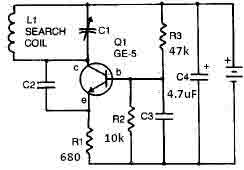
Whistle Responder Schematic

Approximately 20 years ago, small key-holders that emitted an intermittent beep for a few seconds upon detecting a whistle were quite common. These devices utilized a specialized integrated circuit (IC) that made them unsuitable for home construction. The current circuit is designed around a general-purpose hex-inverter CMOS IC, allowing for the use of miniature components and button clock-type batteries, which can be housed in a matchbox. While primarily a gadget, it has potential applications for various users. This device emits intermittent beeping for about two seconds when a whistle is detected within a range of approximately 10 meters. The first two inverters in IC1 function as audio amplifiers; IC1A consistently amplifies the signal received from a small electret microphone, while IC1B operates as a band-pass filter centered around 1.8 kHz. This filter is essential for isolating the specific frequency of the whistle and preventing activation from other frequencies. IC1C is configured as a Schmitt trigger, which squares the incoming audio signal. IC1D serves as a two-second delay monostable circuit, controlling the astable multivibrator formed by IC1E and IC1F. This oscillator generates a square wave with a frequency of 3 to 5 Hz, which drives Q1 and BZ1, resulting in the intermittent beeping operation.
The circuit design employs a hex-inverter CMOS IC, specifically the CD40106 or similar, which integrates multiple functions into a single package, thus enhancing the compactness of the overall assembly. The electret microphone, chosen for its sensitivity and low power consumption, captures the sound of a whistle and converts it into an electrical signal. The signal is first amplified by IC1A, which increases its strength to a level suitable for further processing. IC1B, configured as a band-pass filter, utilizes passive components such as resistors and capacitors to create a filter circuit that allows only the frequency of interest (approximately 1.8 kHz) to pass through, effectively rejecting unwanted noise.
The output from the band-pass filter is then fed into IC1C, where the Schmitt trigger action ensures that the signal is cleanly squared, providing a digital output that is less susceptible to noise. This digital signal triggers IC1D, which is designed as a monostable multivibrator. Upon receiving the trigger from IC1C, IC1D generates a high output for a fixed duration of two seconds, after which it returns to a low state.
The output from IC1D is utilized to initiate the astable multivibrator configuration formed by IC1E and IC1F. This configuration generates a square wave output at a frequency of 3 to 5 Hz, which is then used to drive a transistor (Q1). The transistor acts as a switch, controlling the current flow to the piezo buzzer (BZ1), which produces the audible beeping sound. The intermittent nature of the beeping is achieved through the oscillation of the multivibrator, providing a simple yet effective solution for the intended application.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies an efficient design that leverages common electronic components to create a functional device with practical uses, particularly in personal item tracking or alert systems.Some 20 years ago it was common to see small key-holders emitting an intermittent beep for a couple of seconds after its owner whistled. These devices contained a special purpose IC and therefore were not suited to home construction. The present circuit is designed around a general purpose hex-inverter CMos IC and, using miniature components and b
utton clock-type batteries can be enclosed in a matchbox. It is primarily a gadget, but everyone will be able to find suitable applications. This device beeps intermittently for about two seconds when a person in a range of around 10 meters emits a whistle. The first two inverters contained in IC1 are used as audio amplifiers. IC1A amplifies consistently the signal picked-up by the small electret-microphone and IC1B acts as a band-pass filter, its frequency being centered at about 1.
8KHz. The filter is required in order to select a specific frequency, the whistle`s one, stopping other frequencies that would cause undesired beeper operation. IC1C is wired as a Schmitt trigger, squaring the incoming audio signal. IC1D is a 2 second-delay monostable driving the astable formed by IC1E & IC1F. This oscillator generates a 3 to 5Hz square wave feeding Q1 and BZ1, thus providing intermittent beeper operation.
🔗 External reference
The circuit design employs a hex-inverter CMOS IC, specifically the CD40106 or similar, which integrates multiple functions into a single package, thus enhancing the compactness of the overall assembly. The electret microphone, chosen for its sensitivity and low power consumption, captures the sound of a whistle and converts it into an electrical signal. The signal is first amplified by IC1A, which increases its strength to a level suitable for further processing. IC1B, configured as a band-pass filter, utilizes passive components such as resistors and capacitors to create a filter circuit that allows only the frequency of interest (approximately 1.8 kHz) to pass through, effectively rejecting unwanted noise.
The output from the band-pass filter is then fed into IC1C, where the Schmitt trigger action ensures that the signal is cleanly squared, providing a digital output that is less susceptible to noise. This digital signal triggers IC1D, which is designed as a monostable multivibrator. Upon receiving the trigger from IC1C, IC1D generates a high output for a fixed duration of two seconds, after which it returns to a low state.
The output from IC1D is utilized to initiate the astable multivibrator configuration formed by IC1E and IC1F. This configuration generates a square wave output at a frequency of 3 to 5 Hz, which is then used to drive a transistor (Q1). The transistor acts as a switch, controlling the current flow to the piezo buzzer (BZ1), which produces the audible beeping sound. The intermittent nature of the beeping is achieved through the oscillation of the multivibrator, providing a simple yet effective solution for the intended application.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies an efficient design that leverages common electronic components to create a functional device with practical uses, particularly in personal item tracking or alert systems.Some 20 years ago it was common to see small key-holders emitting an intermittent beep for a couple of seconds after its owner whistled. These devices contained a special purpose IC and therefore were not suited to home construction. The present circuit is designed around a general purpose hex-inverter CMos IC and, using miniature components and b
utton clock-type batteries can be enclosed in a matchbox. It is primarily a gadget, but everyone will be able to find suitable applications. This device beeps intermittently for about two seconds when a person in a range of around 10 meters emits a whistle. The first two inverters contained in IC1 are used as audio amplifiers. IC1A amplifies consistently the signal picked-up by the small electret-microphone and IC1B acts as a band-pass filter, its frequency being centered at about 1.
8KHz. The filter is required in order to select a specific frequency, the whistle`s one, stopping other frequencies that would cause undesired beeper operation. IC1C is wired as a Schmitt trigger, squaring the incoming audio signal. IC1D is a 2 second-delay monostable driving the astable formed by IC1E & IC1F. This oscillator generates a 3 to 5Hz square wave feeding Q1 and BZ1, thus providing intermittent beeper operation.
🔗 External reference