voltage of 12.3 volts.
The circuit's design allows for a maximum load current of 500 mA, making it suitable for various applications that require a stable power supply. The use of a zener diode for voltage regulation in conjunction with transistor amplification provides a robust solution for maintaining output voltage under different load conditions. This configuration is particularly useful in power supply circuits where consistent voltage levels are critical for the proper functioning of electronic components.
In summary, the amplified zener circuit is an effective voltage regulation solution that combines a zener diode with transistor amplification to deliver a stable output voltage capable of supporting moderate load currents. Its design principles can be applied to a variety of electronic applications requiring reliable power supplies.This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0. 7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12. 3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit. 🔗 External reference
The amplified zener circuit is designed to provide stable output voltage regulation while allowing for higher current delivery compared to a standard zener diode configuration. The 13-volt zener diode (D2) acts as a reference voltage, ensuring that the output remains consistent despite variations in input voltage or load conditions.
The transistors in the circuit function as current amplifiers, which means they are capable of increasing the current supplied to the load while maintaining the desired voltage level. The base-emitter junction of the transistors introduces a voltage drop of approximately 0.7 volts, which is crucial for the operation of the transistors in the active region. This drop must be accounted for in the overall voltage output, leading to the effective output voltage of 12.3 volts.
The circuit's design allows for a maximum load current of 500 mA, making it suitable for various applications that require a stable power supply. The use of a zener diode for voltage regulation in conjunction with transistor amplification provides a robust solution for maintaining output voltage under different load conditions. This configuration is particularly useful in power supply circuits where consistent voltage levels are critical for the proper functioning of electronic components.
In summary, the amplified zener circuit is an effective voltage regulation solution that combines a zener diode with transistor amplification to deliver a stable output voltage capable of supporting moderate load currents. Its design principles can be applied to a variety of electronic applications requiring reliable power supplies.This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0. 7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12. 3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit. 🔗 External reference