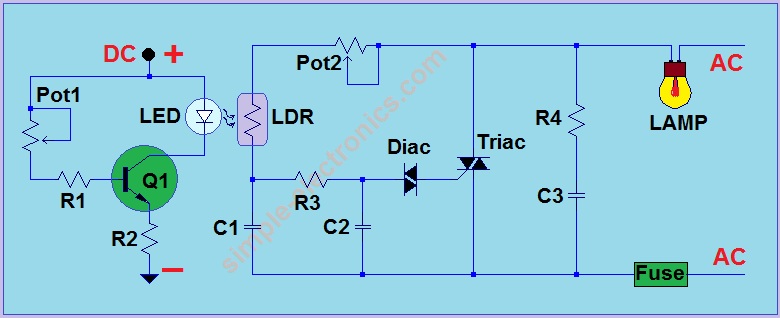
Reversing motor drive dc control
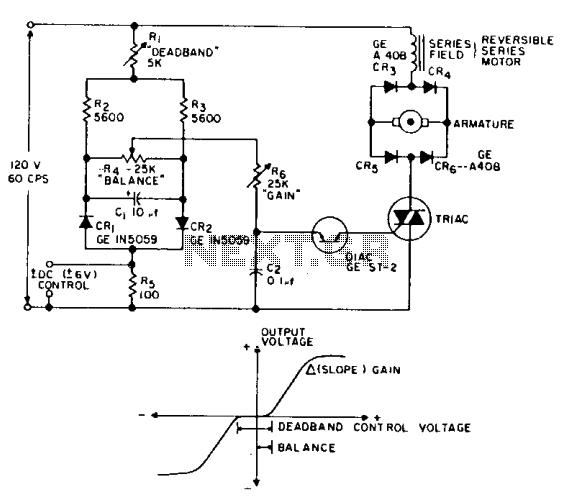
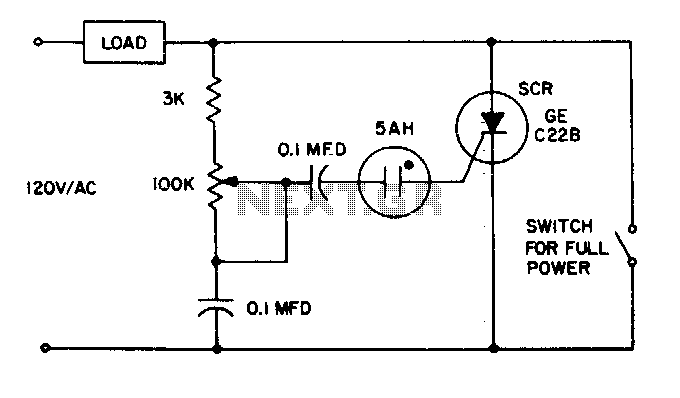
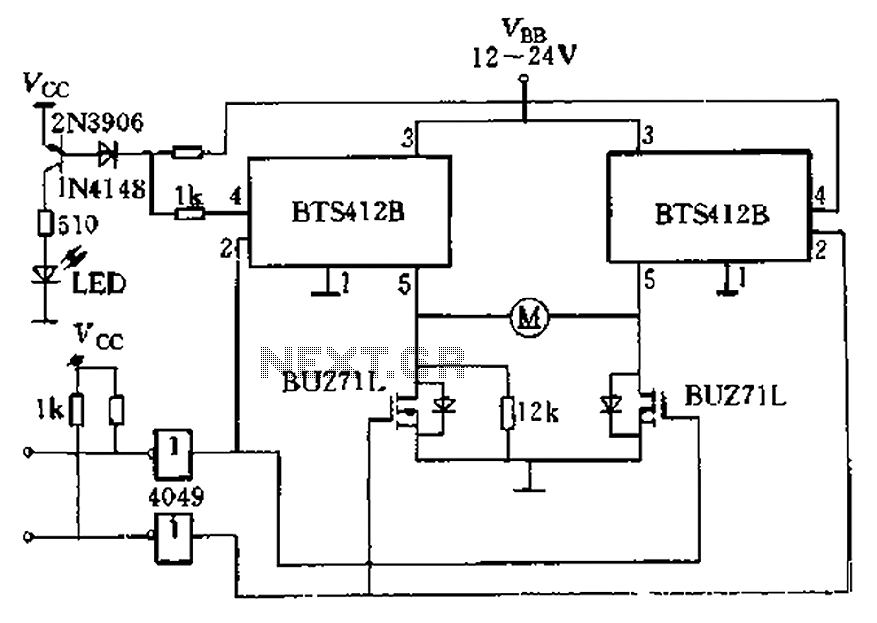
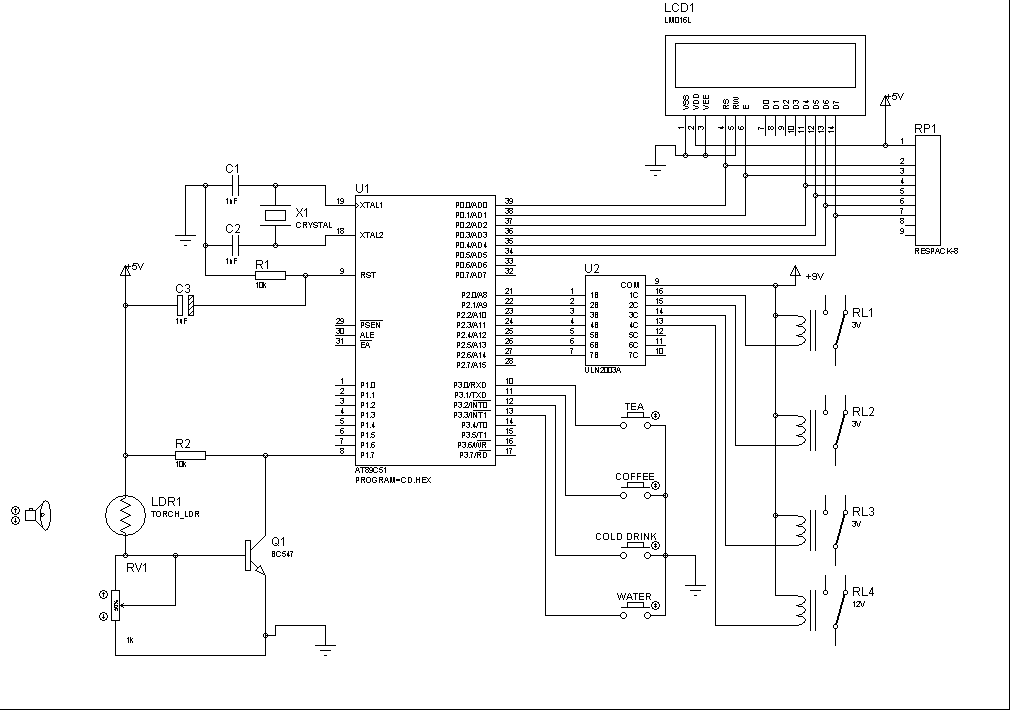
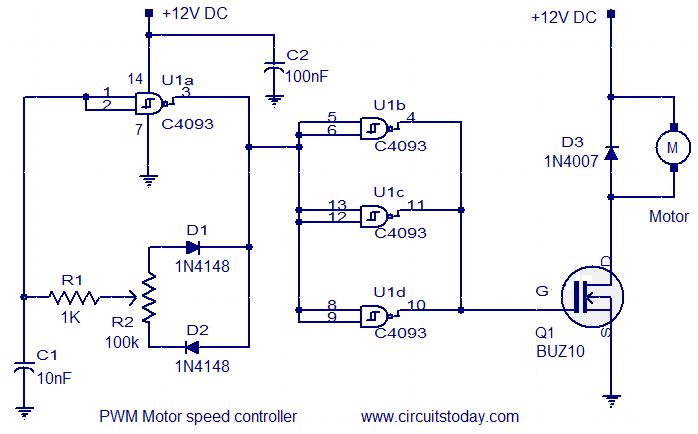
This is a positioning servo drive that includes adjustments for balance, gain, and deadband. In addition to receiving control from a DC signal, a mechanical input can be utilized for the balance control. Alternatively, this balance control can be substituted with a pair of resistance transducers for control via light or temperature.
