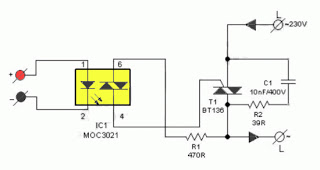
Relay Coil Energy Saver
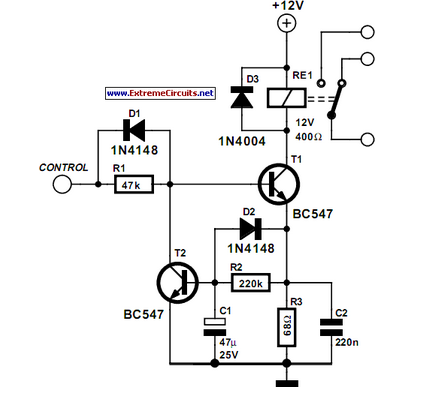
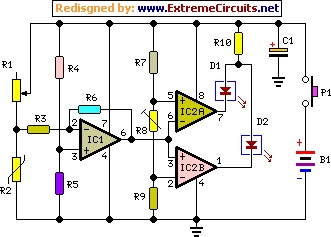
Some relays will become warm if they remain energized for some time. The circuit shown here will actuate the relay as before but then reduce the hold current.
The described circuit addresses the issue of heat generation in relays due to prolonged energization. In typical applications, relays are used to control high-power devices, and when they are continuously energized, they can generate excessive heat, potentially leading to premature failure. The proposed circuit operates by initially energizing the relay to close the contacts, allowing current to flow to the load. After a predetermined time, the circuit reduces the hold current required to keep the relay in the energized state.
This is typically accomplished through the use of a resistor or a secondary control mechanism that modifies the current flowing through the relay coil after the initial actuation. The circuit may incorporate a timing element, such as a capacitor and resistor combination, or a dedicated timing IC, to provide a delay before the hold current is reduced.
The design must ensure that the relay remains in a closed position while the load is powered, even with the reduced current. This can be achieved by utilizing a latching mechanism or a relay with a low holding current specification. Additionally, it is essential to select a relay that can withstand the initial inrush current without damage and to calculate the resistance value for the hold current accurately to ensure reliable operation without risking relay dropout.
In summary, this circuit effectively manages the thermal characteristics of the relay during operation, enhancing reliability and longevity while maintaining functionality in controlling the connected load. Proper component selection and timing considerations are crucial in achieving the desired performance and preventing overheating.Some relays will become warm if they remain energized for some time. The circuit shown here will actuate the relay as before but then reduce the ‘hold cu.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit addresses the issue of heat generation in relays due to prolonged energization. In typical applications, relays are used to control high-power devices, and when they are continuously energized, they can generate excessive heat, potentially leading to premature failure. The proposed circuit operates by initially energizing the relay to close the contacts, allowing current to flow to the load. After a predetermined time, the circuit reduces the hold current required to keep the relay in the energized state.
This is typically accomplished through the use of a resistor or a secondary control mechanism that modifies the current flowing through the relay coil after the initial actuation. The circuit may incorporate a timing element, such as a capacitor and resistor combination, or a dedicated timing IC, to provide a delay before the hold current is reduced.
The design must ensure that the relay remains in a closed position while the load is powered, even with the reduced current. This can be achieved by utilizing a latching mechanism or a relay with a low holding current specification. Additionally, it is essential to select a relay that can withstand the initial inrush current without damage and to calculate the resistance value for the hold current accurately to ensure reliable operation without risking relay dropout.
In summary, this circuit effectively manages the thermal characteristics of the relay during operation, enhancing reliability and longevity while maintaining functionality in controlling the connected load. Proper component selection and timing considerations are crucial in achieving the desired performance and preventing overheating.Some relays will become warm if they remain energized for some time. The circuit shown here will actuate the relay as before but then reduce the ‘hold cu.. 🔗 External reference