Reverse RIAA Equaliser
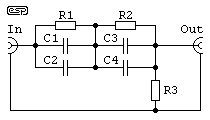
I came up with this idea when I was in a situation where I had an amplifier with an unused RIAA input and I was missing another input for a standard audio signal at this amplifier. So I designed a miniature passive network to convert a normal audio signal into the signal that phono inputs require. More: As the amplification of a phono input is quite high, this pre-equaliser network can be made completely passive. The frequency response of the current through the network formed by R1, R2, C1 - C4 corresponds to the inverse of the standard RIAA curve, so t
The described circuit is a passive RIAA equalizer designed to adapt a standard audio signal for use with a phono input on an amplifier. This circuit is particularly useful for integrating devices that do not have dedicated phono inputs, allowing them to connect to turntables or other audio sources that utilize the RIAA equalization standard.
The circuit consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) and four capacitors (C1 to C4). The resistors are configured to form a voltage divider, while the capacitors are arranged to shape the frequency response of the audio signal. The combination of these components creates a network that inversely matches the RIAA equalization curve, which is essential for reproducing the correct frequency response of vinyl records.
In operation, the incoming audio signal passes through the passive network, where it is attenuated and filtered. The values of R1 and R2 are selected to set the gain of the circuit, while the capacitors (C1, C2, C3, and C4) are chosen to define the cutoff frequencies that correspond to the RIAA standard. This ensures that the low frequencies are boosted while high frequencies are attenuated, effectively compensating for the pre-emphasis applied during the recording process of vinyl records.
The passive nature of this equalizer means that it does not require an external power source, making it a compact and efficient solution for audio signal processing. This design can be implemented on a small PCB, allowing for easy integration into existing audio systems. The passive equalizer is ideal for audiophiles looking to enhance their listening experience without the complexity and cost associated with active equalization circuits.I came up with this idea when I was in a situation where ... * I had an amplifier with an unused RIAA input and * I was missing another input for a standard audio signal at this amplifier. So I designed a miniature passive network to convert a normal audio signal into the signal that phono inputs require.
As the amplification of a phono input is quite high, this pre-equaliser network can be made completely passive. The frequency response of the current through the network formed by R1, R2, C1 - C4 corresponds to the inverse of the standard RIAA curve, so t
🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a passive RIAA equalizer designed to adapt a standard audio signal for use with a phono input on an amplifier. This circuit is particularly useful for integrating devices that do not have dedicated phono inputs, allowing them to connect to turntables or other audio sources that utilize the RIAA equalization standard.
The circuit consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) and four capacitors (C1 to C4). The resistors are configured to form a voltage divider, while the capacitors are arranged to shape the frequency response of the audio signal. The combination of these components creates a network that inversely matches the RIAA equalization curve, which is essential for reproducing the correct frequency response of vinyl records.
In operation, the incoming audio signal passes through the passive network, where it is attenuated and filtered. The values of R1 and R2 are selected to set the gain of the circuit, while the capacitors (C1, C2, C3, and C4) are chosen to define the cutoff frequencies that correspond to the RIAA standard. This ensures that the low frequencies are boosted while high frequencies are attenuated, effectively compensating for the pre-emphasis applied during the recording process of vinyl records.
The passive nature of this equalizer means that it does not require an external power source, making it a compact and efficient solution for audio signal processing. This design can be implemented on a small PCB, allowing for easy integration into existing audio systems. The passive equalizer is ideal for audiophiles looking to enhance their listening experience without the complexity and cost associated with active equalization circuits.I came up with this idea when I was in a situation where ... * I had an amplifier with an unused RIAA input and * I was missing another input for a standard audio signal at this amplifier. So I designed a miniature passive network to convert a normal audio signal into the signal that phono inputs require.
As the amplification of a phono input is quite high, this pre-equaliser network can be made completely passive. The frequency response of the current through the network formed by R1, R2, C1 - C4 corresponds to the inverse of the standard RIAA curve, so t
🔗 External reference