The positioning servo drive circuit operates on the principle of feedback control to maintain the desired position of a mechanical element. The core components include a servo motor, a control circuit, and feedback sensors. The adjustments for balance, gain, and deadband are critical for optimizing the performance of the servo system to accommodate various operating conditions and loads.
1. **Servo Motor**: The servo motor is the actuator that moves the mechanical element to the desired position. It is typically a DC motor equipped with a feedback mechanism, such as an encoder or a potentiometer, to provide real-time position data.
2. **Control Circuit**: The control circuit processes the input signals and generates the necessary control signals for the servo motor. The circuit may include operational amplifiers for signal conditioning, and microcontrollers for more complex control algorithms. The gain adjustment allows for tuning the responsiveness of the system, while the deadband setting helps to prevent oscillations around the target position by introducing a threshold that must be exceeded before corrective action is taken.
3. **Balance Control**: The balance control can be adjusted using a mechanical input or replaced with resistance transducers. The mechanical input allows for manual tuning of the system, while resistance transducers can provide automatic adjustments based on environmental factors such as light intensity or temperature variations. This adaptability enhances the versatility of the servo drive in different applications.
4. **Feedback Sensors**: Feedback sensors are integral to the operation of the servo drive. They provide continuous information about the position of the mechanical element, allowing the control circuit to make real-time adjustments. The choice of sensors, whether optical, resistive, or capacitive, can significantly affect the performance and accuracy of the servo system.
Overall, the described positioning servo drive is a sophisticated system designed for precise control in various applications, leveraging both electrical and mechanical inputs to achieve optimal performance.This is a positioning servo drive featuring adjustment of balance, gain, and deadband. In addition to control from a dc signal, mechanical input can be fed into the balance control, or that control could be replaced by a pair of resistance transducers for control by light or by temperature. the circuit shown.
The positioning servo drive circuit operates on the principle of feedback control to maintain the desired position of a mechanical element. The core components include a servo motor, a control circuit, and feedback sensors. The adjustments for balance, gain, and deadband are critical for optimizing the performance of the servo system to accommodate various operating conditions and loads.
1. **Servo Motor**: The servo motor is the actuator that moves the mechanical element to the desired position. It is typically a DC motor equipped with a feedback mechanism, such as an encoder or a potentiometer, to provide real-time position data.
2. **Control Circuit**: The control circuit processes the input signals and generates the necessary control signals for the servo motor. The circuit may include operational amplifiers for signal conditioning, and microcontrollers for more complex control algorithms. The gain adjustment allows for tuning the responsiveness of the system, while the deadband setting helps to prevent oscillations around the target position by introducing a threshold that must be exceeded before corrective action is taken.
3. **Balance Control**: The balance control can be adjusted using a mechanical input or replaced with resistance transducers. The mechanical input allows for manual tuning of the system, while resistance transducers can provide automatic adjustments based on environmental factors such as light intensity or temperature variations. This adaptability enhances the versatility of the servo drive in different applications.
4. **Feedback Sensors**: Feedback sensors are integral to the operation of the servo drive. They provide continuous information about the position of the mechanical element, allowing the control circuit to make real-time adjustments. The choice of sensors, whether optical, resistive, or capacitive, can significantly affect the performance and accuracy of the servo system.
Overall, the described positioning servo drive is a sophisticated system designed for precise control in various applications, leveraging both electrical and mechanical inputs to achieve optimal performance.This is a positioning servo drive featuring adjustment of balance, gain, and deadband. In addition to control from a dc signal, mechanical input can be fed into the balance control, or that control could be replaced by a pair of resistance transducers for control by light or by temperature. the circuit shown.