PLL FM demodulator LM565CN RC4558DN schematic
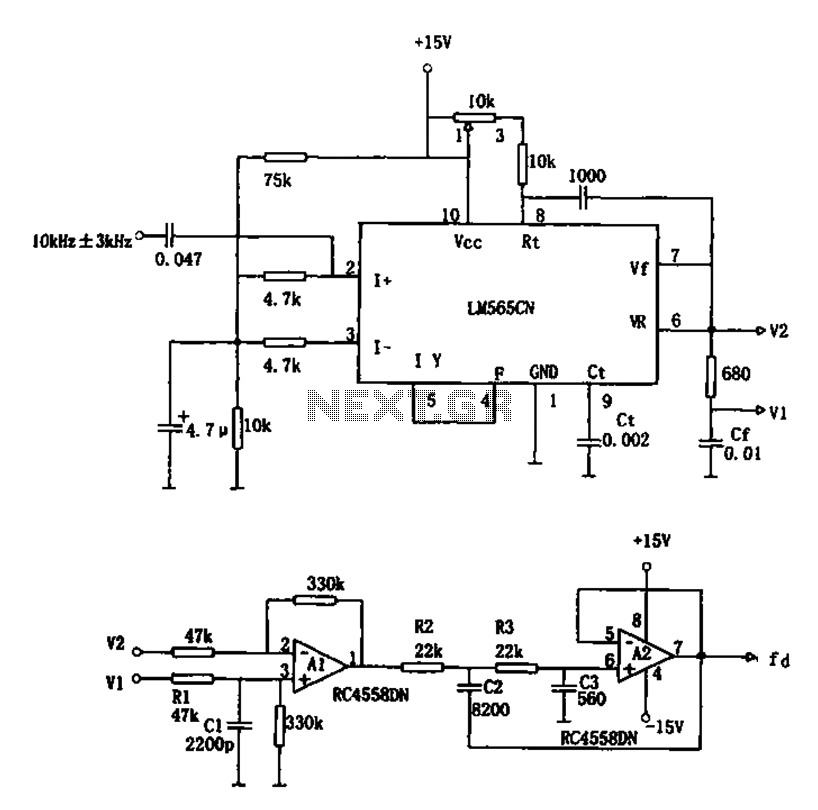
The circuit utilizes a 10 kHz and 3 kHz LM565CN to create an FM demodulation setup. The output diagram (b) illustrates the differential demodulation outputs V1 and V2 from the differential amplifier A1, which provides level displacement and amplification. Subsequently, the A2 active low-pass filter (LPF) is employed to filter out the pulsating component at 20 kHz.
The FM demodulation circuit described employs the LM565CN, a versatile integrated circuit designed for frequency demodulation applications. The circuit operates at two specific frequencies, 10 kHz and 3 kHz, which are essential for effective demodulation of frequency-modulated signals. The differential amplifier A1 plays a crucial role in processing the incoming modulated signal. It generates two outputs, V1 and V2, which represent the demodulated signals. The function of A1 is to amplify the difference between the two input signals, ensuring that the output signals are properly displaced in amplitude for further processing.
Following the differential amplification stage, the outputs V1 and V2 are fed into an active low-pass filter (A2). The purpose of A2 is to remove unwanted high-frequency components, specifically targeting the pulsating component at 20 kHz that may interfere with the desired demodulated signal. The active low-pass filter is designed to allow frequencies below a certain cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating frequencies above this threshold. This characteristic is vital in ensuring that the output signals are clean and free from high-frequency noise, thus improving the overall quality of the demodulated output.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines differential amplification and active filtering to achieve high-quality FM demodulation, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems where signal integrity is paramount.Circuit is shown using 10kHz 3kHz LM565CN constitute the FM demodulation circuit. The V1 and V2 differential demodulation output diagram (b) of the differential amplifier A1 level displacement and amplification, and then by the A2 active LPF filtered pulsating component of 20kHz.
The FM demodulation circuit described employs the LM565CN, a versatile integrated circuit designed for frequency demodulation applications. The circuit operates at two specific frequencies, 10 kHz and 3 kHz, which are essential for effective demodulation of frequency-modulated signals. The differential amplifier A1 plays a crucial role in processing the incoming modulated signal. It generates two outputs, V1 and V2, which represent the demodulated signals. The function of A1 is to amplify the difference between the two input signals, ensuring that the output signals are properly displaced in amplitude for further processing.
Following the differential amplification stage, the outputs V1 and V2 are fed into an active low-pass filter (A2). The purpose of A2 is to remove unwanted high-frequency components, specifically targeting the pulsating component at 20 kHz that may interfere with the desired demodulated signal. The active low-pass filter is designed to allow frequencies below a certain cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating frequencies above this threshold. This characteristic is vital in ensuring that the output signals are clean and free from high-frequency noise, thus improving the overall quality of the demodulated output.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines differential amplification and active filtering to achieve high-quality FM demodulation, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems where signal integrity is paramount.Circuit is shown using 10kHz 3kHz LM565CN constitute the FM demodulation circuit. The V1 and V2 differential demodulation output diagram (b) of the differential amplifier A1 level displacement and amplification, and then by the A2 active LPF filtered pulsating component of 20kHz.